
Читайте также:
|
| Figure: body mass relative to height | number | Type of skin | number | Sex, age | number | Special risk factors | number |
| Middle Above middle Obesity Below middle | Healthy Cigarette Paper Dry Edematous Sticky (increased to) Color change Cracked, blotchy | Male Female 14-49 50-64 65-74 75-81 More than 81 | Violation of skin feeding, for example, terminal cachexia Heart insufficiency Diseases of peripheral vessels Anemia Smoking |
www.myshared.ru
Picture 66.
The Waterlow scale
According to the Waterlow scale: the higher the score, the greater the risk. Points are summed up the total is defined by degree of risk:
1-9 points-no risk
10-14 points -there is a risk
15-19 points-high risk
more than 20 points- a very high risk.
The assessment of the risk of bedsores development should be carried out regularly, even if the primary inspection, the risk was low, and changes in the patient's condition. If a patient is at risk, you should immediately start preventive activities.
To prevent the formation of exogenous pressure ulcers should eliminate the possibility for grave and prolonged pressure on the same areas of the skin and subjacent tissues with plaster bandage, curative, adhesive bandage etc. Located in the wound drains, catheters, and other tools should be replaced or change their position.
For prevention of endogenous bedsores in weakened restrained patients it is recommended the following activities:
• Regularly assess a patient's condition, using the Norton or Waterlow scale.
• Change the position of a patient's body every 1.5 -2 hours (even at night): the Fowler's position, the Sims', on the right side, on the left side, on the abdomen (if no contraindications). Position types depend on the disease and a patient's condition. If a patient is trying to turn around in bed alone, it is necessary to encourage and assist to move by themselves.
• To move a patient in bed -change the position of the body, raising him above the bed.
• Use special devices:
hand and foot cushions (instead of cushions you can use regular pillows), feet supports.
The possible occurrence of bedsores and put of special fabric cushions, placed in a bag or covered with draw-sheet, thus the bedsore is in place over the opening laps and not touching the a bed.
• Use beds with Anti bedsore air mattresses with corrugated surface.
Thanks to the automatic cell mattress filled with air compressor every 5-10 minutes, therefore changes the degree of tissue compression of the patient.
Tissue massage by changing the pressure on the surface of the patient's body supports the normal blood circulation, providing a supply of skin and subcutaneous tissue with nutrients and oxygen.
• Monitor a comfortable position of the patient in bed, in accordance with the biomechanics rules.
• Check the condition of the bed (remove crumbs, smooth edges, remove the folds in the bedding).
• Check the condition of the patient's underwear (to change wet dirty and underwear; do not use underwear that has rough seams, fasteners, buttons on the side facing to the patient).
• Daily examine the skin condition.
• Wash with soap and warm water or a disinfectant solution the vulnerable areas of skin at least 2 times a day (more often if necessary).
• When dry skin use moisturizing and nourishing creams, camphor spirit especially in possible future bedsores.
When hidrosis- talcum powder.
• Monitor the patient's diet (the quality and quantity of food consumed by humans).
The diet should be a sufficient amount of protein, minerals and vitamins.
If necessary, carry out dietary adjustment.
• Control mode of drinking-how much fluid per day shall not be less than 1.5 l, if there is no evidence for its limitations.
Decrease the amount of fluid increases the concentration of the urine and increases the risk of urinary tract infection.
• Inn case of uroclepsia you can use diapers for adults in a timely manner by changing their (at least every 4 hours).
For men, you can apply external catheter bags.
When changing diapers (draw-sheets) is sanitized with soap and warm water for all contaminated sites, followed by careful drying.
• When the first occurence of redness or a patient's skin blanching smear the redness with lemon juice, or a 10% solution of camphor, or wipe with a wet towel and then carefully wipe and provide irradiation a quartz lamp.
• In case of occurence of bedsores should immediately begin treatment with a solution of potassium permanganate, Vishnevsky ointment, synthomycin emulsion or mixture of fir balsam with peruvian oil.
Prevention is always better than treatment.
If begin it on time, then in 95% of cases you can escape bedsores.
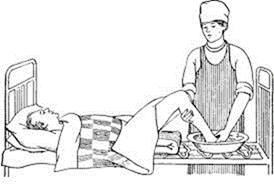
2.7 Washing a patient’s feet in bed
Washing a patient's feet is carrying out 1-2 times a week, placing the bowl in bed (if the patient is unable to sit).
Wash patinet's nails with brush, the hyponychial space clean with special nail cleaner.
Nails are cut as necessary (not too short).
Patients take hygienic bath in a satisfactory condition in half-sitting position, plunging into the water to the top of the chest.
Water temperature should be 36-380 C, the duration is less than 30 minutes.
In strict bedrest regimen the patient’s feet washes at least three times a week, putting bowl a for this procedure.
To prevent the spread of athlete’s foot, a patient's footwear need to be disinfected and prevent it has worn by other members of the family (Pic. 67).
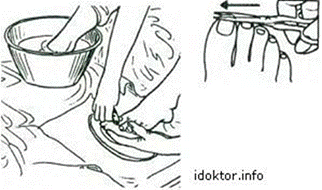
Picture 67.
Washing a patient's feet in bed
Equipment:
draw-sheet, water tank, oilcloth, towel, scissors, gloves, private sponge or body scrubber, bag for dirty linen, softening cream.
The procedure:
1. Put on gloves
2. Prepare a bowl with warm water (t -34 -37° C).
3. Help a patient sit comfortably on a chair.
4. If the patient cannot sit down, lay him on his back or give the Fowler's position.
Lay waterproof napkin (oilcloth) on the mattress.
5. Bend the patient's leg at the knee and put his feet in a tank of water for 5 minutes.
6. Wash your feet with a sponge and soap, starting with the lower leg from the knee, and then the dorslim of foot, then the toes and interdigital space, nail bed, finish with the plantar aspect of the foot from the toes to the heel.
7. Rinse the feet with clean water by lifting them above the pelvis.
8. Wipe dry with a towel.
9. Apply foot cream.
10. Remove the water tank and take out the oilcloth.
11. Place the waterproof napkin (oilcloth) in the bag for dirty laundry.
Nail care
Once every ten days hygienic procedures include trimming nails on the hands and feet of the patient.
Nail care should be undertaken very carefully.
Otherwise, this could lead to injury of the skin around the nail bed and subsequent infection.
No need to cut the nails to the bottom or you may injure your skin.
Before cutting the nails put patient's hands and feet in warm water for 5 minutes.
You must be especially careful when cutting nails of patients suffering from diabetes, hemiplegia and other disease, coupled with a decrease in the sensitivity of the skin (Pic. 68-69).


Picture 68. Picture 69.
Nails in the elderly people Cutting nails
Necessary equipment:
• Rubber gloves.
• Scissors and nail nippers.
• Warm water, liquid soap, cream for hands and feet, rubbing alcohol (70%).
• the basin and water tray, towels
The procedure execution order:
1. Prepare for the sanitary-hygienic processing:
Arrange necessary equipment, heat water, put on gloves.
2. Add some warm water and liquid soap into the tray for 2-3 minutes, the patient's hands (in turn as far as trimming the nails).
3. In turn take the patient's fingers out of the water, wipe them and gently cut the nails.
4. Apply the patient's hand with cream.
5. Add to the basin with warm water and liquid soap in it for 2-3 minutes the patient's foot (turn as far as trimming the nails).
6. Put the foot on the towel (in turn as far as trimming the nails), wipe it and cut nails by special nippers.
7. Apply the foot cream.
8. Sterilize scissors and nippers with alchohol or 5 % of the chloramine solution
9. Take off the gloves and wash your hands.
Oral care
Oral care need to be undertake all patients because accumulate germs in the mouth.In weakened and febrile patients on the mucosa of the mouth, the buildup of dental plaque on teeth which consists of a viscous mucus, squamous epithelial cells, decaying food debris, bacteria. As a result there is appear caries, inflammatory diseases mucous membranes of the mouth (stomatitis), gums (gingivitis), etc. Patients experience discomfort: feeling violated, there is pain when eating, excessive salivation, halitosis, reduced appetite, sometimes dry lips, cracks at the corners of your mouth (Cheilitis).
Patients who have a common regime autonomous toilet mouth. Each patient should brush his teeth after sleep and after each meal. For brushing your teeth use toothpaste that contains fluoride to strengthen tooth enamel. The toothbrush should be very soft and not to traumatize the gum, for weak patients use gauze swabs or cotton balls. For mouthwash, use 0.5% solution of sodium carbonate (solution of sodium bicarbonate) or 0.9% solution of sodium chloride (saline solution). Tinse your mouth a decoction of chamomile, sage, St. John's wort is useful. Complete oral care, be sure to clear brush, removing from it language plaque.
In case of inflammation of mucous membranes of the oral cavity treatment following with applications: On the inflamed facial mucous, impose sterile gauze napkins soaked disinfectant solution for 3-5 minutes several times a day. It is possible to use irrigation by medicinal solutions using Zhane syringe, 20-gram syringe or a special bulb syringe. To do this, pull the cheek by tongue depressor and rinse the mouth.
Patients with dentures leave them out at night, wash thoroughly with soap and water and to keep them in a clean individual glass, in the morning rinse them under running water and wear.
For seriously ill people who are unable to brush their teeth, a nurse or family members should perform the mouth cleansing 2 times a day. The cavity should be cleaned with a weak solution of baking soda or special antiseptic solutions (furacilin rivanol) with a rubber cylinder or drinking bowl. The position of the patient - the inclination of the head forward (to avoid any liquid in the respiratory tract), pulling the angle of the mouth (for better outflow).Oral irrigation with Zhane syringe to seriously ill patients is not used because of the risk of aspiration in the upper respiratory tract.
If the patient is unconscious, oral care should be performed every 2 hours, day and night. To prevent dry lips and cheilitis is by applying on the lips gauze soaked in the furacilin solution (1: 5000), which replace the gauze as it dries (Pic. 70).


Picture 70.
Oral care
Oral care algorithm:
Equipment:
Oilcloth, rubber gloves, a glass of water, toothpaste, soft toothbrush, vaseline, sterile gauze balls, the capacity for the collection of sewage, garbage bag;
The procedure:
1. Explain the patient at first about the services you are going to give him.
.2. Place the patient in one of the following position:
at the back at an angle of more than 45°; lying on his side or lying on his stomach (or back), turning his head sideways.
3. The patient's neck and chest covered with oilcloth put a tray under the patient's chin.
4. Wash your hands, wear gloves.
5. Ask the patient to hold the bowl, dial in the mouth water and rinse the mouth.
6. Wet the toothbrush with water and apply on the toothpaste.
7. Clean the teeth.
Clean each tooth from the inside, starting with the root to bits (better to start brushing the patient's teeth from the upper jaw).
Consistently clean inner and outer, chewing surfaces of his teeth.
The procedure is repeated at least twice.
8. Ask the patient to put out his tongue (or gently pull it out of the mouth, after wrapping up the tongue with a sterile gauze napkin).
9. Rub the tongue with gauze ball, dipped in antiseptic solution in the direction from the root to the tip of the tongue.
10. Change the gauze ball and wipe the inside of the cheeks, the space under the tongue, the patient's gums.
11. Help the patient rinse his mouth with water (or perform irrigation using pear-shaped cans).
12. Wipe your chin, smear the patient's lips with vaseline, and process the cracks with 1% solution of brilliant green.
13. Remove the water tank, oilcloth, collect supplies for care in a garbage bag and send them for disinfection.
14. Remove rubber gloves and wash your hands.
Care of dentures (the patient is conscious):
Dentures often cause irritation to the gums, aphthous stomatitis, and fungal diseases.
Therefore, you should regularly clean them.
Every evening dentures should be thoroughly washed and put in a dry bowl.
Keep dentures in a glass of water is not recommended, because in a humid environment well preserved fungi/microbes on the surface of the prosthesis.
Equipment:
towel, rubber gloves, paper tray, cup for artificial teeth, toothpaste, tooth brush, lip cream, gauze napkins, glass of water, garbage bag.
The procedure:
1. Explain to the patient the upcoming procedure.
2. Ask the patient to turn his head to one side.
3. Unwrap the towel, which is covered the patient's chest to his chin.
4. Wash your hands, wear gloves.
5. Put a tray under the patient's chin;
6. Ask the patient to hold the tray by one hand, use the other hand to take a glass of water, dial some water in the mouth and rinse it.
7. Ask the patient to remove the dentures.
If the patient is not able to remove them, then grab it with your thumb and index finger of the right hand with swipe dentures; by oscillatory movements carefully remove the denture.
8. Put the dentures in special cup.
9. Ask the patient to rinse his mouth with water.
10. Help the patient to treat oral cavity with a damp cloth:
brush his teeth, tongue, palate, inside of the cheeks, gums, subglossal region.
11. Dump the used wipes in a garbage bag.
12. Ask the patient to rinse his mouth.
13. Wipe the patient's chin.
14. Place the cup with the dentures in the sink.
15. Turn on the water and adjust water temperature.
16. Clean with toothpaste and brush all surfaces of the denture.
17. Rinse dentures and a cup under cold running water.
18. Put the dentures in a cup to keep them at night or help the patient to wear them.
19. Remove gloves and fold them into a garbage bag.
20. Wash your hands.
Oral care for the unconscious patients:
Equipment:
2 towels, rubber gloves, tray, glass with a solution for gargle, gauze swabs, adhesive tape, scissors, tongue depressor, small brush, soft toothbrush, petroleum butter (lip cream), cup, garbage bag.
The procedure:
1. Wash your hands, wear gloves.
2. Wrap a napkin around the wooden tongue depressor cloth and fix it with adhesive tape.
3. Pour antiseptic solution into a cup for oral cavity treatment.
4. Place the patient in a lying position on his side, the patient should be on the edge of the cushion.
5. Put a towel under the patient's head.
6. Deploy the second towel and cover his chest.
7. Put a tray under the patient's chin;
8. Gently open the patient's mouth, without using force.
9. Enter the jaw gags between the upper and lower set of teeth 1, 2, 3 p. fingers of one hand and gently increase the separation between the upper and lower set of teeth to press with the same fingers on the upper and lower teeth.
10. Put the prepared wooden tongue depressor between the teeth to keep his mouth open.
11. Wrap a napkin around the forefinger and holding it with your thumb, soaked it in 0.02% furacilin solution or 2 percent solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate.
12. Treat the palate, inside of the cheeks, teeth, gums, tongue, lips, changing napkins as soon as they are dirty.
13. Throw used napkins in the garbage bag or tray.
13. Clean the patient's teeth with a soft brush (without toothpaste)
14. Smear his lips with vaseline
15. Remove the towel, turn the patient on his back
16. Remove the gloves and wash your hands.
Hair care
Patients who are able to take care of themselves without assistance take care of their hair alone. To do this, daily monitor hairdo (combing should be performed by individual comb) and at least 1 times a week wash my hair using shampoo.
Relatives or medical staff performs hair care for seriously ill patients. For hygiene of patients, men should be cut shortly, and women combed it daily. Patients with infectious diseases in obtaining consent better to shave the heads bold.
Combing the lying patient turn his head in one, then in the other side. Combing should be performed by fine-tooth comb, taking care not to pull out hairs, comb each strand separately: beginning from the ends, not from the roots, and gradually move to the roots of the hair.
Knotted hair should be used an individual comb with few teeth. Comb must have blunt teeth, so as not to injure his head and does not cause pain. Keep the combs clean, wipe with alcohol, vinegar and wash in hot water with soda or ammonia (Pic. 71 a).




а б
Picture 71.
а –combing the patient
б – washing patient's in bed
Seriously ill patients' head washed in bed 1 time in 7-10 days. For this patient, lean his head and give an elevation and head washed in a basin, which put at the head end of the bed. In some hospitals for this purpose, there are special beds with removable backrest or a convenient headrest (Pic. 69 b).
Equipment:
a jug of warm water, clean Bowl, oilcloth, shampoo, towel, hair dryer, comb hair, gloves, apron, oilcloth bag for dirty laundry.
The procedure:
1. Explain to the patient the upcoming procedure.
2. Wash your hands, put on an apron and gloves.
3. Examine the patient's head and straighten his hair.
4. Place the patient on his back, remove the cushion, lay an oilcloth with cervico-occipital region of the patient.
5. Put the headrest under the patient's shoulders and pelvis at the headboard
6. The head of the patient lean back so that the head is over the basin.
Wet his hair by pouring warm water from the pitcher.
8. Apply a little bit of shampoo and lather the patient's head.
9. Wash his hair and parotid area thoroughly.
10. Wash off soapy suds by pouring from jug on the patient's head.
11. Wash his hair with clean water.
12. Wipe dry his hair, ears with a clean towel.
13. It is advisable to dry the hair with a hair dryer.
14. Slowly and gently comb the hair.
15. Remove headrest and bowl, oilcloth, pour out the water, and remove the towel in bag for dirty laundry.
16. Lay the patient on the pillow with a clean pillowcase.
17. Remove the apron, gloves, fold them into a garbage bag.
18. Wash your hands.
Modern technologies for care of seriously ill patient's make it much easier to provide medical manipulations.
If you use these techniques, washing the patient's hair performs with a special shampoo without water. Shampoo contains active substances that cleanse the hair and scalp from pollution. This shampoo is applied to the hair, whipped, and easily rubbed in for 2-3 minutes. The head should be wiped with a dry absorbent towel.
In addition, there is special inflatable bath (basins) to wash a head in bed using water. Inflatable bath inflates quickly and softly captures the patient's head, relieves pressure on shoulders, as it is constructed with a small notch for the neck (Picure. 72-73).

|

Picture 72 Picture 73
Inflatable bath for washing the patient's head Using inflatable bath
Eyes care
Walking patients during morning toilet care of their eyes alone. Special attention should be paid to the eyes of seriously ill patients. If in the patient appears eye discharge, gluing eyelashes, you should wipe his face with sterile or cotton swabs, soaked in disinfectant (1: 2000 solutions of furacilin, rivanol).
Be sure that you use sterile swab for each eye, by which you wipe patient's lashes and eyelids from the outer corner of the eye to the inner. To collect discharged fluid use the tray that patient holds the under his chin. Repeat wiping 4-5 times, changing the tampons. At the end of the procedure, drain swab with the residual solution.
In inflammatory diseases of the eye carry out instillation of drops or rubbing the eye ointments.
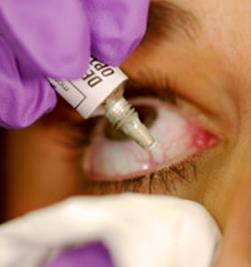
Instillation of eye drops (pic. 74)


|

Equipment:
bottle of eye drops, sterile pipette, a cotton swab.
Picture 74
Instillation of drops into the eye
The procedure:
1. Wash your hands, wear gloves.
2. Seat or lay the patient, ask him to lean his head back slightly and look up.
3. In the left hand take a cotton ball and hold it with your thumb, pull the lower eyelid down with same hand's index finger hold the upper eyelid.
4. Avoid touching by the tip of the pipette eyelashes and eyelid edges (do not hold the dropper to the eye closer than 1.5 cm), drip 1 drop of fluid in the space between eyelids and eye at a distance of 1 cm from the inner canthus.
5. Wipe excess liquid from under your eye with wet dry swab.
6. Drip the drops into the other eye in the same sequence.
7. Put the dropper into the container with the disinfecting solution.
Putting the ointment in eyes (Pic.75)
Equipment:
ointment, sterile glass rod, a cotton swab.
 http://www.atitesting.com
http://www.atitesting.com
Picture 75
Applying eye ointment
The procedure:
1. Wash your hands, wear gloves.
2. Seat or lay the patient, ask him tilt his head back slightly and look up
3. The spatula full to the brim with ointment put onto the sterile glass rod type
4. Pull down the lower eyelid down with your thumb.
5. Holding the spatula along eyelid, place the tip of the wand cream over inferior eyelid to bulb of eye, and the free surface to the eyelid.
Squeezing the ointment is possible directly from the tube.
6. Light stroking movements spread ointment on the private eye.
7. Remove the excess wax with a cotton ball.
8. Remove gloves and wash your hands.
Nose care
Patients who are able to serve themselves during morning toilet wash out their nasal passages.
On seriously ill and bedridden patients' nasal mucosa accumulate particles of dust, mud, slime, hampering breathing and the deteriorating condition of the patient, so the nasal cavity care implements is conducted by nurse.
Remove crusts from the nose (Pic. 76)
Equipment:
turunda, little Vaseline (or Glycerin).


Picture 76
Remove crusts from the nose
The procedure:
1. Pour a few Vaseline into graduated glass (or Glycerin).
2. Take turunda by tweezers, moisten in the oil, and squeeze it slightly.
3. Tilt the patient's head back so nasal passages are visible well.
4. Enter turunda in nasal passage by rotary movements for 1-3 minutes.
5. Remove turunda from nasal passage by rotary movements and remove the crust.
6. Repeat the procedure.
Installation of drops in nose
Previously buried nose drops (or emulsion) should be entered to the patient in a sitting position or lying on his back.
Instillation of nasal drops.
The equipment:
sterile pipette, liquid paraffin (or Glycerin).
The procedure:
1. Tilt his head to the opposite direction to the nose passage and lean it back slightly.
2. Lift the patient's nasal tip with your finger.
3. Avoid touching the nostril wings, drip drops in the nose passage.
4. Tilt the patient's head to the side, in which the drops were dropped.
5. After 1-2 minutes, drip drops in another nose passage.
6. Put the dropping pipette in the disinfectant solution.
Ear care
Caring for healthy ears means regular washing them with soap and warm water.
Not suitable for cleaning the ear canal with sharp objects (including a match), as this may damage the eardrum or ear canal wall.
The external auditory passages should be washing 2-3 times a week to prevent sulfur plugs.
Instillation of drops in the ear
The equipment:
dropper, bottle of ear drops, sterile cotton wool.
The procedure
1. Warm up drops to patient's body temperature.
2. Tilt the patient's head in the opposite direction to the ear in which you are going to drop it.
3. Pick the required amount of drops in the dropper.
4. Pull the auricle with your left hand back and up, and drip drops the with pipette into the auditory meatus with your the right hand to;
5. Offer to patient keep the position with tilted head for 15-20 min (to prevent bleeding the liquid)
6. Enter a cotton swab in the external nasal passage.
Removing earwax
Earwax is very important for the normal functioning of the organs of hearing, it protects against penetration inside the ear bacteria, viruses, fungi, outputs dead epithelium. Under normal circumstances, the excess earwax with accumulated dirt out by naturally way in chewing, swallowing movements. In accumulation of cerumen, produce an earwax.
Causes of condensation of sulfur can be:
• Excessive earwax output due to enhanced work glands
• Structure of the ear passage is narrower and sinuous.
• Damage the skin inside the ear canal with cotton buds, hearing aids, headphones.
• Past medical history-otitis, sinusitis.
• Permanently stays in the dusty room.
• Continuous "compaction" ear wax when you try to clean your ears.
If the earwax does not fully close the sulfuric passage, the man does not know about its existence for a long time. When the gap between the auditory duct and the eardrum is reduced more than 70%, you might see: the feeling of stuffiness in the ear, autophony (you can hear your own voice in your ear), hearing impairment. When pressure on the eardrum of sulfuric cork man hears a noise in the ears, he is reflexology cough, periodically appears dizziness, pain occurs in the ear.
Flushing ear canal
To remove earwax first soften it by dropping a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide in the ears. The procedure provides at night, for sleep time the earplug is soft and it will be easier to remove (Pic. 77).
The equipment: dropper, cotton swabs, hydrogen peroxide
 Picture 77
Picture 77

Remove the impacted cerumen (ear plug)
The procedure:
1. Tilt the patient's head to the opposite direction.
2. Gently pull the auricle back and up (straighten ear canal).
3. Drop a few drops of 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide into the external nasal passage and close acoustic meatus with cotton ball.
4. In the morning, provide irrigation after softening the wax with warm water, fill Zhane syringe (water enters into the ear under the pressure).
5. If the aural calculus is not completely removed, you can repeat it after a couple of days.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-29; просмотров: 171 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Signs of bedsores | | | Using bedpan and urine-collecting bags |