
Читайте также:
|
(a): The diagram of a "typical" neuron has many features of a motor neuron, but shows the three major parts of every neuron. The cell body is large and has a large, euchromatic nucleus with a well-developed nucleolus. The perikaryon also contains chromatophilic substance or Nissl bodies, which are large masses of free polysomes and RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum) and indicate the cell's rate of protein synthesis. Numerous short dendrites extend from the perikaryon, carrying input from other neurons. A long axon carries impulses from the cell body and is covered by a myelin sheath composed of other cells. Arrows show the direction of the nerve impulse. The ends of axons usually have many small branches called terminal arborizations, each of which usually has a swollen end called bouton which forms a functional connection (synapse) with another neuron or other cell. Axons can also branch closer to the cell bodies and form collateral branches that connect to other groups of cells. (b): Micrograph of a large motor neuron showing the large cell body with a long axon and several dendrites emerging from it. Evenly dispersed chromatophilic substance can be seen throughout the cell body and cytoskeletal elements can be detected in the processes. X100. H&E.
Neurons and their processes are extremely variable in size and shape. Cell bodies can be very large, measuring up to 150 m in diameter. Other cells are among the smallest cells in the body; for example, the cell bodies of granule cells of the cerebellum are only 4–5 m in diameter.
Neurons can be classified according to the number of processes extending from the cell body:
- Multipolar neurons, which have one axon and two or many dendrites;
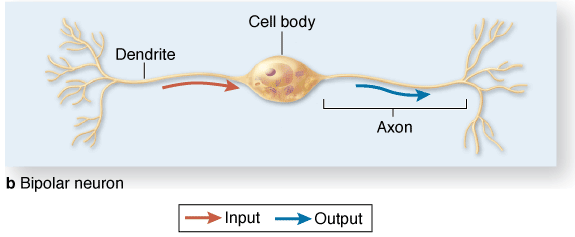
- Bipolar neurons, with one dendrite and one axon; and
- Unipolar or pseudounipolar neurons, which have a single process that bifurcates close to the perikaryon, with the longer branch extending to a peripheral ending and the other toward the CNS.
| NEURON (TYPES) | |
| Multipolar neuron | It has one axon and several dendrites. |
| Bipolar neuron | It has one axon and one dendrite. |
| Unipolar neuron | It has one axon |
| Pseudounipolar neuron | It has a single process which after a very short course divides into two. |


Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 139 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Striated skeletal muscle in longitudinal section. | | | Cell Body (Perikaryon) |