
|
Читайте также: |
i. Distr. by factor (functional distribution) – factors are: land(rent), labour(wages), entrepr. ability(profit), capital(interest).
!!! In Russia today – wages = 30-40% of GDP è labour isn’t a major source of income and people often try to find some illegal sources of income.
ii. By size of income (we can divide population into groups(10%(decile), 20%(quintile), 25%(quartile))
| Population | % of income | Sum of pop. | % sum |
| 20% | 6% | 20% | 6% |
| 20% | 10% | 40% | 16% |
 20% 20%
| 17% | 60% | 33% |
| 20% | 22% | 80% | 55% |
| 20% | 45% | 100% | 100% |
1. Lorenz curve(LC) – graphical income device, which shows the degree of inequality in income distribution by size.
2. 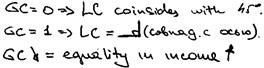 Gini coefficient (GC) – shows the degree of inequality in income distribution.
Gini coefficient (GC) – shows the degree of inequality in income distribution.
!!! Soc. countries GC = 0,2 – 0,25
iii.  By occupation (region, industry, etc)
By occupation (region, industry, etc)
!!! Income – flow concept(received regularly)
!!! Wealth – stock concept(estimated at a particular time moment)
b. Inequal. in wealth distrib > Ineq. in income distrib.
i. Factor of inheritance
ii. Differences in persomal propensities to save
iii. Inequality in income distribution
iv. Inequl. in individual productivity, talents, skill, etc…
 Pareto improvement – takes place, when changes in production and consumption can make at least one person better off, without making anyone worth off(X à Y)
Pareto improvement – takes place, when changes in production and consumption can make at least one person better off, without making anyone worth off(X à Y)
i. Pareto efficiency allocation:
1. takes place, when there is no way to make all the people better off.
2. all the gains from trade have been exhausted
3. there are no mutually advantageous trades to be made.
ii. Contract curve (CC) – each person is on his highest possible IC, given the IC of the other person.

 | |||
 | |||
i. Perfect competition.
ii. No externalities.
iii. Hicks – Coldu (?????) criteria of efficiency. It says that an economic project is efficient if all the possible gains can compensate all the possible losses. And still they remain net gain.
 Principle possibility of losses compensation.icks
Principle possibility of losses compensation.icks Social Influence Curve (SIC) slope = MSBx / MSBy
Production Possibility Curve (PPC) slope = MSCx / MSCy
i. External costs of production.
ii. External costs of consumption.
iii. External benefits of production.
iv. External benefits of consumption.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 126 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Monopolistic competition. | | | Namo Tassa Bhagavato Arahato Sammа Sambuddhassa |