
|
Читайте также: |
Light micrographs of each type, accompanied by labeled drawings. (a): Skeletal muscle is composed of large, elongated, multinucleated fibers that show strong, quick, voluntary contractions. (b): Cardiac muscle is composed of irregular branched cells bound together longitudinally by intercalated disks and shows strong, involuntary contractions. (c): Smooth muscle is composed of grouped, fusiform cells with weak, involuntary contractions. The density of intercellular packing seen reflects the small amount of extracellular connective tissue present. (a, b): X200. (c): X300. All H&E.
Some muscle cell organelles have names that differ from their counterparts in other cells. The cytoplasm of muscle cells is called sarcoplasm (Gr. sarkos, flesh, + plasma, thing formed) and the smooth ER is called sarcoplasmic reticulum. The sarcolemma (sarkos + Gr. lemma, husk) is the cell membrane, or plasmalemma.
Skeletal muscle
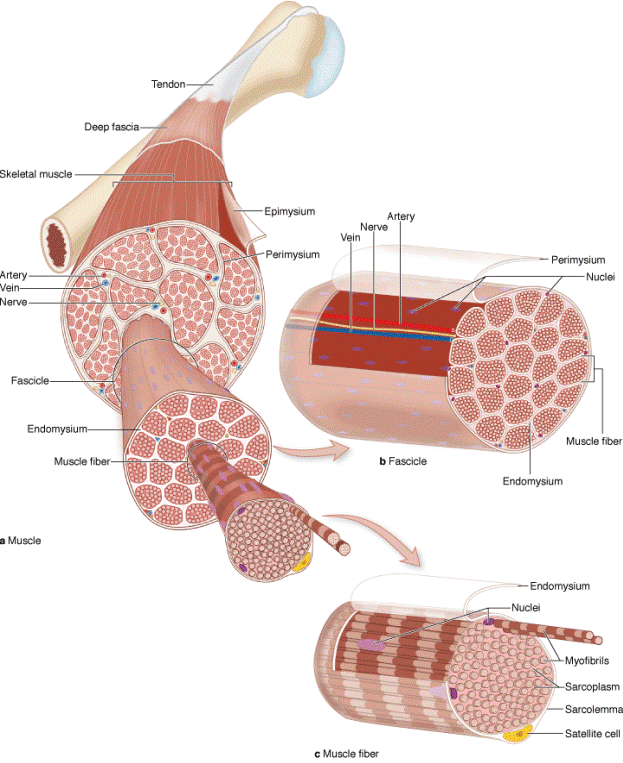
Skeletal muscle consists of muscle fibers, which are long, cylindrical multinucleated cells with diameters of 10–100 m. Multinucleation results from the fusion of embryonic mesenchymal cells called myoblasts. The long oval nuclei are usually found at the periphery of the cell under the cell membrane. This characteristic nuclear location is helpful in discriminating skeletal muscle from cardiac and smooth muscle, both of which have centrally located nuclei.
Organization
The masses of fibers that make up the various types of muscle are arranged in regular bundles surrounded by the epimysium, an external sheath of dense connective tissue surrounding the entire muscle. From the epimysium, thin septa of connective tissue extend inward, surrounding the fascicles or bundles of fibers within a muscle. The connective tissue around each fascicle is called the perimysium. Each muscle fiber is itself surrounded by a more delicate connective tissue, the endomysium, composed of a basal lamina synthesized by the multinucleated fibers themselves as well as reticular fibers and fibroblasts. Within each fiber the nuclei are displaced peripherally against the sarcolemma.


Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 162 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Neutrophil ultrastructure. | | | Striated skeletal muscle in longitudinal section. |