
Читайте также:
|
PRICING IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS
The Concept of Pricing in International Business
Pricing in Foreign Trade Agreements (Contracts)
Price Fixing Methods
Types of Prices
Price Extra Charges and Discounts
THE CONCEPT OF PRICING
IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS
The prices in international business are determined by the parties on a contractual basis. The contract prices of foreign trade transactions are formed depending on the prices and conditions of the global market, taking into account supply and demand, as well as other factors which are in force in the respective markets at the time of conclusion of international business agreements (contracts).
Contract Price – a certain amount of monetary units of currency per unit (number of units) of goods which the buyer must pay to the seller in accordance with the terms of foreign trade agreement (contract) for sale.
Exercise#1. Please, place the price-determining factors given below either to market-oriented or cost-oriented pricing.
1) cost of raw materials; 2) buyers’ behavior; 3) fixed production cost; 4) channels of distribution; 5) price policy of the company; 6) substitutes; 7) tariffs; 8) shipment cost; 9) demand (purchasing power); 10) product and company positioning; 11) marketing expenses; 12) trade brand; 13) post-sold service; 14) logistic and finance expenses; 15) price elastisity; 16) inflation; 17) transport charges; 18) seasonality; 19) taxes, duties; 20) regulatory and other legal factors; 21) exchange rate; 22) target profit; 23) standards; 24) variable production cost; 25) competition; 26) short-term and long-term goals of the company; 27)labor cost; 29) currency and political risks; 30) governmental protectionist policies.
| Cost-oriented pricing factors | Market-oriented pricing factors |
PRICING IN FOREIGN TRADE AGREEMENTS (CONTRACTS)
Contract Prices – exact prices on products determined by a salesman and buyer during negotiations.
Pricing in foreign trade contracts includes the following steps.
1. Units of goods. The choice of such units depends on the nature of the goods and the practice that has prevailed in the trade in the commodity on the world market. The price of the commodity can be established for a quantitative unit of goods (pc, m, L) or per unit of weight (kg, g, t). In the supply of goods of different quality and range prices are set per unit of each type (class, mark). Generally the prices of a large variety of goods are given in the specifications and applications, which are an integral part of the contract.
2. Price basis is set in accordance with delivery terms INCOTERMS. Price basis determines the costs of delivery of goods (transport, insurance, customs duties) included into the price of goods.
3. Price currency.
PRICE FIXING METHODS
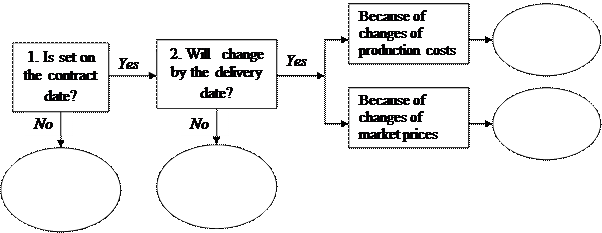
Fixed Price – a price which is set at the conclusion of the contract and can not be changed during its execution period.
Mobile Price – a price which is set at the conclusion of the contract, but may be changed if the market price of goods changes by the time of delivery. In this case there is a stipulation in the contract stating that if by the time of the delivery market price for the goods rises or falls, then, accordingly, should be changed and the price fixed in the contract. Typically, the contract specifies an interval of market price deviation from the contract price (2-5%), within which a revision of the price is not done. The source of market price changes should be stipulated in the contract.
 PRICES BY FIXING METHODS:
PRICES BY FIXING METHODS:
Price with Subsequent Fixation is not set at the conclusion of the contract. The contract stipulates the term and agreed sources for establishing prices in the future. Prices with subsequent fixation are used in the supply of goods over a long period of time, when the situation in world commodity markets can change dramatically.
Sliding Price is determined at the time of delivery by converting the base price specified in the contract, taking into account changes in production costs during the execution of the contract. The contract indicates base price and specifies its structure (share of profits, material costs, wage costs etc). The contract also must specify the terms and sources as to changes in the production costs. Method for calculating a sliding price is recommended by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe.
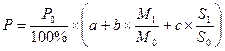 ,
,
P0 – negotiated base unit price, which is set at the date of the contract;
a – the share of fixed costs and profits in the base unit price,%;
b – the share of raw materials and components costs in the base unit price,%;
с – the share of wage costs in the base unit price,%;
a + b + c = 100%
M1 – the unit price of raw materials at the date of delivery or payment;
M0 – the unit price of raw materials at the date of the contract;
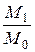 – raw materials and components cost change index (the coefficient that takes into account changes in the cost of raw materials and components for the period of the contract);
– raw materials and components cost change index (the coefficient that takes into account changes in the cost of raw materials and components for the period of the contract);
S1 – average wages at the date of delivery or payment;
S0 – average wages at the date of the contract;
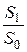 – wages change index (the coefficient that takes into account change in the wages for the period of the contract).
– wages change index (the coefficient that takes into account change in the wages for the period of the contract).
Exercise#2. What kind of prices (by price fixing method) is used in the
contract clauses below?
1. The price of oil is set $100 per barrel. If oil prices by the world market
quotations according to the New York Mercantile Exchange NYMEX change
more than 3%, the price of this contract will be changed respectively.
________________________________________________________
2. The price of the equipment under this contract is $10,000. However,
if the price of energy resources required to manufacture this equipment
varies by more than 5%, the price of the equipment is adjusted according
to the estimates taking into account the changes in prices of energy resources.
______________________________________________________
Exercise#3. Under the terms of foreign trade contract with a long period of production of goods, the partners agreed on the "sliding price" as a method of price fixing. There are the following data for price calculating per unit:
1) $ 1000 - base unit price at the date of the contract;
2) 40% - the share of raw materials in the base unit price;
3) 45% - the share of wages in the base unit price;
4) 15% - the share of fixed costs and profits in the base unit price;
5) $ 30 - unit price of raw materials at the date of the contract;
6) $ 45 - unit price of raw materials at the date of delivery;
7) $ 5 - full-time wage rate per worker at the date of the contract;
8) $ 6 - full-time wage rate per worker at the date of delivery.
Please, calculate the unit price of the goods at the date of delivery.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Дата добавления: 2015-10-29; просмотров: 116 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| in the event of an invasion of Japan. | | | CHAPTER EIGHT |