
|
Читайте также: |
(a): TEM (transmission electron microscopy) of a typical cell nucleus clearly shows the electron-dense heterochromatin (HC) and the more diffuse euchromatin (EC). The arrows indicate the nucleolus-associated heterochromatin.
Arrowheads indicate areas where the perinuclear space between the two membranes of the nuclear envelope is clearly seen. Just inside the nuclear envelope is a thin electron-dense region containing and more heterochromatin. X26,000. (b): Schematic representation of a cell nucleus shows that the nuclear envelope is made of two membranes separated by the perinuclear space. The outer membrane bound to it and is continuous with the ER (endoplasmic reticulum). The two membranes fuse at many places to form nuclear pores. Heterochromatin clumps (HC) are associated with the meshwork of the nuclear lamina just deep to the envelope, whereas the euchromatin (EC) appears dispersed in the interior of the nucleus. The nucleolus contains distinct regions called the pars granulosa (G) and the pars fibrosa (F).
| CELL ORGANELLES | |
| MEMBRANOUS ORGANELLES | |
| - ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM | A cytoplasmic system of membranes that may be arranged in the form of flattened sacs (or cisternae) or of tubules. |
| - granular endoplasmic reticulum | A system of membranes studded with ribosomes. It represents the site at which proteins are synthesized. |
| - agranular endoplasmic reticulum | Cell organelle that is composed of smooth-surfaced membranes unassociated with ribosomes. It is responsible for further processing of proteins synthesized in rough endoplasmic reticulum. |
| - GOLGI COMPLEX | A number of flattened sacs (cisternae) that form an independent system. The function of the Golgi apparatus is to accept vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum, to modify the contents and to distribute the products to other parts of the cell or to the cellular environment. |
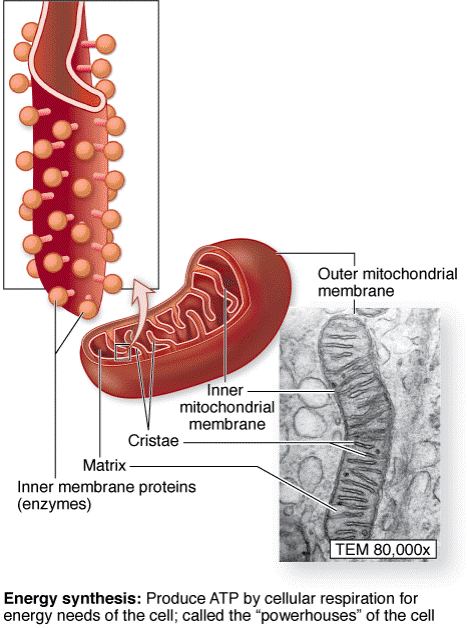
| - MITOCHONDRIA | Cytoplasmic organelles enclosed by a double membrane. Mitochondria are the main source of energy in the cell. |
| - outer membrane | It is smooth. |
| - inner membrane | It forms cristae. |
| - intermembranous space | It separates the outer and inner membranes. |
| - matrix | Granular material that fills the space bounded by the inner membrane. It contains numerous enzymes, RNA and DNA. |
| - LYSOSOM ES | A membrane-limited cytoplasmic organelle containing hydrolytic enzymes. The enzymes can destroy unwanted material present within a cell. |
| NONMEMBRANOUS ORGANELLES | |
| - CYTOSKELETON | A number of fibrillar elements (permeating the cytoplasm) that collectively form a supporting network. |
| - CENTRIOLES | Short cylinders that lie at right angles to each other. They play an essential role in mitosis. |
| - RIBOSOMES | Cytoplasmic organelles that consist of proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Each ribosome is made up of two subunits one of which is larger than the other. They play an essential role in protein synthesis. |
| - monosomes | Ribosomes that are present singly. |
| - polyribosomes (polysomes) | Ribosomes that are present in groups. |
Mitochondria
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 139 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure. | | | Golgi apparatus. |