
|
Читайте также: |
GENERAL HISTOLOGY
CONTENTS:
Epithelia....................................................................................3
Connective tissue......................................................................15
Blood...................................................................................... 69
Muscular tissue....................................................................... 89
Nervous tissue....................................................................... 110
Sense organs.......................................................................... 140
EPITHELIUM
Epithelial tissues are formed by closely apposed polygonal cells with little or no intercellular material.
EPITHELIUM:
- SURFACE
- GLANDULAR
- SENSORY
| SURFACE EPITHELIUM: | It lines the outer surface of the body and the luminal surfaces of cavities within the body. |
| UNILAYERED: | It consists of only one layer of cells. |
| - Simple: | All the cells are adjacent to the basal membrane and have equal height. |
| 1. squamous | Its cells are flattened, their height being very little as compared to their width. |
| 2. cuboidal | The height and the width of its cells are more or less equal. |
| 3. columnar | The height of its cells is distinctly greater than their width. |
| - Pseudostratified | All the cells are adjacent to the basal membrane, but have different height. The cell nuclei lie at different level. |
| MULTILAYERED (STRATIFIED): | It consists of several layers of cells. |
| - Squamous | Superficial cells are squamous in shape. |
| 1. non keratinized | Superficial cells are living and contain nuclei. |
| 2. keratinized | Superficial cells are dead and are devoid of nuclei. |
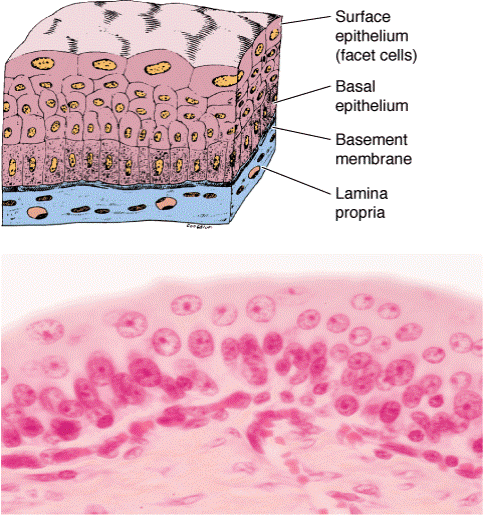
| - Transitional | Superficial cells are able to change their form depending upon the degree of distention. |
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM


SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM

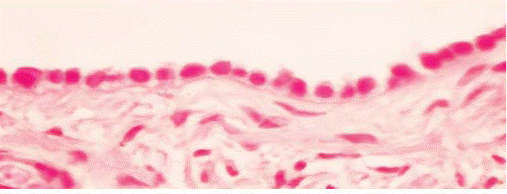
SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
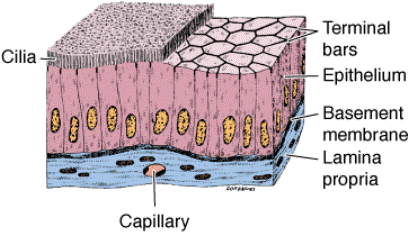

Pseudostratified epithelium

STRATIFIED NONKERATINIZED EPITHELIUM

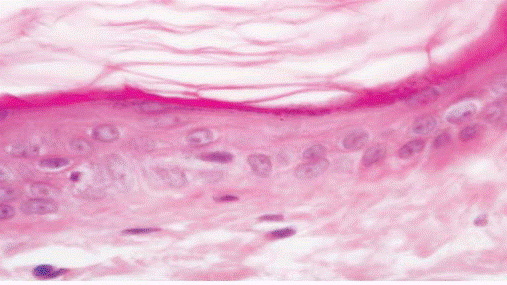
TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM
| GLANDS: | Epithelial cells that are specialized to perform secretory function. |
| UNICELLULAR | Gland that consists of one cell. |
| MULTICELLULAR: | Gland that consists of a lot of cells. |
| - Endocrine | Gland that pours its secretion into blood. |
| - Exocrine: | Gland that pours its secretion on to an epithelial surface, directly or through a duct. |
| 1. simple | All the secretory cells of an exocrine gland discharge into one duct. |
| - unbranched | It contains one excretory duct and one acinus. |
| - branched | It contains one excretory duct and several acini. |
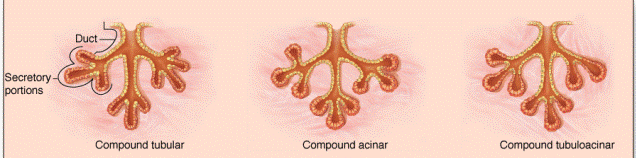
| 2. compound | There are a number of groups of secretory cells, each group discharging into its own duct. These ducts unite to form a larger duct which ultimately drain on to an epithelial surface. |
| Exocrine glands consist of: - dicts; - acini. |
| Both in simple and compound exocrine glands the secretory cells of acini may be arranged in various ways: (a) The secretory elements may be tubular. (b) The secretory elements may form flask shaped structures called alveoli. |
| Exocrine glands may also be classified on the basis of the nature of their secretions into: - mucous glands; - serous glands. |


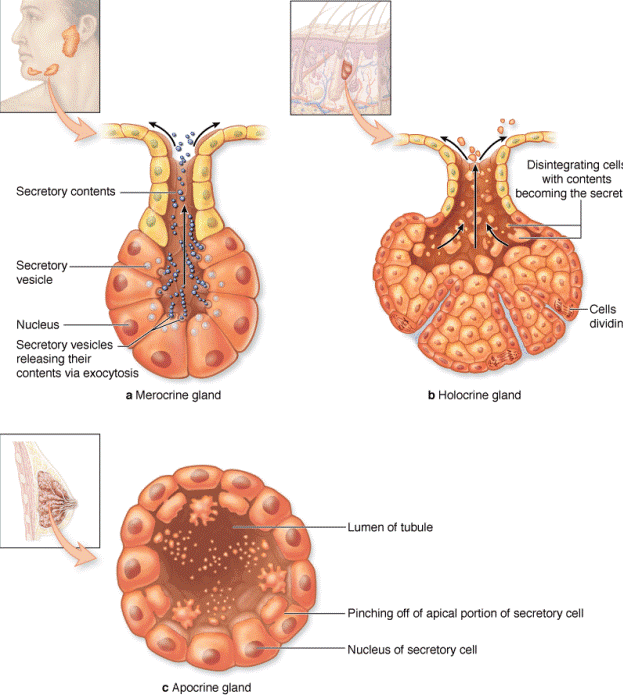
| Types of secretion of exocrine glands: | |
| Merocrine type of secretion | Secretions are thrown out of the cells by a process of exocytosis the cell remaining intact. |
| Apocrine type of secretion | The apical parts of the cells are shed off to discharge the secretion. |
| Holocrine type of secretion | The entire cell disintergates while discharging its secretion. |
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 139 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Sclera, choroid, and retina. | | | CONNECTIVE TISSUE |