
|
Читайте также: |
A general characteristic of cells is their microscopic size. Because cells are so small, no one observed them until scientists invented microscopes in the mid-seventeenth century. Robert Hooke first described cells in 1665, when he used a microscope that he had built to examine a thin slice of cork, a non-living tissue found in the bark of certain trees. Hooke observed a honeycomb of tiny, empty (because the cells were dead) compartments. He called the compartments in the cork cellulae (Latin, “small rooms”), and the term has come down to us as cells. A few years later the Dutch naturalist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cells and called the tiny organisms that he observed “animalcules,” meaning little animals. For another century and a half, however, biologists failed to recognize the importance of cells. In 1838, botanist Matthias Schleiden made a careful study of plant tissues and developed the first statement of the cell theory. He stated that all plants “are aggregates of fully individualized, independent, separate beings, namely the cells themselves.” In 1839, Theodor Schwann reported that all animal tissues also consist of individual cells.
The cell theory, in its modern form, includes the following three principles:
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells.
2. Cells are the smallest living things, the basic units of organization of all organisms.
3. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing cell. Although life likely evolved spontaneously in the environment of the early earth, biologists concluded that no additional cells are originating spontaneously at present. Rather, life on earth represents a continuous line of descent from those early cells.
Notes to the texts:
cork – кора пробкового дерева
tissue  – тканина
– тканина
bark – кора
honeycomb 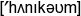 – медові стільники
– медові стільники
IX. Look through the text and decide whether the following sentences are true or false:
1. A tiny size is a basic feature of all cells.
2. Robert Hooke was the first who examined cells.
3. The first attempt to state the cell theory was in the 18th century.
4. According to the modern version of the cell theory cells exist not in all organisms.
5. Tissues are the place where metabolism and heredity take place.
6. Nowadays cells appear voluntarily.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 137 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| VOCABULARY EXERCISES | | | X. Put as many questions as possible to the text and be ready to answer them. |