
Читайте также:
|
1- Biological macromolecules
2- Carbohydrates
3- Lipids
4- Oils
5- Fats
6- Waxes
Lesson (2) Chemical structure of living organisms' bodies
(Proteins and nucleic acids)

à Proteins form the bodies of all living organisms, they also take part in the biological reactions occurring within living organisms which help them sustain life.
The importance of proteins
1 - The basic component of cell membranes
, ligaments and tendons 2 - They form muscles, fingernails, hair, organs, glands
3- They form liquids in human body such as lymph and blood
4- They are necessary for human growth
5- The main component of chromosomes
6- They form enzymes and hormones
à hooves and horns of animals, and spider webs are formed from proteins
The molecular structure of proteins
Polymers of proteins are composed of monomers called " amino acids"
Amino acids:-
à The building units of proteins, they are organic compounds which consist of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen atoms.
Structure: An amino acid is composed of a carbon atom linked with:-
- An acidic functional group called amine NH2
- A basic functional group called carboxyl COOH
- R Group (side group) which differs according to the type of amino acid
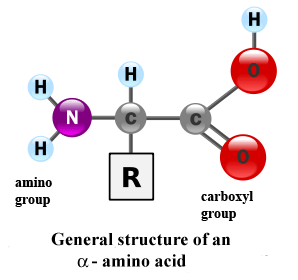
Fig. (4) The structure of amino acids
Amino acids and building proteins
Proteins are formed from groups of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
Peptide bond: A bond between two molecules which is formed when the carboxyl group of an amino acid reacts with the amine group of another one releasing water molecule (H2O)

Fig. (5) How peptide bonds form
à Two amino acids linked by peptide bond are called Dipeptide, while a protein chain formed from many amino acids linked by peptide bonds is called polypeptide
à Proteins are formed from the same 20 amino acids, but with different arrangements.
Example of amino acids:-
1- Alanine
2- Glycine
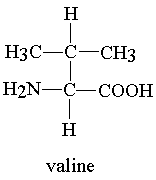
3- Valine
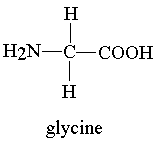
How to detect proteins in substances
We detect proteins by using Biuret reagents, proteins change the colours of these reagents from blue to purple
 |
Fig. (6) Biuret reagents
The classification of proteins
Proteins are classified according to their structure into:-
Simple proteins:-
Structure: They consist of only amino acids
Examples: Albumin, which is found in blood plasma, leaves and seeds of plants
Associated proteins:-
Structure: They consist of amino acids associated with other elements.
Examples:-
1- Nuclear-associated proteins:
2- Phosphoproteins: They contain phosphorus element (ex. Casein – milk protein)
3- Thyroxin: Hormone secreted by thyroid gland and contains iodine element.
4- Blood hemoglobin: Its protein contains iron element.

Primary structure of protein:-
It describes the arrangement of amino acids in polypeptides of a certain protein.
This level determines the no., kind and the arrangement of the amino acids forming protein.
Secondary structure of protein:-
It describes the way by which polypeptides are coiled.
This structure is formed due to the hydrogen bonds between carboxyl and amine groups in close amino acid monomers.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 171 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Fats (Glycerides) | | | Quaternary structure of protein |