
Читайте также:
|
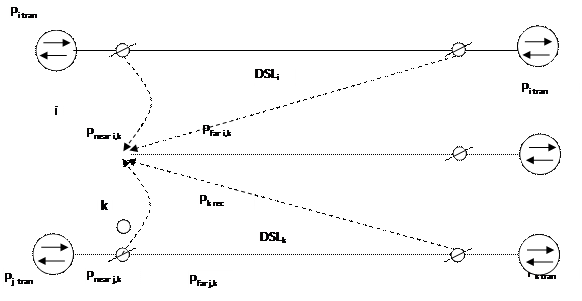
One of the main factors which limit the speed and distance of transmission in subscriber lines are transitive noises, appeared at parallel work of DSL in multipair telephone cables. The algorithm of calculation transitive influences between DSL are shown on figure 2.1 where shown two influencing DSL (DSLi and DSLj) and one influenced DSL (DSLk). Power of incoming signal at the input of i-th SL is Pi trans . On the input of DSLk receiver comes attenuated useful signal with power Pk rec and transitive noises (from near Pnear i,k , Pnear j,k and far Pfar , i,k и Pfar,j,k ends) caused by transmitting signals DSLi и DSLj .
Signal – noise ratio at the input of receiving device DSL is:
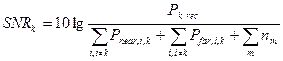 ,
,
where 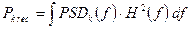
PSD – dependence of signal on frequency at the output of transmitter of k -th DSL;
H – amplitude-frequency characteristic of SL (communication channel);
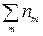 – sum of other noises, acting on the input of receiving device DSLk .
– sum of other noises, acting on the input of receiving device DSLk .
 | |||||||
|
| ||||||
| |||||||
Values Pnea i,k и Pfar i,k can be defined by analogy accordingly to formulas, where H 2(f) is substituted frequency functions of transitive characteristics between i -th and и k- th SL on near and far end Hnear i,k (f) и H far i,k (f) accordingly:
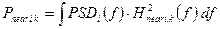
In accordance to model of electromagnetic compatibility it is possible to calculate acceptable lengths of SL and their transmission rates into upstream and downstream directions along DSL at different variants of xDSL equipment, loading, level of noise, number of pairs, diameter of core, using of homogeneous and non-homogeneous cables.
In the Figure 2.2, 2.3 are shown examples of calculations (with the help of program «xDSL-Liner») the maximum length ADSL2+ line at the using 10-pair ТП cables with bunchy twisting of core where diameters of wire are 0,32 mm; 0,4 mm; 0,5 mm and 0,64 mm for different types of white noise at the input of receiver. It also depends on percent of cable pairs using for transmitting of ADSL2+.
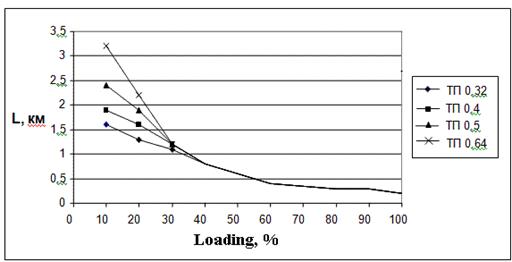
а) White noise equals minus 140 dBm/Hz
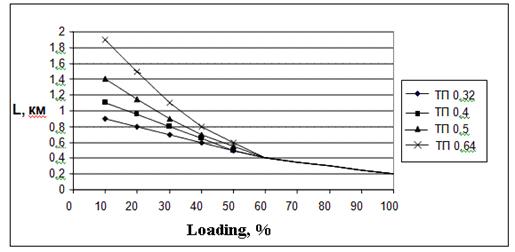
b) White noise equals minus 120 dBm/Hz
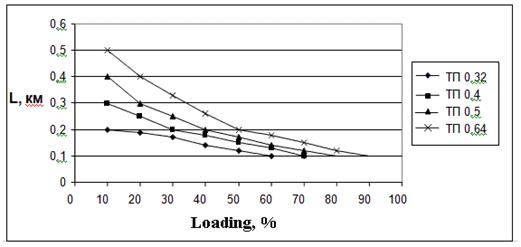
c) White noise equals minus 100 dBm/Hz
Figure 2.2 - Accessible length of ADSL2+ line for rate 19648 kbps for upstream and 928 kbps for downstream, direction at using of 10-pair TП cable and white noise 140, 120, 100 dBm/Hz which depend on percent of loading by cable at ADSL2+
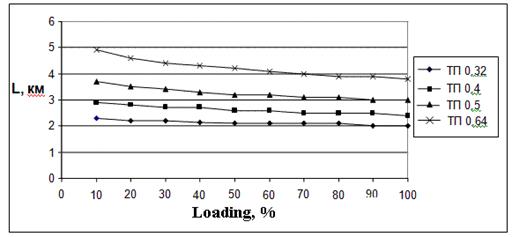
а) White noise equals minus 140 dBm/Hz

b) White noise equals minus 120 dBm/Hz
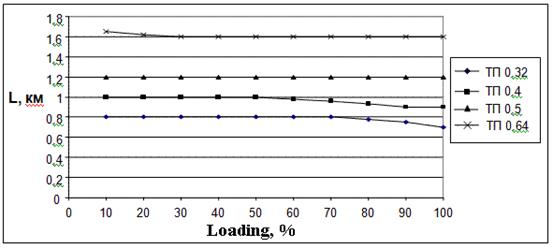
c) White noise equals minus 100 dBm/Hz
Figure 2.3 - Accessible length of ADSL2+ line for rate 19648 kbps for upstream and 928 kbps for downstream, direction at using of 10-pair TП cable and white noise 140, 120, 100 dBm/Hz which depend on percent of loading by cable at ADSL2+
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 130 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| The dependence of the crosstalk at the near-end and far-end immunity on the frequency | | | Measurement error is the measured result deviation from the true value of the measured quantity. (Errors show accuracy of measured values.) |