
Читайте также:
|
Laboratory work 5. Identifying the activity of enzymes
Factors determining enzymatic activity are enzyme and substrate concentrations; presence of inhibitors and activators. Activators of enzymes are substances increasing catalytic activity, for example, ions of some metals: Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, К+, Со2+. Inhibitors inhibit enzymes action. Any agent that causes protein denaturation leads to irreversible enzyme deactivation.
Reversible inhibitors are compounds which form weak bonds with the enzyme and can be separated from the enzyme. Specific inhibitors act on one enzyme or enzyme group.
Reversible inhibition can be competitive and non-competitive. Competitive inhibition is based on the binding of substances similar to substrate in structure to enzyme active site. The degree of inhibition depends on the ratio of enzyme and substrate concentration. Competitive inhibition method is widely used in medical practice (sulfonamides).
Non-competitive inhibition is when the substrate and the inhibitor bind to different sites. It leads to the changes in the conformation of the enzyme active site and decreases enzymatic activity.
The enzyme activity can be estimated by the rate of substrate disappearance or by the rate of product formation.
International Unit of enzyme activity (IU) is an amount of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1 micromole of substrate or formation of 1 micromole of product per 1 minute.
Enzyme activity also can be expressed in katal (kat): 1 kat denotes conversion of 1 mole of substrate per 1 second. 1 IU corresponds to 16.67 nkat.
The specific activity is the number of IU per 1 mg of protein or the number of katal per 1 kg of active protein.
The most of enzymes of the organism are functioning intracellularly, and their activity in blood is low. Pathological processes accompanied by the cell destruction are often lead to the appearance of enzymes in blood. Increase in enzyme activity in blood can be used for diagnostics of pathologies of specific organs and tissues.
The influence of activators and inhibitors upon activity of enzymes.
1.1. The influence of activators and inhibitors upon α-amylase.
Pour 1 ml. of 1% sodium chloride solution in the first test tube, 1 ml of 1% copper sulfate solution into the second test tube, and 1 ml of distilled water into the third one. Add 12 ml of 0,5% starch solution and 2 drops of saliva dissolved with water (1:5) to each test tube. Mix the contents of the test tubes by shaking and place them into the water thermostat with the temperature of 37°С. In intervals of 1 minute take 0.3-0.5 ml of every solution from clean test tubes and make Lugol’s tests (with iodine solution in potassium iodide). Put down results in the table 1. Pass hydrolysis process for 5 minutes. Make a conclusion about the action (activator, inhibitor) of the investigated components.
Table 1. Results of starch hydrolysis in presence of different additives
| № of the test tube | ||||
| Additive | NaCl | CuSO4 | H2O | |
| Time, min | ||||
2. Identifying the activity of α-amylase according to Wolgemut.
The method is based on identifying the ultimate dissolving of α–amylase solution which still allows splitting of the given quantity of starch up to erythrodextrine under certain conditions. Wolgemut’s method can be used to approximately identify the activity of α–amylase in pancreatic juice, blood, urine and other biological liquids.
Put 1 ml of saliva into a test tube; add 9 ml of distilled water and mix. You get saliva solution 1:10.
Pour 1 ml of water into 10 enumerated test tubes. Add 1 ml saliva solution to the first test tube and mix: take in the liquid in the pipette and pour it out by three times. Then replace 1 ml of the liquid from the first test tube into the second one, mix the contents as it is mentioned before. Replace 1 ml of the liquid from the second test tube into the third one and so on. Remove 1 ml of the liquid from the tenth test tube after mixing it. Add 2 ml of 0.1% starch solution to all test tubes beginning with the tenth one and mix the contents. Place the test tubes into the thermostat at a temperature of 37°С for 30 minutes.
In 30 minutes cool the test tubes and add 1 drop of iodine solution in potassium iodide to all the test tubes. Put down results in the table 2. Mark the test tube where splitting of starch up to erythrodextrine has taken place and the latter gives red-brown coloring in reaction with iodine. The activity of α-amylase is expressed by the quantity of milliliters of 0.1% starch solution which can be split by 1 ml of undiluted saliva at a temperature of 37°С up to the stage of erythrodextrine during 30 minutes.
For example: if you observe red-brown coloring in the fourth test tube where the saliva is 160 times diluted, it means that 1 ml of undiluted saliva would split 160 times more starch solution. Therefore, 1 ml of undiluted saliva splits during 30 minutes at 37°С: 2×160 = 320 ml of 0.1% starch solution.
It corresponds to 320 units of α-amylase according to Wolgemut: А 37°/30' = 320 un.
Table 2. Results of starch hydrolysis
| № | Dilution of saliva | Color in the reaction with iodine |
Tasks
1. The specimen containing 2 mg of arginase enzyme catalyzed formation of 30 mcmol of urea at pH 9 in 10 min. Calculate specific activity of arginase.
2. Trypsin enzyme catalyzes breakdown of proteins at optimal conditions as pH 8 and 37oС. How will trypsin activity change and why, if: a) pH is 3? b) temperature is 78oС?
Test Questions
1. What are activators and inhibitors of enzymes?
2. How can the influence of activators and inhibitors upon the work of enzymes be investigated?
3. The enzyme acetylcholine esterase catalyses the hydrolysis of acetylcholine. It is a neurotransmitter produced in the synapses of cholinergic nerves. Its breakdown products - acetate and choline – are unable to work as neurotransmitters. The hydrolysis of acetylcholine is stopped by calimine – a medicinal preparation used to heal motor disturbance after injuries, paralysis, in rehabilitating periods after having poliomyelitis, encephalitis, etc. The following scheme reflects the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase:
Inhibitor calimine
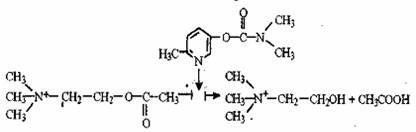
acetylcholine choline acetic acid
Compare the structural formulas of the inhibitor and the substrate. Why can one suppose that the inhibitor can bound to the active site of the enzyme? How will the influence of calimine change the conduction of nerve impulse (increase, reduce or will not change)?
4. Give examples of enzyme use in medicine.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 176 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Specificity of amylase and sucrase. | | | Experiment 3. Qualitative reactions to vitamin D (calciferol) with aniline. |