
Читайте также:
|
Monitoring of anthropogenic contamination of soil.
Goal of the work
To study types and causes of soil contamination. To master the methods of monitoring of anthropogenic pollution.
Key condition
The word "monitoring" - Latin origin. It means: one who remind, warn, alert. Canadian scientific R. Mann introduce this term before the Stockholm’s’ conference on Environment (June 1972). Professor Mann offer to call Monitoring "system of repeated observations by one or more elements of surroundings in space and time with specific goals and predetermined program”.
Y.A. Izrael (1978) think that most rightly called monitoring "a system of observation, that gives ability to fix change of biosphere state under the influence of anthropogenic activities”.
Ukrainian researchers P.G. Tishchenko, and M.M. Padun (1988) offer that definition of monitoring “System of observation and control of environmental states for testing tendencies of it’s changing and notification of undesirable phenomenons by corresponding regulating means”.
Consequently, we have several modifications of monitoring. Priorities belong to Canadian scientific. This notion has gained international recognition, and that is why interpretation of R. Mann, in our view, should be left in scientific use.
General scheme of monitoring
All territorial objects divide into three-level scale: global, regional and local. This partition is necessary such aspect of territory size and such that geographic patterns, which inherent to geosystems of global level, aren’t inherent in geosistems of other level- regional or local.
Controlled objects. They are closely related to massive levels. For example, the biosphere as a whole and its part (land and ocean) is under the control of global objects; geographical country, province and region- regional; geographical districts, districts (landscapes) - local monitoring.
Controlled objects of Geosystems monitoring may be not only geographical (natural), but also state- administrative formation, especially transnational association of countries (Common Market countries, Scandinavian countries, CIS), national country, historical and administrative regions, drainage area and selective structures.
-1-
To ensure interested enterprises and private persons trustworthy information about environmental state of territory on state level,we must firstly organize observation and control to geosystems of local level that is wish of similar landscapes (of landscapes) and their morphological units.
Structure. Structure, functions and monitoring controls, like controlled objects, are directly dependent on the scale level of geosystems. The structure of global level consists of the World coordination monitoring center and also a network of background monitoring observatory, located on dry land, mainly in biosphere reserves, and in the ocean (on the islands and special research water craft) and correspondent communication and control tools. Regional coordination centers and station network (impactor, background, regional), located in a certain region with means of observation and communications, create structure of region level.
National monitoring service structures largely equate to the structure of reegional level.
The structures of local-level consist of peopleware, network stations and observation posts, analytical laboratories, and communication and control tools. They have a intimate contact with departmental monitoring services (monitoring of land, water monitoring, forest monitoring, etc.).
Table 1.1 - General scheme of monitoring Geosystems.
| Level | Controlled object | Structure | Function | Machinery of government |
| Global | Geographic cover Continents and oceans | World coordination monitoring center Continental ocean center Global station network | Finding tendency to change | UNO through their organization in different countries |
| Regional | Land,region, nation state | Region coordination centers | Appraisal of state of environment | International, governmental and public structure |
| Local | District, region, Production objects | Region monitoring service | Analytical- prognostic- voluntary block | Official ecological services |
-2-
The structure of the national monitoring service is three-stage: local (district) links are unification in the region regional institutes(Polish, Donets, Carpathian, Crimean), which locked in the National Center of monitoring of geosystems. The main element in this structure is the Regional Institute. Its function is not limited to conversion information of regional expeditions local observations, but it complement data about economical progress of district and exact indices relatively anthropogenic impact on geosystem.
National Organization Geosystems monitoring service does not exclude the existence of alternative (departmental) services. On the contrary, the availability of such services will stimulate the search of new concepts, methods, analysis, and therefore contribute to the objectivity of information.
Functions of Monitoring of different scales levels have substantial differences. If on the global level information generalized from regions and tendencies become apparent concerning of changing of biosphere in whole and its continental and oceanic parts, then in the regional level this information gathering, working out and pass through the National Centre for Monitoring out the World coordination center. Besides that, there describe state estimate of Geosystems, modulate forecast of ecological situation and display nature trend and geosystem components within the region.
Functions of monitoring local Geosystems is too diverse. They can be reduced to the following four blocks: inventory-control-supervisory, analytical-prediction-rekmendatsiynoho, accumulate - savings (bank data) and commercial.
Bodies that provide organization and management of monitoring of geosystems. These bodies at the global level ere governmental and non-governmental structure of the world community, which operate under the auspices of the UNO and other international institutions.
International, governmental, scientific and public structures operate within a region(Baltic, Carpathian etc).
Executive powers create and protect national structure through the relevant ministries (Environment Protection, Health, Agriculture and Forestry, etc.) assistance of scientists of NAS(National Academy of Sciences) of Ukraine, sectoral academies and institution of higher education.
Municipal administration realize organization and management by local level through corresponding executive powers assistance of academies and institution of higher education of corresponding type.
Man-made pollution of soil-covering
Soil-covering of Earth is an extremely important component of the biosphere, which is responsible for many processes occurring in the biosphere. Nature created him
-3-
for millennia, now thanks to "unreasonable use" it stay in a state of exhaustion.
Soil is biological absorber, converter and destroyer of various pollutants. If this part of the biosphere will be destroyed, then the functioning of the biosphere irreversibly negatively. In this regard, too important to study global biochemical state of the soil, timely notice negative of occurring changes under the influence of anthropogenic activity.
Today, protection and rational use of earth resources - one of the most pressing problems.
Importance of protection of soil-covering.
Soil Protection from pollution is too important task of people, since any harmful compounds,which are in the soil, sooner or later fall into the human body.
Firstly, there is unintentional washing pollution to open water bodies and groundwater, which can be used by man for drinking and other needs.
Secondly, pollution get from ground water, ground moisture and open water body to organisms of animals and plants that use this water, and then to organism of man.
Thirdly, many harmful for human body compound have the ability cumulate in the tissues, especially in the bones.
According to the researchers, annually about 20... 30 billion tons of solid waste receives to the biosphere, from them 50... 60% of organic compounds, as well as acid gas or aerosol character - about 1 billion tons.
Various soil pollution, most of which are anthropogenic nature can be divided according to the source of pollution to ground:
q With atmospheric precipitations. Many chemicals that get into the atmosphere from industry, then they dissolve in atmospheric moisture and with precipitation get into the soil. It is mostly gases - oxides of sulfur, nitrogen and others. Most of them don’t simply dissolve, but they form a chemical compound with water, which have acid character. In this way, acid rain formed.
q Dust, precipitable in the form of aerosols. In consequence of dry weather solid and liquid compounds usually settles directly in the form of dust and aerosols. Such contamination can be observed visually, for example, in winter near boiler houses snow becomes black, get covered of soot particles. Cars, especially in cities and near highways, making significant share in the replenishment of soil pollution.
q For direct absorption of gaseous compounds by soil. In dry weather soil can
directly too damp absorb gases.
-4-
q For leaf fall. Different harmful substances in any aggregate state, are absorbed through the leaves through pass or settle on its surface. Then, when the leaves fall, these compounds get to the ground again.
Classification of soil pollution
Land pollution is difficult to be classified, but if you highlight and summarize important, then there is the following picture:
q Garbage, emissions, dumps etc. This group includes different pollution of mix type, including both solid and liquid substances, not too harmful for human body but which can accumulate in plants.
q Heavy metals. This type of pollution is very dangerous for people and other living organisms, because heavy metals often have high toxicity and ability to cumulate in the body. The most widespread automotive fuels - gasoline has too toxic compounds - tetraethyl lead, which contains heavy metal lead, which gets to the soil. In the midst of other heavy metal compounds which pollute the soil, we can enumerate:Cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), Mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), manganese (Mn).
q Pesticides. These chemicals widely used today as a means to combat pests, diseases, weeds therefore they can stay in the soil in significant quantities. By its dangerous for animals and humans they are close to the previous group. Exactly for this reason, drug DDT was banned for use (дихлор-дифеніл-трихлорметилметан), which is chemically stable, not decompose for decades. Traces of DDT were found by researchers, even in Antarctica! Pesticides fatal influence of the soil microflora: bacteria, actinomycetes, fungus, algae.
q Mycotoxins. Some mushrooms highlighted these pollution, but on its harmfulness to the organism they listed in the same number with soil contamination.
q Radioactive substances. Radioactive compounds don’t differ their chemical properties from similar non-radioactive elements and easily penetrate to all living organisms, include food chains. In the midst of radioactive isotopes we can noted,as an example, one of the most dangerous - strontium-90 (90Sr). This radioisotope has a high output at nuclear decay (2... 8%), large period of half life (28.4 years), chemically similar to calcium and so then it has the ability to delayed in bone tissues of animals and humans.
q Waste - raw material,which is unsuitable for the production of definite production, it’s unused remains or substance formed in the flow process (solid, liquid, gaseous) are not used in this mode of production. And the term
-5-
"production" in this context includes scope and consumption. Depending on the
location of formation (by the principle of industry) wastes are divided into industrial, construction, transportation, agricultural, military, appliance, etc.
Sanitary protection of ground
The purpose of soil protection is maintaining of such it’s quality, on which soil would not transfer dangerous for human and animals diseases and it would not lead to direct or indirect, with the environmental chain (soil - plant - animal - man; soil - air - man), acute or chronic poisoning by exogenous chemical agent with possible remote consequences.
Measures of sanitary protection of soil divided into the following groups:
1. Sanitary- technical measures (cleaning, exempt, decontaminate and utilize waste that contaminate soil);
2. Technological measures directed to create non-polluting and short-retracting technological production schemes that reduce formation of waste to a minimum;
3. Planning measures, which are concerning scientific- western and keeping the size of sanitary protective zones between treatment facilities and residential buildings, places of water intake, selection of traffic schemes, selection of land for treatment facilities;
4. Legislative, organizational and administrative measures.
However, if the soil is already infected, it should be cleared and restored. Often in decontamination of soil we used washing process. This process aims to:
• Mechanical effect of water (sometimes with additives). Physically we remove pollutants from soil particles;
• Mixing of soil particles,which help to separate small particles from larger soil particles, thereby reducing the volume of material, which requiring further treatment and the costs to decontamination process.
Thus, this process is based on the use of water with further reduce the amount of work, at which dangerous dirty contaminants are removed and concentrated by physical and chemical methods in a small part of the sediment. The basic concept of process is to transfer pollutants from the soil in the wash water, followed by their removal. Cleaned soil can be returned to the field or for it, it may be discovered useful application. Substances that destroy or bind pollutants can cultivate the small amount of dirty
-6-
contaminated soil. Physical methods of soil include: grinding, sifting, sorting wet, separation in a dense medium, flotation, gravity precipitation and mechanical dehydration. Detergents, surface-active substances, substances that cause the formation of chelate compounds, coagulants, flocculants are the relevant chemical facilities. Lavage is an effective method of treatment of soils and ground sediments of rivers, lakes, etc.
Process can be an effective and economically when contaminated soil or ground adjournment contain not more than 40% silt and clay particles are no larger than 63 microns. Content of solid organic matter should not exceed 20% of the volume.
Typical hazardous impurities, which are effectively removed by this method are: sediment, saturated with oil, radioactive pollution, heavy metals, creosote, pesticides, cyanide, etc.
Key Questions
1. Definition of monitoring.
2. Structure monitoring.
3. What is the ecological meaning of soil and the importance of its protection?
4. What are the sources of find of anthropogenic pollution of soil?
5. Classification of ground pollution.
6. What industry waste belong to the extremely dangerous?
7. What is the danger of pesticides?
8. Hygienic significance of soil.
Homework
1. Student should study the literature [6... 8] for successfully use and protection of laboratory work.
2. Prepare for discussion on: "Ecological importance of soil.
Methods of conducting of work.
Before work student should acquaint with literature [15] then, solving situational problem, he should master technique of contaminate and clearing of ground.
Laboratory task
1. To learn and to make an abstract about: what is monitoring, his types, types of soil contamination, and methods of purification.
2. To familiar with the technique of solving problems.
3.To solve the situational problem.
-7-
4.To give the results in the protocol with conclusions.
5.2 Situational problem with application of linear programming in the environmental problems associated with soil.
Problem 1. Building of three plants for processing waste, which are supply from five industrial cities and conurbations, forecast in the region. Daily planed finding of waste (cotton, food, waste plastic, glass and construction waste) according 2,4,8,10,6 million tons. Coefficient matrix Cij is known distances (in km) from the i-th provider to j-th plants for processing, 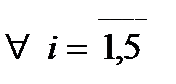 and
and  .
.
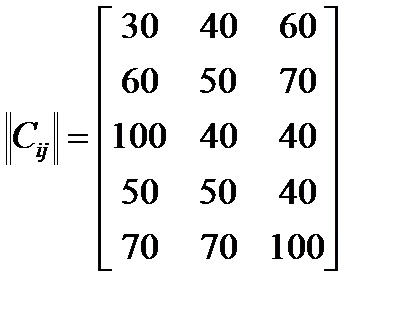
Determine optimal power of plants in million tons of garbage converting in a year, so that industrial and cities waste was recycled and the cost (in tone-kilometers) was minimal. Capacity of each plant does not exceed 20 million tons of garbage in a year.
Problem 2. Five mines operate in the region Pi ( ), which have homogeneous waste of production. These wastes have to carry of four combines Kj (
), which have homogeneous waste of production. These wastes have to carry of four combines Kj ( ) with treatment of waste. Matrix coefficients Cij - the cost of transportation of waste from the i-th mine to th j-th plant, is known
) with treatment of waste. Matrix coefficients Cij - the cost of transportation of waste from the i-th mine to th j-th plant, is known 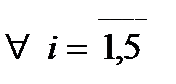 ,and
,and  .
.

-8-
The number of waste pits 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, power plants 45,55, 51, 49.
To calculate the transport plan for meet power of plants with minimal cost of transportation.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 160 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Порядок виконання лабораторної роботи | | | Production of hemin crystals. |