
Читайте также:
|
The following notations are used in this group of problems:
kps = the cost of preferred stock.
kcs = the cost of internally generated common funds
kncs = the cost of new common stock.
g = the growth rate.
kd = the before-tax cost of debt.
T = the marginal tax rate.
Dt = dollar dividend per share, where Do is the most recently paid dividend and D1is the forthcoming dividend.
P = the value (present value) of a security.
NP = the value of a security less any flotation costs incurred in issuing the security
12-1A.
a. Net price after flotation costs = $1,125 (1 -.05)
= $1068.75
$1068.75 =  +
+ 
kd = 9.89%
= kd(1-T)
= 6.53%
b. kncs =  + g
+ g
=  +.07
+.07
=.1437 = 14.37%
c. kcs =  + g
+ g
=  +.07
+.07
=.1514 = 15.14%
d. kps = 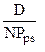 =
= 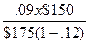
= 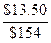
=.0877 = 8.77%
e.  = kd(1 - T)
= kd(1 - T)
= 12% (1 -.34)
= 7.92%
12-2A.
a.  = kd(1 - T)
= kd(1 - T)
= 8%(1 - 0.34)
= 5.28%
b. kncs = 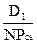 + g
+ g
kncs =  + 0.05 = 9.85%
+ 0.05 = 9.85%
c. $1,150(.90) = $1,035 = net price after flotation costs
$1,035 =  +
+ 
RateValueValue
For: 11% $1,079.56 $1,079.56
kd% 1,035.00
12% 1,000.00
$ 44.56$ 79.56
kd = 0.11 + 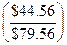 ´ 0.01 =.1156 = 11.56%
´ 0.01 =.1156 = 11.56%
 = kd(1 - T)
= kd(1 - T)
 = 11.56% (1 - 0.34) = 7.63%
= 11.56% (1 - 0.34) = 7.63%
d. kps = 
kps = 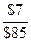 = 8.24%
= 8.24%
e. kcs =  + g
+ g
kcs = 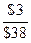 + 0.04 = 11.90%
+ 0.04 = 11.90%
12-3A. kncs =  + g
+ g
kncs = 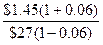 + 0.06 =.1206 = 12.06%
+ 0.06 =.1206 = 12.06%
12-4A. $958 (1 - 0.11) = $852.62 = the net price (value less flotation costs).
$852.62 =  +
+ 
RateValueValue
For: 8% $914.20 $914.13
kd% 852.62
9% ______ 839.27
$61.58 $74.86
kd = 0.08 + 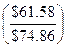 ´ 0.01 =.0882 = 8.82%
´ 0.01 =.0882 = 8.82%
= 8.82% (1 - 0.18) = 7.23%
12-5A. kps =  =
= 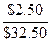 = 7.69%
= 7.69%
12-6A. NPd =  +
+ 
$945 = 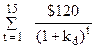 +
+ 
Since the net price on the bonds, $945, is less than the $1,000 par value, the before-tax cost of the debt must be greater than the 12 percent coupon interest rate ($120 ÷ $1,000).
RateValueValue
12% $1,000.00 $1,000.00
kd% 945.00
13% _______ 935.44
$ 55.00$ 64.56
kd =.12 +  ´.01 =.1285 = 12.85%
´.01 =.1285 = 12.85%
 = kd(1 - T) = 12.85%(1 -.34) = 8.48%
= kd(1 - T) = 12.85%(1 -.34) = 8.48%
12-7A. Cost of preferred stock (kps)
kps =  =
= 
=  =
= 
= 14.29%
12-8A. kcs =  + g
+ g
=  + 0.15
+ 0.15
=.1874 = 18.74%
12-9A.If the firm pays out 50 percent of its earnings in dividends, its recent earnings must have been $8 ($4 dividend divided by.5).
Thus, earnings increased from $5 to $8 in five years. Using Appendix C and looking for a table value of.625 ($5/$8), the annual growth rate is approximately ten percent.
a. Cost of internal common stock (kcs):
kcs =  + g
+ g
=  +.10 =
+.10 =  +.10
+.10
=.1759 = 17.59%
b. Cost of external common (new common) stock, kncs
kncs =  + g
+ g
=  +.10
+.10
=  +.10
+.10
=.1825 = 18.25%
12-10A.
a. Price (Pd) =  +
+ 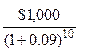
= $140(6.418) + $1000(.422)
= $1,320.52
b. NPd = $1,320.52(1 - 0.105)
= $1,181.87
c. Number of Bonds = 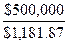 = 423.06 ≈ 424 Bonds
= 423.06 ≈ 424 Bonds
d. Cost of debt:
$1,181.87 =  +
+ 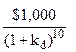
RateValueValue
For 10% $1,246.30 $1,246.30
kd% 1,181.87
11% ________ 1,176.46
$ 64.43$ 69.84
kd = 0.10 +  =.1092 = 10.92%
=.1092 = 10.92%
 = 10.92%(1 - 0.34) = 7.21%
= 10.92%(1 - 0.34) = 7.21%
12-11A.
a. 1. Price (Pd) =  +
+ 
= $100 (6.418) + $1,000 (.422)
= $1,063.80
2. NPd = $1,063.80 (1 - 0.105)
= $952.10
3. Number of Bonds = 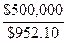
= 525.15 ≈ 526 Bonds
4. Cost of debt:
$952.10 =  +
+ 
RateValueValue
For: 10% $1,000.00 $1,000.00
kd% 952.10
11% ________ 940.90
$ 47.90$ 59.10
kd = 0.10 +  =.1081 = 10.81%
=.1081 = 10.81%
 = 10.81%(1 - 0.34) = 7.13%
= 10.81%(1 - 0.34) = 7.13%
b. There is a very slight decrease in the cost of debt because the flotation costs associated with the higher coupon bond are higher ($138.65 in flotation costs for the 14 percent coupon bond versus $111.70 for the 10 percent coupon bond).
12-12A.
| Source | Capital Structure | After-tax cost of capital | Weighted cost |
| Common Stock | 40% | 18% | 7.2% |
| Preferred Stock | 10% | 10% | 1.0% |
| Debt | 50% | 8% x (1-.35) | 2.6% |
| kwacc = | 10.8% |
12-13A.
Net price after flotation costs = $975 - $15
= $960.00
Cost of debt:
$960.00 =  +
+ 
RateValueValue
For: 6% $1,000.00 $1,000.00
kd% 960.00
7% ________ 908.48
$ 40.00$ 91.52
kd = 0.06 +  =.064 = 6.4%
=.064 = 6.4%
 = 6.4%(1 - 0.30) = 4.48%
= 6.4%(1 - 0.30) = 4.48%
Cost of common stock, kncs
kncs =  + g
+ g
=  +.05
+.05
=.129 = 12.9%
| Source | Capital Structure | After-tax cost of capital | Weighted cost |
| Debt | 60% | 4.48% | 2.69% |
| Common Stock | 40% | 12.9% | 5.16% |
| kwacc = | 7.85% |
12-14A.
Net price after flotation costs = $1,050 (1-.04)
= $1,008.00
Cost of debt:
$1,008.00 =  +
+ 
RateValueValue
For: 6% $1,096.84 $1,096.84
kd% 1,008.00
7% ________ 1,000.00
$ 88.84$ 96.84
kd = 0.06 +  =.069 = 6.9%
=.069 = 6.9%
 = 6.9 %(1 - 0.30) = 4.8%
= 6.9 %(1 - 0.30) = 4.8%
Cost of preferred stock (kps)
kps =  =
= 
=  =
= 
=.091 = 9.1%
Cost of common stock, kncs
kncs =  + g
+ g
=  +.10
+.10
=.166 = 16.6%
| Source | Market Value | Weight | After-tax cost of capital | Weighted Cost |
| Bonds | $4,000,000 | .33 | 4.8% | 1.6% |
| Preferred Stock | 2,000,000 | .17 | 9.1% | 1.5% |
| Common Stock | 6,000,000 | .50 | 16.6% | 8.3% |
| 12,000,000 | 1.00 | kwacc = | 11.4% |
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 100 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS | | | SOLUTION TO INTEGRATIVE PROBLEM |