
Читайте также:
|
1. Zona pellucida
2. Blastmere

|




Scanning electron micrographs of A uncompacted and B compacted eight-cell mouse embryos. In the uncompacted state, outlines of each blastomere are distinct, whereas after compaction, cell–cell contacts are maximized, and cellular outlines are indistinct.
Blastocyst
]


The blastocyst consists of two parts:
- an outer layer of small slightly flattened cells (light blastomeres) the trophoblast;
- an inner cell mass consisting of a small group of larger polyhedral cells (dark blastomeres) contained within the trophoblastic vesicle;
The cavity of the blastocyst (blastocoele) separates the trophoblast from inner cell mass except for the small area where they are in contact.
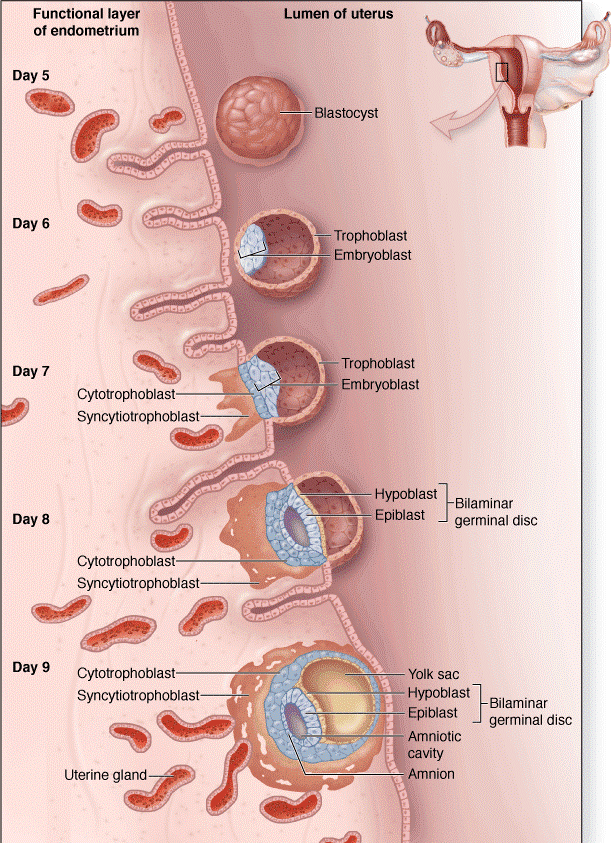
GASTRULATION
Formation of the three germ layers: ectoderem, endoderm and mesoderm.



| EXTRAEMBRYONIC ORGANS | |
| UMBILICAL CORD | Vascular cable (~fifty-five centimeters in length) that connects the embryo to placenta. The umbilical cord of the fetus is covered by the amniotic epithelium and contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein embedded into the Wharton’s jelly. It also contains remains of allantois and vitelline sac. It is first formed during the fifth week of embryonic life. |
| AMNION | The thin, transparent, tough membrane lining the fluid-filled cavity which contains the embryo |
| ALLANTOIS | One of the extraembryonic membranes, providing respiratory exchange. It is covered by a conjoined vascular layer containing umbilical or allantoic vessels which are the vascular connections with the placenta. |
| VITELLINE SAC | An extraembryonic structure, attached to the umbilical cord and lined by endoderm. Vitelline sac is a site of hematopoiesis. |
| CHORION | The outermost of the fetal membranes of mammals, formed from extraembryonic somatopleuric mesoderm and the overlying trophoblast. The trophoblast divides into an outer syncytiotrophoblast and inner cytotrophoblast. The chorion develops villi, engaged in fetal-maternal exchange. |
| PLACENTA | An organ with many physiologic functions destined to assure the development of the fetus. The human placenta is hemochorial in type, the maternal and fetal blood being separated only by the chorionic epithelium covering the villi. Placenta is the organ that facilitates nutrient and gas exchange between the maternal and fetal compartments. |

PLACENTA





Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 229 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Junctional complexes of epithelial cells. | | | Membrane proteins. |