
|
Читайте также: |
External force feed. A shaft under the seed hopper carries a number of revolving fluted rollers, one for each coulter. The flutes carry grain from the hopper to the flexible plastic seed tubes at the required rate. Many external force feed drills are only suitable for cereal crops but some models have an adjustable shutter close to the fluted rollers. The clearance between shutters and feed rollers can be varied to suit different sizes of seed.
Seed rate is altered by:
1. Changing the length of fluted roller in contact with the seed. A lever is used to adjust the amount of fluting carrying seed from the hopper. A graduated scale provides a guide for setting the seed rate.
2. The speed of the fluted rollers is changed with a gearbox. Maximum seed rate is achieved with the highest roller speed and the full length of the fluted rollers in contact with the grain.

Figure 16. The grain metering unit on this drill is driven by the land wheel and the seed tubes deliver grain to three staggered rows of coulters. Compression springs on the coulter arms maintain the required sowing depth.
Studded roller feed. This is another form of external force feed. The fluted rollers are replaced with studded or pegged rolls. Seed is carried from the hopper to the seed tubes by the studs as the mechanism turns on its shaft. Seed rate is controlled by:
1. The speed of the studded rolls.
2. The position of an adjustable flap which controls seed flow from the hopper to the feed mechanism.
3. The type of studded roll. With some drills, rolls with different sizes and numbers of studs can be used.
The studded roller feed is suitable for drilling most types of seed.
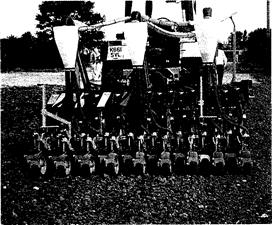
Figure 17. This modular precision grain drill is made in working widths of 2.5 to 8 m
and has a 166 mm (6.6 in) row spacing.

Figure 18. Studded roller force-feed mechanism

Figure 19. Fluted roller force-feed mechanism.
Coulters
Suffolk (Fig.20).This has a cast iron shoe which cuts a narrow furrow for the seed. Its shape helps to keep a straight and even depth furrow. Suffolk coulters do not block easily and are not affected by stony land. There are no moving parts to lubricate but soil contact wears the bottom of the coulters rather quickly. Penetration can be difficult in hard ground. Suffolk coulters are suitable for sowing both root and cereal crops.
Ceramic tipped coulters with a life up to five times longer than steel are used on some Suffolk-type coulters.
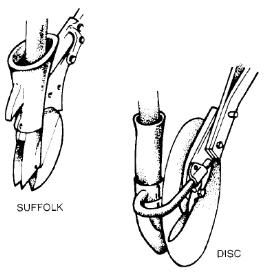
Figure 20. Two types of drill coulter.
Disc coulters (Fig.20).are saucer shaped and cut a rather irregular depth furrow. Their cutting action helps with penetration and they work well in most soils. Stones can stick between the disc and its support and cause uneven wear. Different manufacturers use various types of disc. Some use double discs usually staggered in two or three rows across the drill. Others use a single serrated edge disc for added grip. Disc coulters are not suitable for drilling root crops.
Hoe coulters. (Fig.21)Their main use is for minimal seedbed techniques with a cultivator/drill combination. Hoe coulters can have various width shares usually with replaceable points, which are bolted to spring tine shanks and mounted in staggered rows across the full width of the drill. The coulters stir the soil and make a shallow furrow for the seed. The seed tubes from the feed mechanisms are attached to the back of the coulter tines.
Some drills have hinged flaps (see Figure 22) on the coulters to prevent soil blocking the seed outlet if the coulters are lowered when the drill is stationary or it is accidentally reversed while they are in the ground.

Figure 21. The tension spring on this Suffolk-type coulter maintains the correct sowing depth.
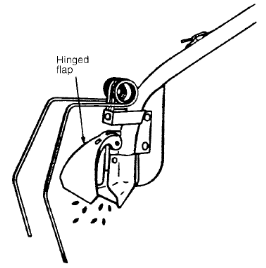
Figure 22. A Suffolk coulter with covering tines and a hinged flap which prevents soil blocking the coulters if the drill is reversed when they are in the ground.
Sowing depth. A regular sowing depth is important for even emergence of the seedlings. The coulters are carried on arms which pivot individually at the front of the drill. Sowing depth is altered by adjusting a depth limiting stop on the hydraulic ram used to raise and lower the coulters. A hand lever or screw adjuster is used to set coulter depth on some mechanical lift drills.
Compression springs above or tension springs below the coulter arms are used to set the coulters at the correct depth in the soil. The spring pressure is adjusted to suit soil conditions with the most pressure required on compacted ground. Some minimal tillage and plain grain drills have hydraulic rams to increase or decrease the working depth of the coulters.
Row width. Row widths of 180 mm (7 in) are traditional for cereal crops but drills with coulter spacings from 90 to 150 mm (ЗУ2-6 in), depending the preference of the farmer, are in current use. Some single-pass cultivator drills with pneumatic seeding have wider row widths. One model has double disc coulters 240 mm (9Vi in) apart; another, with special coulters spaced at 500 mm, drills seed in wide bands giving the plants more room to grow.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 720 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Precision Drilling | | | Pneumatic Grain Drills. |