
Читайте также:
|
It describes proteins which consist of two or more chains of polypeptide.
This structure is formed due to the linkage of polypeptide chains with each other.
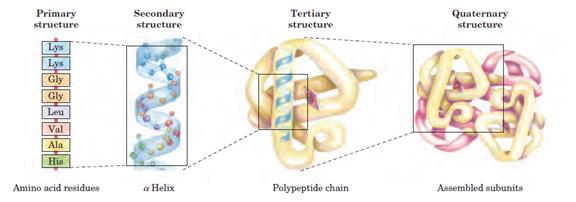
Fig. (7) Levels of protein structure

à They are biological macromolecules which consist of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Nucleic acids have two kinds which are:-
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
à Nucleic acids consist of structural units called nucleotides which are bound together by covalent bonds forming polynucleotide
Nucleotides:-
à The building units of nucleic acids, each one of them is composed of three units which are:-
- Pentose (5 carbon) sugar:
There are two types of pentose sugar which form nucleic acids, these types are:-
Ribose: forms RNA
Deoxyribose: forms DNA
- Phosphate group
It's linked by a covalent bond to the carbon atom no. 5 of sugar molecule of the nucleic acid.
- Nitrogenous base
There are five nitrogenous bases which are:-
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T) à Replaced by Uracil (U) in RNA molecules
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
à Each of the previous bases link with the 1st carbon atom of sugar molecule in covalent bond.
à Nucleic acids differ according to their pentose sugars and nitrogenous bases
à Uracil base in RNA molecule is the equivalent to thymine base in DNA molecule.
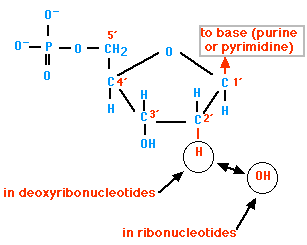
Fig. (8) The structure of a nucleotide
The importance of DNA
1- It is from the basic components of chromosomes.
2- It is responsible for transferring hereditary traits through generations.
3- It carries the hereditary information responsible for the characteristics of living organisms and organization of the biological processes within cells.
à DNA molecule consists of two strands coiled around each other.
à Guanine base binds to Cytosine base with triple hydrogen bond.
à Thymine base bind to Adenine base with double hydrogen bond
 |
Fig. (9) The structure of DNA molecule
The importance of RNA
à It copies the information of DNA, then it transports to cytoplasm to be used in making proteins which are responsible for the hereditary traits and organization of biological processes.
à Guanine base binds to Cytosine base with triple hydrogen bond.
à Uracil base bind to Adenine base with double hydrogen bond.

Fig. (9) The structure of RNA molecule

Proteins: They are complex biological macromolecules which consist of oxygen, hydrogen and carbon atoms basically, they have heavy molecular weights, and their structural units (monomer) are amino acids.
Amino acids: The building units of proteins, they are organic compounds which consist of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen atoms.
Peptide bond: A bond between two molecules which is formed when the carboxyl group of an amino acid reacts with the amine group in another one, which releases water molecule (H2O)
Dipeptide: Two amino acids linked by peptide bond.
Polypeptide: protein chain formed from many amino acids.
Nucleic acids: They are biological macromolecules which consist basically of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen. They are composed of structural units called nucleotides. Nucleic acids divide into RNA and DNA.

Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 158 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Write the scientific term | | | Choose the correct answer |