
Читайте также:
|
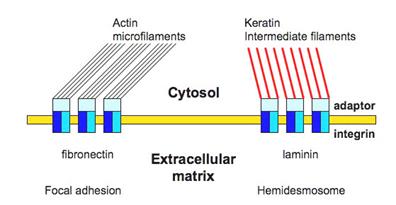
Structural glycoproteins are a group of molecules composed principally of protein chains bound to branched polysaccharides. The structural glycoproteins include two fibril-forming molecules, fibrillin and fibronectin, and a number of non-filamentous proteins including laminin which function as links between cells and extracellular matrix.
FIBERS
Connective tissue fibers are long, slender protein polymers that are present in variable proportions in the different types of connective tissue.
There are 3 main types of connective tissue fibers:
Collagen and reticular fibers are known to be formed by the protein collagen, and the elastic fibers are composed mainly of the protein elastin.
Collagen is the most abundant protein of the human body, representing 30% of its dry weight. The collagens of vertebrates are a family of proteins, produced by several cell types, that are distinguishable by their differing chemical compositions, morphologic characteristics, distribution, functions, and pathologies.
Although more than 19 types of collagen have been described, the most common, most important, and best-studied are types I, II, III, IY, and Y.
• Collagen type I is the most abundant and has a widespread distribution. It occurs in tissues as structures that are classically designated as collagen fibers and that form bones, dentin, tendons, organ capsules, dermis, etc.
• Collagen type II is present mainly in hyaline and elastic cartilage. Only very thin fibrils are formed.
• Collagen type III makes up the fibril type known as reticulin.
• Collagen type IY is present in the basal lamina. This type of collagen does not form fibrils or fibers but rather a mesh-like structure.
• Collagen type Y is present in fetal membranes, in blood vessels, and in small amounts in other tissues.
Collagen proteins are synthesized by a wide number of cell types, including fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, odontoblasts reticular cells and others. The principal amino acids that make up collagen are glycine (33.5%), proline, and hydroxyproline.
Collagen is secreted into the extracellular matrix in the form of tropocollagen. Tropocollagen consists of 3 subunit polypeptide chains intertwined in a triple helix. Tropocollagen molecules aggregate into microfibrillar subunits that are packed together to form fibrils.
Collagen fibrils are thin, elongated structures with a variable diameter. They have transverse striation with a characteristic periodicity of 64 nm, which is due to the stepwise overlapping arrangement of the rodlike tropocollagen subunits. Collagen fibers consist of closely packed thick fibrils. Collagen fibers are the most numerous fibers in connective tissue. They are inelastic and, have a tensile strength greater than steel. Consequently, collagen imparts a unique combination of flexibility and strength to the tissues in which it lies.

Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 172 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Ground substance | | | Fig.3. Formation of collagen fibers |