
|
Читайте также: |
1.Measure the cylinder parameters (height with the help of slide-clipper, diameter with the help of micrometer). All measurements are carried out five times. Take the mass of a given cylinder from a teacher. Write down obtained values in table 1.1.
2.To perform data processing of direct measurements calculate:
— mean values of  ,
,  and
and 
— deviations of mean values:
 ,
, 

— root-mean-square deviations:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
Take into account not more than four significant digits in your calculations. Enter the obtained data into table 3.
Table 3
| Exp No | Mass m, g | Diameter d, mm | Height h, mm | Deviations from mean values | ||
 , g , g
|  , mm , mm
|  , mm , mm
| ||||
| Mean values | Root-mean-square deviations | |||||
 , kg , kg
|  , m , m
|  , m , m
| 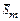
| 
| 
|
3.Determine random errors  ,
,  ,
,  . Multiply root-mean-square deviations
. Multiply root-mean-square deviations  ,
,  ,
,  by the Student’s coefficient for confidence probability a and measurements number n. For a = 0,95 and n = 5, t = 2,78.
by the Student’s coefficient for confidence probability a and measurements number n. For a = 0,95 and n = 5, t = 2,78.
4.Approximate the values of random errors to one significant digit, if the first digit is bigger than 3. If it equals 3 or less than 3, then approximate to two significant digits and enter the results into table 4. For example, if obtained values are 0,419 and 0,123, after approximations they will be 0,4 and 0,12.
5.Taking into account random and systematic errors, determine the total error of the direct measurements. Determine instrumental errors  ,
, 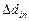 ,
,  and enter them into table. 4. Compare instrumental
and enter them into table. 4. Compare instrumental  and random
and random  errors. If one exceeds the other more than three times, the smaller error is ignored and the bigger one is taken as the total error of direct measurement. If opposite, a total error is calculated according to a formula:
errors. If one exceeds the other more than three times, the smaller error is ignored and the bigger one is taken as the total error of direct measurement. If opposite, a total error is calculated according to a formula:
 .
.
Calculated values are approximated in accordance with item 4. Enter the data into table 4.
Table 4
| Instrumental error | Random absolute error | Total absolute error of the direct measurements 
| |
| Mass | |||
| Diameter | |||
| Height |
6. Calculate value  in SI units according to the formula (5), using the value
in SI units according to the formula (5), using the value 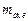 ,
,  and
and  from table 3.
from table 3.
7. C alculate value of indirect measurements error of  according to the formula (7) using the values
according to the formula (7) using the values 
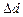 and
and  from table. 4. Calculated values are approximated in accordance with item 4.
from table. 4. Calculated values are approximated in accordance with item 4.
8. A pproximate value  to the first significant digit. Write down the final result in the following form:
to the first significant digit. Write down the final result in the following form:
 kg/m3.
kg/m3.
 questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work and its defence
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work and its defence
1. Give the definition of physical quantity measurement.
2. Is it possible to obtain the true value of physical quantity during measurements? Why?
3. Give the definition of measure.
4. Give the definition of a measuring device.
5. Give the definition of a measurement error.
6. Give the definition of absolute and relative errors of measurements.
7. What is measurement accuracy?
8. Give the definition of the direct measurement. Give an example.
9. Give the definition of the indirect measurement. Give an example.
10. Give the definition of systematic error. What types of systematic errors do you know?
11. Characterize the methodical systematic error.
12. Characterize the instrumental systematic error.
13. Characterize the personal systematic error.
14. Define and characterize the random errors.
15. Give the direct measurements error estimation rules.
16. How can random and systematic errors be taken into account?
17. Give the indirect measurements error estimation rules.
18. What demands for error measurements accuracy do you know?
19. Define and characterize gross (rough) errors.
Part ІІ. Random Distribution Study and Determination
of Gravity Acceleration Using Mathematical Pendulum
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 116 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Indirect measurement error estimation rules | | | Work procedure and data processing |