
|
Читайте также: |
I. Translate the following words and word combinations into Ukrainian and use them in the sentences of your own:
a gene mutation, a permanent change, to range in size, to occur in two ways, hereditary mutations, germ cells, after fertilization, de novo mutations, an affected child, family history of the disorder, environmental factors, an early embryo, common genetic changes, normal differences between people, the risk of developing.
II. Find in the text English equivalents to the following Ukrainian expressions:
послідовність ДНК, великий сегмент хромосоми, можуть бути успадкованими, набуті мутації, присутні у яйцеклітині, протягом життя людини, фактично, можуть пояснити, генетичний розлад, окремі клітини, у певний час, ультрафіолетове випромінювання, ДНК копіює себе, клітинний поділ, наступне покоління, індивід, колір очей, група крові, незважаючи на те, що.
III. Choose the pairs of antonyms:
rare, permanent, development, next, present, inherited, negative, responsible, illness, common, previous, absent, degradation, positive, acquired, irresponsible, temporary, health.
IV. Make 10 questions of your own to the text including:
- special questions;
- general questions;
- alternative questions;
- question tags.
V. Guess the word by its definition:
Example: The person who gives the tissue or organ – the donor.
1. The human product of conception up to approximately the end of the second month of pregnancy.
2. Something relating to the soma.
3. The act or process of mutating; change; alteration.
4. The occurrence of more than one form of individual in a single species.
5. The state of being bodily and mentally energetic and free from disease.
6. A male reproductive cell; male gamete.
7. A simple structure, such as a fertilized egg, that is capable of developing into a complete organism.
8. The union of male and female gametes, during sexual reproduction, to form a zygote.
9. The individuals produced at each stage.
10. The star at the centre of our solar system.
VI. Look through the text and decide whether the following sentences are true or false:
1. Mutations do not occur in a large segment of a chromosome.
2. Acquired mutations occur in the DNA of individual cells at a certain time during a person’s life.
3. Ultraviolet radiation from the sun can cause a mutation.
4. Mutations that occur only in an egg or sperm cell are called new (de novo) mutations.
5. The egg and sperm cells are also called germ cells.
6. Eye color, hair color, and blood type can be different between people as a result of polymorphism.
7. Many polymorphisms have negative effects on a person’s health.
8. Genetic changes that occur in more than 10 percent of the population are called polymorphisms.
9. Mosaicism is a situation when only some cells of the individual have the genetic change.
10. Neutral mutations are mutations whose effects do not influence the fitness of an individual.
11. Conditional lethal mutations are changes in the sequence of genetic material, which kill the organism, but only when it faces certain environmental conditions.
VII. Translate the following text into English using the words from the text:
Мутації можуть виникати в будь-яких клітинах організму і спричиняти різноманітні зміни генетичного матеріалу. Мутації, які виникають у статевих клітинах, успадковуються при статевому розмноженні. Залежно від характеру впливу на життєдіяльність організмів, розрізняють летальні (lethal), сублетальні (sublethal) та нейтральні (neutral) мутації. Летальні мутації, проявляючись у фенотипі, спричиняють загибель організмів ще до моменту народження або до настання здатності до розмноження. Сублетальні мутації знижують життєздатність організму. Нейтральні мутації у звичних для організмів умовах існування не впливають на їхню життєздатність. Імовірність (probability) того, що мутація, яка щойно виникла, виявиться корисною, незначна. Але у деяких випадках, особливо за змін умов існування, нейтральні мутації можуть виявитися для організму корисними.
VIII. Read the text using a dictionary and speak on it:
Chromosomal Mutation
Chromosomes come in pairs with half of each inherited from each parent. Each cell of an organism have the same number of chromosomes except the gametes, which only have half as many chromosomes as the somatic (body) cells. However, size and number of chromosomes vary among species. Chromosome mutations are different from gene mutations in that a spontaneous modification results in more strong effects.
Chromosomal mutations take place when the number of chromosomes changes or when structural changes occur in the chromosomes. This process occurs generally during the formation of a zygote.
Structural changes in chromosomes may occur in several ways including inversion, in which a chromosomal segment rotates 180-degrees around the same point, duplication, in which the addition of a chromosomal segment occurs and deletion, in which the loss of a segment results. The shifting of chromosomal segments is known as translocation.
These processes do not change the amount of DNA in an organism and their importance to evolution is their contribution to variability via a change in the pattern of gene interaction.
A common example of chromosomal mutation in humans is the Down’s syndrome where a person has either one less or one more chromosome.
Notes to the texts:
to vary – змінюватися
spontaneous – спонтанний
to rotate – обертатися
addition – додавання, доповнення
loss – втрата
shifting – переміщення
IX. Put questions to the following statements:
1. Chromosomes come in pairs with half of each inherited from each parent. 2. The gametes only have half as many chromosomes as the somatic (body) cells. 3. Size and number of chromosomes vary among species. 4. Chromosome mutations are different from gene mutations. 5. Chromosomal mutations take place when the number of chromosomes changes or when structural changes occur in the chromosomes. 6. Structural changes in chromosomes may occur in several ways.
X. Look at paragraphs 1-2 and say which words are used to mean:
- corresponding parts that together comprise a whole;
- a haploid germ cell, such as a spermatozoon or ovum, that fuses with another germ cell during fertilization;
- relating to the soma;
- any of the taxonomic groups into which a genus is divided;
- to happen; take place;
- the cell resulting from the union of an ovum and a spermatozoon.
XI. Look at paragraphs 3-4. Can you explain the following words?
- inversion
- duplication
- deletion
- translocation
- evolution
- variability
XII. Insert the missing letters and translate the following words:
…ygo..e, s…mat…c, p…r…nt, spe…ies, e..f..ct, in…er…ion, ga..et…, str…ctur…l, o…cur, d…leti…n, pa…te…n, s…nd…om, co…m…n, im…o…tance.
XIII. Read the text “Chromosomal Mutations” again and retell it using phrases:
I know that…, as I remember…, if I am not mistaken…, if my memory serves me right….
GRAMMAR EXERCISES
I. Complete the sentences with the verbs in brackets:
1. I'll be ready as soon as you _____________________________(be) back.
2. We'll stay here till she__________________________________(return).
3. Please, call us when you _______________________________ (arrive).
4. I'm going to tell her before she ___________________________(leave).
5. I don't know when the party _______________________________start).
6. He'll drive you there whenever you ________________________(need).
7. The moment summer ________(be) here, the garden will be so beautiful!
8. I am going to take the exam after I ____________all these books. (study).
9. He will wait for you until you __________________________ (be) back.
10. Don't worry! I'll watch you while you ____________ in the lake (swim).
II. Join the sentences and use the words in brackets:
Example: We will buy it. We will have enough money. (as soon as)
We will buy it as soon as we have enough money.
1. We'll get there. We'll send a message. (soon after)
2. I would like to finish it. It will get dark. (before)
3. We are going to have a rest. We'll be on holiday. (while)
4. He will not regret it. She'll move away. (until)
5. Can you water the flowers? We'll leave the house. (when)?
6. Get in touch with him. I'm going to write to him. (as soon as)
7. Come to see me. You'll feel alone. (whenever)
8. I will find the opener. I will open the bottle. (the moment)
9. We will go to the shop. We will be walking the dog. (while)
10. I'll have finished my lesson by noon. I'll come round. (after)
III. Complete the sentences:
Example: He is going to leave. The room will be empty. – The moment he leaves, the room will be empty.
1. Jack is seeing the doctor tomorrow. He will be all right.
Soon after Jack …
2. We are going to get married. We will live in Bristol.
As soon as we …
3. You'll be hungry. You can take anything from the fridge.
Whenever you …
4. I'm going to change my job. I must tell my boss.
Before I …
5. They will be waiting for me. They will have enough time to prepare it.
While they …
6. Peggy is coming tonight. She will help you.
As soon as Peggy...
IV. Choose the correct ending:
1. I'll do it as soon as… a) I will finish my first project
b) I have finished my first project.
2. I have to tidy the room before … a) my mum appears.
b) my mum will appear.
3. He is going to stay in our flat while …a) we will be in Scotland.
b) we are in Scotland.
4. I'll ring you up after … a) they have repaired my telephone.
b) they repaired my telephone.
5. You'll find some job when … a) you are reading advertisements.
b) you read advertisements.
6. She won't sleep till … a) you read her a fairy-tale.
b) you will read her a fairy-tale.
7. I'll be with you while … a) you will be waiting for the train.
b) you are waiting for the train.
8. Eat your meal before … a) it gets cold.
b) it has got cold.
9. Are they going to visit Rome while… a) they are in Italy?
b) they will be in Italy?
10. Will you help me as soon as … a) you have finished your work?
b) you will have finished your work?
11. Will you recognize him the moment a) you see him?
b) you will see him?
12. Do you know when … a) the shop opens?
b) the shop has opened?
V. Rewrite the complete sentences with who, which or whose. Which of these words do we use for: people? things/animals? objects to show posession?|
Example: My boyfriend is 22 now comes from York. - My boyfriend, who is 22 now, comes from York.
1. Our house is pretty old has 3 bedrooms.
2. A waiter is someone works in a restaurant.
3. The girl you saw at the disco was Susan.
4. My wife was unemployed has a new job.
5. Jack is my neighbour lived in the USA.
6. Was the fax number you gave me correct??
7. Mr. Craig office is on the first floor can help you.
8. Your map was very helpful is on the table.
UNIT 7. MUTATIONS AND ENVIRONMENT
Wordbuilding: Word building components. Revision
Grammar: Sequence of tenses. Reported speech
Text A: Mutagens: How the Environment Affects Mutation Rates
Text B: Mutagenesis in Amphibian Populations
WORDBUILDING
I. Form new words with the help of the following suffixes and prefixes, translate into Ukrainian:
- ify: pure, clear, class, identity, acid, solid, simple.
- ize: character, neutral, sterile, summary, carbon, crystal.
- al: experiment, emotion, classic, globe, mechanic, origin, medicine.
- ic: acid, atom, alcohol, organ, period, cube.
- ical: technology, ecology, physics, biology, theory, botany.
- de: composition, hydrate, constructive, compression, classify.
II. Form new words with the help of word building components, translate into Ukrainian:
health, to prevent, to research, order, nitrogen, synthesis, organ, to digest, hard, fresh, pain, toxic, clear, crystal, solid, cell, cancer, to solve, therapy, character, to construct.
III. Choose the correct word for each blank:
1. comfort / comfortable / uncomfortable / comfortably / discomfort
a) A lot of small cars are not built for __________.
b) They were very __________ when they lived in a small apartment.
c) I love this hotel, it is very _________ to stay here.
d) You can sit very __________ in this car.
2. politics / political / politically / policy
a) I disagree with many of my father’s __________ ideas.
b) Alex is interested in __________.
c) __________, he tends to be rather conservative.
3. possibility / possible / impossible / possibly / impossibility
a) There’s no __________ for her to pass the final exam.
b) I’m really sorry, it is not __________ for me to help you now.
c) __________ my friends will come to visit me next Saturday.
d) My neighbours gave a part last night and it was __________for me to sleep because of the noise.
PRE-TEXT EXERCISES:
I. Read and memorize the following words and word combinations:
an impact вплив, дія
experience зазнавати
integrity цілісність
man made штучний
a chemical хімічна речовина
a fertilizer удобрювач; добриво
а preservative консервант
a drug ліки, медикамент
to ingest глитати, ковтати
X-ray рентгенівські
промені
to punch пробивати отвори
a hole діра, дірка; отвір
directly безпосередньо; прямо
cosmic ra космічні промені
to induce спричиняти
remain bound залишаються
зв’язаними
asbestos азбест
benzopyrene бензопірен
vinyl chloride вінілхлорид
mould цвіль, пліснява
hetrocyclic amines гетероциклічні
аміни
virus вірус
viral вірусний
cancer рак
cancerous раковий
cervical cancer цервікальний рак
liver cancer рак печінки
II. Read the following biological terms and international words. Translate them without a dictionary paying attention to the part of speech:
mutagen [  ] n, mutagenesis [
] n, mutagenesis [  ] n, mutant [
] n, mutant [  ] n, pesticide [
] n, pesticide [ 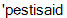 ] n, herbicide [
] n, herbicide [  ] n, radon [
] n, radon [  ] n, carcinogenic [
] n, carcinogenic [  ] adj, plastics [
] adj, plastics [ 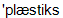 ] n, aflatoxin n.
] n, aflatoxin n.
III. Read the text below using a dictionary where necessary:
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 222 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? | | | Mutagens: How the Environment Affects Mutation Rates |