
Читайте также:
|
§ Profit ↑ as we move 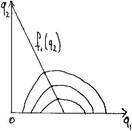 down.
down.
§ As we move down, the firm 2’s output = 0=> firm 1 – monopolist.
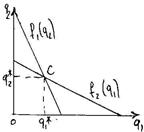
§ Cournot equilibrium.
§ Optimum q2 for F2 will be the function of beliefs concerning the output of F1.
§ C – point when the market is shared – cournot equilibrium.
§  - optimum choices.
- optimum choices.
Market equilibrium in different market structures.
§ 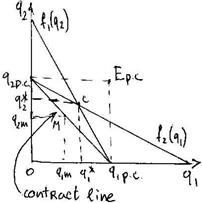 C – Cournot equilibrium.
C – Cournot equilibrium.
§ Contract line – firms collude and become a monopoly.
§ Output under monopoly<Output under duopoly<Output under perfect competition.
§ The final output of the industry and of two firms is now the lowest.
§ 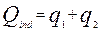
Algebraic explanation of the Cournot model.
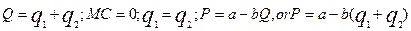
| 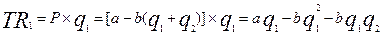
| 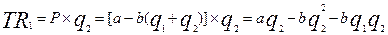
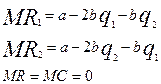 à
à 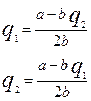 à
à 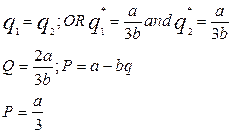
If the costs are intro into the analysis the equilibrium quantities and output will be:
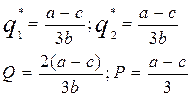
Stackelberg model (quantity leadership model).
2 firms are considered, but not identical. Firm1 is a leader, a dominant one, Firm2 – follower, who builds up the strategy according to the behavior of Firm1. Firm2 has a reaction function.
The leader doesn’t react to the steps of the Firm2. But he recognizes that it reacts to his behavior.
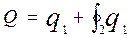 For the leader there won’t be a reaction function:
For the leader there won’t be a reaction function:
§ 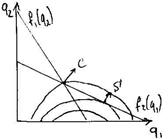 we shall combine reaction function of Firm2 with isoprofit of Firm1.
we shall combine reaction function of Firm2 with isoprofit of Firm1.
§ Firm1 dominates, Firm2 reacts, at point S both MAX their profits.
§ In Stackelberg model the market is not equally shared. Dominant produce more and have more power, the second produces less. Firm1 – leader in Q.
Contestable markets model.
If the costs of entry to an industry and exit from industry are very low, then there is always a high possibility of the numerous new firms appearance on the market. The market will lose its oligopolistic structure and will become competitive.
Oligopoly and public.
Minuses:
Pluses:
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 228 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Rules of thumb models. | | | Monopolistic competition. |