
|
Читайте также: |
Laboratory work № 11
Title: Research of the dependence of data transfer rate (bit rate) DSL on cable parameters and the noise level
Objectives: speed characteristic research of the digital subscriber lines (DSL) based on different types of xDSL transmission systems (SP) depending on the transmission line length, the cable diameter and the power spectral density (PSD) noise.
Key positions
2.1 QAM – Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
According to this algorithm the coding is done by simultaneous changing in-phase (cos2p f н t) and quadrature (sin2p f н t) components of carrier harmonic signal with frequency wн = 2p f н, that have phase difference on 90° (p/2).
A resultant QAMsignal s (t) is equal to sum of components:
 |
where ak і bk – means of symbols, that transmit on k -th clock interval.
QAM signal represented as vector diagram (Fig.1.1). Vector of a signal s(t) has appropriate module and phase.
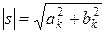 , jк = arctg(bк/ак).
, jк = arctg(bк/ак).
Carriers cosωнt і sinωнt are consider as orthogonal coordinate axes, and transmitted on times slot signals ap і bp determine coordinates of signal points on a phase plane in this coordinate system. Quantity information bits, that transmitted per one clock interval, is a whole numbe of n = 1, 2, 3,…, nmax (usually, nmax not exceed than 15). Quantity of signal points on two-dimensional coordinate system is equal M = 2n. A complex of signaling points on the plane named as signal constellation. On a Fig. 1.1,а is represented signal constellation for an easiest kind of modulation QАМ-4 (a radius-vector can to take up M = 22 = 4 positions on a phase plane, each of them is correspond to some combination of two bits – 00, 01, 10, 11). For the QАМ-16 (Fig. 1.1,b) a radius-vector can to take up 16 positions (n = 4, M = 24 = 16) on the phase plane, each of them is correspond to some combination of four bits.
Advantages of QАМ:
– narrow line spectrum, its location on frequency axis is depend on choice of carrier;
– easy realization of FDC when multichannel (parallel) transmission or when frequency division of specters, that are trasmitted in the opposite direction by one pair of signals in an asymmetrical DSL;
– simplicity of implementation, low price.
Disadvantages – high level of carrier power (relative to the low levels of side bands) on the QАМ spectrum results to energy transition on the neighbor pears. It’s complicate a parallel work of several DTL by one cable.
2. 2 Modulation DMT – Discret MultiTone
In 1987 John M. Cioffi, professor of the Stantford University, proposed a new type of line coding-modulation –DMT (Discret MultiTone). It’s a method of transmitting data with using a lot of subcarriers (FDC principle). Idea DMT has becoming international standard.
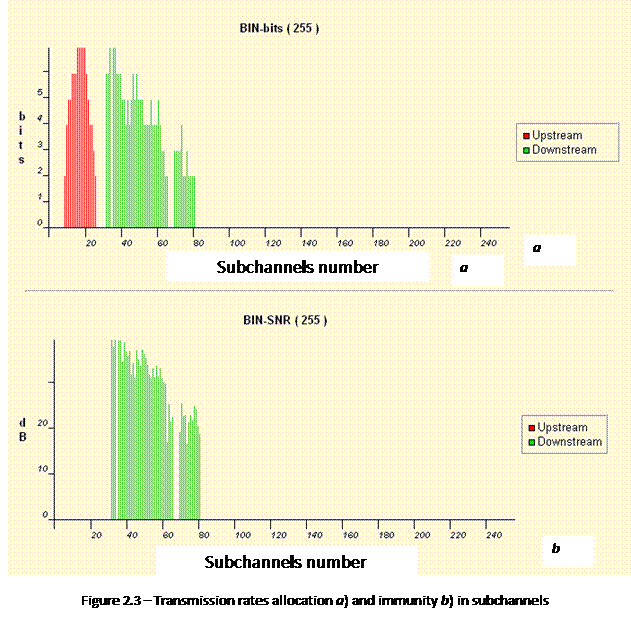
All a frequency range is divide into subchannels (ussually 256 for ADSL). The bandwidth of each subchannel is equal to 4,3125 кHz (Fig. 1.2). Realized QAM of subcarrier on the each subchannel. with spectral efficiency to 15 bits/symbols/Hz or less. Subcarrier is equal to center frequency of subchannel. We can interpret its as simultaneous operation of 256 analog modems with maximal rate 4000 Hz х 15 bits/symbols/Hz = 60 kbit/s for each. So, theoretically possible rate is approximately 15 Мbit/s. In real situation, not all subcarriers can be used. That’s why the bit rate can go down till 4 bits/symbols/Hz on the each subchannel (for example, if there are a noise or attenuation on a line).
DMT became a standard for asymmetrical DSL. It’s allow flexible dynamical frequency planning. This makes it possible to avoid a part of specter, there are noise, that concentrated on the specter. DMT is “intelligent” technology. A modem is automatically determine a level of the noise on the each subchannel and set an optimal quantity of bits per simbol for each subcarrier (Fig. 1.3).
Impulse noises (wideband) are less dangerous for the DMT signal, that for another types of the signal. DMT is allow to change a transmission rate, adapted toconcrete line with individual noises.
    |
A certain complexity creates a splitter when the ADSL-modem connected to subscriber line. This device consists of a pair of lower and higher pass filters for the spectral signals division of telephony and data traffic from the ADSL-modem (variant a in Fig. 1.4). Price of the device along with the work on modem installing close to the value of the modem (about 30... 50 $). And without this device it difficult to work on one phone line with modem. Telephones at the time of dialing, the pick up/hang up of the tube, calling, creates impulse noise in the spectrum of ADSL (25... 40 kHz).
Home task
ADSL equipment by the action of uniformly distributed noise in the spectrum is adapted to new conditions of the transmission. This equipment automatically changes the modulation QAM-64 to the QAM-64 at all used carriers. Calculate the transmission rate for the given type of DSL in the upstream and downstream directions before and after adaptation.
Variant for the calculation is chosen of the table. 4.1.
Comment: The frequency of information frames (symbols) is 4000Hz.
Table. 4.1 – Input data for home work
| № of brigade | Variant of xDSL transmission system and ITU-T recommendation | Quantity of used carriers in one direction (pcs) |
| From a subscriber/to a subscriber | ||
| ADSL (G.992.1) | 26/224 | |
| ADSL (G.992.1) | 18/176 | |
| ADSL G.Lite (G.992.2) | 26/52 | |
| ADSL G.Lite (G.992.2) | 15/35 | |
| ADSL2+ (G.992.5) | 26/289 | |
| ADSL2+ (G.992.5) | 13/395 | |
| ADSL2+ (G.992.5) | 26/480 | |
| ADSL2+ (G.992.5) | 22/317 |
For example, given type of transmission system is ADSL (G.992.1); quantity of carriers is 20 in the upstream direction and 200 in the down stream direction.
Than the calculation of transmission rate is:
In the upstream direction:
Before adaptation 20 х 4000 Hz х 6 bit = 480 кbit/s
After adaptation 20 х4000 Hz х 2 bit = 160кbit/s
In the downstream direction:
Before adaptation 200 х 4000 Hz х 6 bit = 4800 кbit/s
After adaptation 200 х4000 Hz х 2 bit = 1600 кbit/s
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 149 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Quantification of pyruvic acid in urine | | | Parameters of the relative influence |