
Читайте также:
|
LABORATORY WORK
The physical measurement errors calculation
The purpose of the work: to study the rules of physical measurement results treatment; to determine the error of the indirect measurements of the cylinder body density as a result of the repeated direct measurements of its geometrical values and mass; to study the normal random values distribution law; to determine the gravity acceleration.
Theoretical Information
Errors in scientific studies mean the uncertainties in the obtained value of a certain measured quantity. Never mind how carefully and accurately the measurements are made the final result always has some uncertainty. The uncertainties are produced by the precision of used measuring instruments and by the way scales of instruments are read, by measurement procedure itself and also by an observer performing measurements. Error analysis is extremely important especially in the exact sciences; for example, compare measurement results of the same quantity obtained by different observers and by using different methods. The measurements are quite often repeated many times to find reliable estimates of value of the obtained quantity.
Measurement is a process of physical quantity determination using special technical means. The result of measurement shows how the measured value differs from those accepted for a unit of measurement.
Material resources for performing measurements are measurement instrumentation such as measures and measuring devices.
Measure is measurement instrumentation, intended for the reproduction of physical quantity of a given value. Examples of measure of some physical quantities can be length, mass, volume, electric resistance, electric capacity, inductance, electromotive force, frequency of oscillations, and the like. Some physical quantities such as velocity, power, energy, electric current intensity, and the like have no measure.
Measuring device is measurement instrumentation, intended for creating a signal of measured information in applicable form of direct observation.
There are lots of types of measuring devices; they are classified according to different features: measuring quantity type, working principle, the measured information signal registration methods, structural features, performance properties, and others.
Measurement error is the measured result deviation from the true value of the measured quantity. (Errors show accuracy of measured values.)
Measurement errors can be absolute and fractional. Absolute error Δx is the difference between measured x and true X values of physical quantity. Absolute error is always expressed in units of measurement and is calculated as:
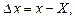
Fractional error ε is determined by the ratio of the absolute error to the true value of measuring quantity and is usually expressed in percents.
Thus, an absolute error is a difference between the measured and true value. The value of absolute error does not characterize measuring quality without pointing the measured quantity value. Accuracy of measurement results is better to characterize by fractional error.
Fractional error is determined by the ratio of the absolute error of measurement to the true value of measuring quantity. As the true value of measuring quantity is not known, the fractional error of measurement (ε) is determined by the ratio of the absolute error of measurement to the measured value of quantity. A fractional error is usually expressed in percents:
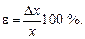
Accuracy of measurements is numerically equal to the general value of a fractional error. For example, if e =10-2 % = 10-4, then measurement accuracy equals  During measuring similar values (for example lengths) a fractional error gives the possibility to judge on the measurement accuracy. For example, measurement of shaft neck of an aviation engine by diameter 50 mm with absolute error 1 mm is considered very incorrect (e»2%). However, measurement of distance to the Moon with absolute error approximately 1 km can be considered quite exact (e = 3 10-4 %).
During measuring similar values (for example lengths) a fractional error gives the possibility to judge on the measurement accuracy. For example, measurement of shaft neck of an aviation engine by diameter 50 mm with absolute error 1 mm is considered very incorrect (e»2%). However, measurement of distance to the Moon with absolute error approximately 1 km can be considered quite exact (e = 3 10-4 %).
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 140 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Evaluation of DSL potential characteristics at parallel work on high-capacity telephone cables. | | | Measurement types |