
Читайте также:
|
CHAPTER 8
Stock Valuation
CHAPTER ORIENTATION
This chapter continues the introduction of concepts underlying asset valuation began in Chapter 7. We are specifically concerned with valuing preferred stock and common stock. We also look at the concept of a stockholder’s expected rate of return on an investment.
CHAPTER OUTLINE
I. Preferred Stock
A. Features of preferred stock
1. Owners of preferred stock receive dividends instead of interest.
2. Most preferred stocks are perpetuities (non-maturing).
3. Multiple classes, each having different characteristics, can be issued.
4. Preferred stock has priority over common stock with regard to claims on assets in the case of bankruptcy.
5. Most preferred stock carries a cumulative feature that requires all past unpaid preferred stock dividends to be paid before any common stock dividends are declared.
6. Preferred stock may contain other protective provisions, such as granting voting rights in the event of non-payment of dividends.
7. Preferred stock may contain provisions to convert to a predetermined number of shares of common stock.
8. Some preferred stock contains provisions for an adjustable rate of return.
9. If there is a participation feature, it allows preferred stockholders to participate in earnings beyond the payment of the stated dividend.
10. Payment-in-kind (PIK) preferred stock, grants the investor additional preferred stock instead of dividends for a given period of time. Eventually cash dividends are paid.
11. Retirement features for preferred stock are frequently included.
a. Callable preferred refers to a feature which allows preferred stock to be called, or retired, like a bond.
b. A sinking fund provision requires the firm periodically set aside an amount of money for the retirement of its preferred stock.
B. Valuation of preferred stock (Vps):
The value of a preferred stock equals the present value of all future dividends. If the stock is nonmaturing, where dividends are expected in equal amount each year in perpetuity, the value may be calculated as follows:
Vps= =
II. Common Stock
A. Features of Common Stock
1. As owners of the corporation, common shareholders have the right to the residual income and assets after bondholders and preferred stockholders have been paid.
2. Common stockholders are generally the only security holders with the right to elect the board of directors.
3. Preemptive rights (if granted) entitle the common shareholder to maintain a proportionate share of ownership in the firm.
4. Common stockholder’s liability as an owner of the corporation is limited to the amount invested in the stock.
5. Common stock’s value is equal to the present value of all future cash flows expected to be received by the stockholder.
B. Valuing common stock
1. Company growth occurs by:
a. the infusion of new capital, or
b. the retention of earnings, which is called internal growth. The internal growth rate of a firm equals:
Return on equity ´
2. Although the bondholder and preferred stockholder are promised a specific amount each year, the dividend for common stock is based on the profitability of the firm and management's decision either to pay dividends or retain profits for reinvestment.
3. The common dividend typically increases with the growth in corporate earnings.
4. The earnings growth of a firm should be reflected in a higher price for the firm's stock.
5. In finding the value of a common stock (Vcs), we should discount all future expected dividends (Dl, D2, D3,..., D¥) to the present at the required rate of return for the stockholder (kcs). That is:
Vcs=  +
+  +...+
+...+ 
6. If we assume that the amount of dividend is increasing by a constant growth rate each year,
Dt = D0 (l + g)t
where g = the growth rate
D0 = the most recent dividend payment
If the growth rate, g, is the same each year, t, and is less than the required rate of return, kcs, the valuation equation for common stock can be reduced to
Vcs = =
III. Shareholder's Expected Rate of Return
A. The shareholder's expected rate of return is of great interest to financial managers because it tells about the investor’s expectations.
B. Preferred stockholder's expected rate of return:
If we know the market price of a preferred stock and the amount of the dividends to be received, the expected rate of return from the investment can be determined as follows:
expected rate of return =
or
 ps =
ps = 
C. Common stockholder's expected rate of return:
1. The expected rate of return for common stock can be calculated from the valuation equations previously discussed.
2. Assuming that dividends are increasing at a constant annual growth rate, g, we can show that the expected rate of return for common stock, kcsis
 cs = +
cs = +
= + g
Since dividend ÷ price is the "dividend yield," the
Expected rate of return = +
IV. Appendix: The Relationship between Value and Earnings
A. Earnings and Value Relationship: The nongrowth firm
1. Nongrowth firms retain no profits for reinvestment purposes.
a. Investments are made to maintain status quo.
b. Earnings and dividend growth stream is constant from year to year.
2. Value on nongrowth common stock, Vng:
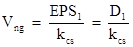
a. Value of share changes in direct relationship with changes in earnings per share.
b. Changes in the investor’s required rate of return will change share value.
B. Earnings and Value Relationship: The growth firm
1. Growth firm reinvests profits back into the business.
2. Value of stock equals the present value of the dividend stream plus the present value of the future growth resulting from reinvesting future earnings.

a. NVDG is the net value of any dividend growth resulting from reinvestment of future earnings.
b. Present value (PV1) from reinvesting part of the firms earnings in year 1 equals:

a. Using the constant-growth model to value NVDG,

b. The value of a share of stock is therefore:

3. Value of stock is influenced by
a. Size of the firm’s EPS,
b. Percentage of profits retained,
c. Spread between return generated on new investments and the investor’s required rate of return.
ANSWERS TO
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 137 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Bond A B C D E | | | END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS |