
Читайте также:
|
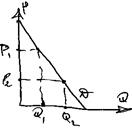 The dem for the prod. of the monopoly is the dem. of the whole market or industry è D-curve is downward sloping.
The dem for the prod. of the monopoly is the dem. of the whole market or industry è D-curve is downward sloping.Oligopoly.
Collusion models. It is very difficult to predict the outcome for a firm – lots of theories.
i. Explicit collusions:
Concentration ratio.
HHI – Herfindale – Hirschman Index. 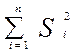 S –share of a firm in industrial output. n – number of firms.
S –share of a firm in industrial output. n – number of firms.
First cartels – end of 19 cent. In many countries they are forbidden – antitrust laws. OPEC – international cartel.
Requirements to be efficient:
1. Demand for product should be inelastic.
2. All the members should play to the rules. There is always an incentive to violate the rules.
ii. Implicit collusions. When there are few firms they know each other very well so it is not necessary to meet, so they work out a mutual behavior concerning price policy.
1. price leadership model. One firm is dominating, it sets a price and other firms follow suit (agree with the policy); if the firms are approximately equal they will become price leaders in turn.
2. barometric form price leadership. Price leader is not always the biggest firm – the most reliable with a good image. Price leader may want to get rid of the rivals à decreases price to the level which is not acceptable to the rivals and keeps at the low level until the weaker rivals go bankrupt and exit the market. Then the price is increased to high level according to the monopolistic position of the price leaderà predatory pricing policy.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 150 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Firms behavior under perfect competition. | | | Rules of thumb models. |