
Читайте также:
|
Модуль 2. Текст «Великобритания»
1. Прочитайте текст, подготовьтесь к ответам на вопросы по географическому положению Великобритании и ее истории:
The United Kingdom. The United Kingdom is made up of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. It has a long history as a major player in international affairs and fulfils an important role in the EU, UN and NATO. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom, the UK or Britain, is a sovereign state located off the northwestern coast of continental Europe.
The United Kingdom is a unitary state consisting of four countries: England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. It is governed by a parliamentary system with its seat of government in London, the capital, but with three devolved national administrations in Belfast, Cardiff and Edinburgh, the capitals of Northern Ireland, Wales and Scotland respectively.
Education is mandatory from ages five to sixteen (15 if born in late July or August). The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, only a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Despite a fall in actual numbers, the proportion of children in England attending private schools has risen to over 7%. Just over half of students at the leading universities of Cambridge and Oxford had attended state schools. State schools which are allowed to select pupils according to intelligence and academic ability can achieve comparable results to the most selective private schools.
England has some of the top universities in the world; University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, and University of London are ranked among the top 20 in the 2007 THES – QS World University Rankings. There are fears, however, that a decline in the number of English students studying a foreign language will have a negative effect on business, which has led to calls for languages to be given greater priority.
Two non-departmental public bodies have key roles in Scottish education: the Scottish Qualifications Authority is responsible for the development, accreditation, assessment and certification of qualifications other than degrees which are delivered at secondary schools, post-secondary colleges of further education and other centers; and Learning and Teaching Scotland provides advice, resources and staff development to the education community to promote curriculum development and create a culture of innovation, ambition and excellence. The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4%, although it has been rising slowly in recent years.
Education in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Minister for Education, currently Caitríona Ruane (Sinn Féin), although responsibility at a local level is administered by five Education and Library Boards, covering different geographical areas.
The National Assembly for Wales has responsibility for education in Wales. A significant number of Welsh students are taught either wholly or largely in the Welsh language; lessons in Welsh are compulsory for all until the age of 16. There are plans to increase the provision of Welsh Medium schools as part of the policy of having a fully bi-lingual Wales. The Program for International Student Assessment ranked the UK 14th in science, which was higher than the OECD average.
Notable civil engineering projects, whose pioneers included Isambard Kingdom Brunel, contributed to the world's first national railway transport system. Other advances pioneered in the UK include the marine chronometer, the jet engine, the modern bicycle, electric lighting, the electric motor, the screw propeller, the internal combustion engine, military radar, the electronic computer, vaccination and antibiotics. Scientific journals produced in the UK include Nature, the British Medical Journal and The Lancet. In 2006, it was reported that the UK provided 9% of the world's scientific research papers and a 12% share of citations, the second highest in the world after the US.
2. Заполните недостающие факты про Великобританию в поля приведенные ниже.
· Full name: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland;
· Geography: …;
· Population: 60.7 million (UN, 2007);
· Capital: …;
· Major language: …;
· Area: 242,514 sq km (93,638 sq miles);
· Head of state:…;
· Major religion: Christianity;
· Famous writers: …;
· Life expectancy: 77 years (men), 82 years (women);
· Monetary unit: 1 pound sterling = 100 pence;
· Internet domain: …;
· International dialing code: +44.
3. Ответьте на вопросы:
· Can you name any members of the British royal family?
· Can you name any of Queen Elizabeth’s children or grandchildren?
· What does the term «constitutional monarchy» mean?
· Which other countries still have a monarchy?
· Do you think there is any place for kings and queens in the 21st century?
4. Сделайте презентацию о своей стране.
5. Напишите сочинение около 350 слов о своей стране по схеме изложения, приведенного выше, текста.
Модуль 3. Страноведческий обзор темы «Англоязычные страны»
1. Ознакомьтесь со схемой изложения темы в таблице 1, приведенной ниже. Используйте для подстановки факты из таблицы 2, 3.
2. Составьте 20 утвердительных, вопросительных и отрицательных предложений с новой лексикой. Будьте готовы их перевести.
3. Напишите сочинение на тему «Место моего будущего путешествия».
4. Подготовьте реферат на тему: «Один из аспектов англоязычной страны: политическая система Новой Зеландии / экономическая система Австралии / достопримечательности Канады», «Высшее образование в англо-говорящих странах».
Таблица 1
Упрощенная схема изложения темы «English Speaking Countries»
| The … of | the USA | Is | stars | in comparison with … |
| flag | the UK | is in | stripes | compared with … |
| motto | the Great Britain | is characterized by | crosses | opposite to … |
| political system | England | consists of | land | in contrast with … |
| climate | America | is formed by | water | on the background of … |
| mountains | the United States of America | includes | «In god we trust» | as well as … |
| rivers | the United Kingdom | is famous for | Democracy | while … |
| lakes | Canada | is well-known for | Republic | for … |
| seas | Australia | belongs to | Constitutional Monarchy | |
| lakes | New Zealand | Has | English | |
| music | India | possesses | French | |
| literature | South Africa | owns | Rock | |
| religion | Russia | borders with | Jazz | |
| national language | the Russian Federation | is washed by | Blues | |
| is called | ||||
| is named | ||||
| is determined as |
Таблица 2
Информация по англоязычным странам
| GENERAL INFORMATION | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Language | The official languages: English The United Kingdom, consisting of Great Britain (England, Wales, and Scotland) and Northern Ireland English. Capital: London. The largest City: London. | The official languages only de facto: English. Capital: Washington. The largest city: New York. | The official languages: English and French. Capital: Ottawa. The largest city: Toronto. | English (not de jure, but de facto) the official language and the national language. Capital: Canberra. The largest city: Sydney. | The official languages: The official languages: English and Maori. Capital: Wellington. The largest city: Auckland. | The official languages: Hindi, English. Capital: New Delhi. The largest city: Mumbai. |
| Flag, year of its official status |  Union Jack
(The Cross of Saint Andrew counterchanged with the Cross of Saint Patrick, over all the Cross of Saint George).
Union Jack
(The Cross of Saint Andrew counterchanged with the Cross of Saint Patrick, over all the Cross of Saint George).
|  The Stars and Stripes
(Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 50 white stars on a blue field).
The Stars and Stripes
(Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 50 white stars on a blue field).
|  The Maple Leaf
(A vertical bicolour triband of red, white, and red, with a red maple leaf charged in the centre).
The Maple Leaf
(A vertical bicolour triband of red, white, and red, with a red maple leaf charged in the centre).
|  (British Union Jack on the left corner and six white stars on blue field).
(British Union Jack on the left corner and six white stars on blue field).
|  (A field of air force blue with the Union Jack in the corner).
(A field of air force blue with the Union Jack in the corner).
|  (Horizontal tricolour flag (deep saffron, white, and green). In the center of the white is a navy blue wheel with 24 spokes).
(Horizontal tricolour flag (deep saffron, white, and green). In the center of the white is a navy blue wheel with 24 spokes).
|
| National colors | Red, white and blue. | Red, white and blue. | Red and white. | Green and gold. | Black. | Saffron, white and green. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| GENERAL INFORMATION | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Coat of arms | 
| 
| 
| 
|  1911 (1956)
1911 (1956)
| 
|
| Motto | - | In God We Trust (official) E Pluribus Unum (traditional) (Latin: Out of Many, One). | «A Mari Usque Ad Mare» (Latin) «From Sea to Sea». | - | - | «Satyameva Jayate» (Sanskrit) «Truth Alone Triumphs». |
| Anthem | God Save the Queen. | The Star-Spangled Banner. | O Canada. | Advance Australia Fair. | God Defend New Zealand (God Save the Queen). | - |
| National animal | Lion (England), Unicorn (Scotland), European Dragon (Wales). | Bald Eagle. | Beaver. | Kangaroo. | Kiwi, sheep. | Bengal Tiger. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| GEOGRAPHIC POSITION | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Continent; Part of the continent | The total area is approximately 245,000 square kilometers. It comprises the island of Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales) and the northeastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland (Northern Ireland), together with many smaller islands. | USA comprises fifty states and a federal district The country is situated mostly in central North America, where its forty-eight contiguous states and Washington, D.C., the capital district, lie between the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, bordered with Canada in the north and Mexico in the south. | Canada is located in the northern-most region of North America. | Australia is a country, an island, and a continent. It is located at 27°S 144°E. It is the sixth largest country in the world with a total area of 7,686,850 square kilometers, making it slightly smaller than the states of the United States and 31.5 times larger than the United Kingdom. | New Zealand comprises two main islands, the North and South Islands, Te Ika a Maui and Te Wai Pounamu respectively in Māori. The total land area, 268,680 square kilometers (103,738 sq mi). | Bounded by the Indian Ocean in the South, the Arabian Sea in the West, and the Bay of Bengal on the east, India has a coastline of 7,517 kilometers. It is situated in the south of Asia. |
| Ocean, sea | It lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea. | Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. | Stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; the Arctic Ocean lies in the north. | In the west there is the Indian Ocean and in the east there is the Pacific Ocean. South of Tasmania is in the Southern Ocean. In North of Australia there are the Timor and Arafura seas, in the southeast there is the Tasman Sea, and in the northeast there is the Coral Sea. | South-western Pacific Ocean. | Indian Ocean Arabian Sea. |
| Mountain | The ten tallest mountains in the UK are all found in Scotland. The highest peaks in each part of the UK are: Scotland: Ben Nevis (Aonach Mòr, 1,344 meters). Wales: Snowdon (Snowdonia, 1,085 meters). England: Scafell Pike (Cumbrian Mountains, 977 meters). Northern Ireland: Slieve Donard (Mourne Mountains, 852 meters). | The Rocky Mountains, at the western edge of the Great Plains, extend from north to south across the country, reaching altitudes higher than 14,000 feet (4,300 m) in Colorado. | Mount Logan in Yukon is the highest peak of Canada. | The tallest mountain in Australia is Mt Kosciuszko, at 2228m. | Aoraki / Mount Cook is the highest mountain in New Zealand. | The Himalayas form the mountainous landscape of Northern India. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| GEOGRAPHIC POSITION | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Rivers | The longest rivers in the UK are: England: River Thames (215 mi, 346 km) Scotland: River Tay (117 mi, 188 km). | The Mississippi–Missouri River, the world's fourth longest river system, runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. | The Mackenzie River is the longest river in Canada. | Longest rivers: Murray River 2,375 kilometers Murrumbidgee River - 1,485 kilometers. | The longest river in New Zealand is the Waikato River with a length of 425 kilometers. | Ganga Brahmaputra. |
| 3. Climate | The United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round. Classified as a mid-latitude oceanic climate and in the Scottish Highlands with warm summers, cool winters and plentiful precipitation throughout the year. | The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. In the east of the 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south. The southern part of Florida is tropical, as is Hawaii. The Great Plains in west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. | Canada's climate is not as cold all year around as some people believe. In winter, temperatures fall below freezing point throughout most of Canada. But the south-western coast has a relatively mild climate. Along the Arctic Circle, mean temperatures are below freezing for seven months a year. | The climate of Australia varies widely, but by far the largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid – 40% of the landmass is covered by sand dunes. Only the south-east and south-west areas have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate: there is tropical rainforests, grasslands, and deserts. | The climate throughout the country is mild and the temperate falls below 0 °C (32 °F) or rises above 30 °C (86 °F) in populated areas. | Four major climatic groupings predominate in India: tropical wet, tropical dry, subtropical humid, and mountain. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| SOCIAL SYSTEM / POLYTICS | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Political system | Parliamentary Democracy and Constitutional Monarchy. | Federal constitutional republic. | Constitutional monarchy. | Federal constitutional monarchy under a parliamentary democracy. | Parliamentary democracy and Constitutional monarchy. | Federal republic, parliamentary democracy. |
| Head of the country | Queen Elizabeth II. | The president. | Elizabeth II, Queen of GB and Canada. | English Monarch - Queen Elizabeth II. | English Monarch - Queen Elizabeth II. | President. |
| Government Exertive Power | Prime Minister of the United Kingdom is the head of the government. Executive power is exercised by the UK government. | Prime Minister is the head of government. | Westminster style federal parliamentary democracy within a constitutional monarchy. | The Federal Executive Council (the Governor-General as advised by the Executive Council). | Prime Minister is the head of government. The Governor General chairs the Executive Council, which is a formal committee consisting of all ministers of the Crown. | Prime Minister. |
| Legislature | Legislative power is presented by both the government and the two chambers of Parliament, the House of Commons and the House of Lords. | The bicameral Congress, made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The executive power: The president is the commander-in-chief of the military forces. | The bicameral Parliament of Canada consists of three parts: the monarch, the Senate, and the House of Commons. | Legislative power rests with the Parliament of Australia, which consists of an upper house, the Senate, and the House of Representatives. | New Zealand's main legislative body is a unicameral Parliament known as the House of Representatives. | The parliament consists of the President and the two Houses. |
| Judicial | The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature, though several senior judges are still members of the House of Lords. | The Supreme Court and lower federal courts. | Independent of executive. | The High Court of Australia and other federal courts. | The highest court in New Zealand is the Supreme Court of New Zealand. | Independent of the executive power. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| SOCIAL SYSTEM / ECONOMY | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Industry; Agriculture; Natural resources; Transport; Communication; Networks | The United Kingdom is a major developed capitalist highly mechanized economy. Agriculture is intensive. The UK retains a significant, although vastly reduced, fishing industry. Transport in the United Kingdom is facilitated with well-developed road, air, rail, and water networks. | The economy of the United States is the largest national economy in the world in both nominal value and by purchasing power parity. The United States is the largest importer of goods and third largest exporter, though exports per capita are relatively low. | Major industries: automobile manufacturing, pulp and paper, iron and steel work, machinery and equipment manufacturing, mining, extraction of fossil fuels, forestry and agriculture. The main highway system (completed in 1962) is called the Trans-Canada Highway. The highway is 7 604 km long. | The economy of Australia is a prosperous, free market economy dominated by its services sector, representing 68% of Australian GDP. The agricultural and mining sectors (10% of GDP combined) is 57% of the nation's exports. Transportation in Australia is a highly significant part of the infrastructure of the Australian economy, since the distances are large and the country has a low population density. | The Economy of New Zealand is a market economy highly mechanized. Agriculture is intensive. 80% of the land was forested Transport is facilitated with well-developed road, air, rail, and water networks. | Major industries include textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transport equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, software. Transport in the Republic of India is an important part of the nation's economy. |
| Literature | Playwright and poet William Shakespeare. English writers are Geoffrey Chaucer (14th century), Thomas Malory (15th century), Sir Thomas More (16th century), and John Milton (17th century). | Modern Voices in Prose and Poetry: Ernest Hemingway, William Faulkner, Robert Lowell. | Canada’s literature, whether written in English or French, often reflects the Canadian perspective on nature, frontier life. | Literature, philosophy, music | Much of contemporary New Zealand culture is derived from British roots. It also includes significant influences from American, Australian and Māori cultures, along with those of other European cultures and – more recently – non-Māori Polynesian and Asian cultures. | Religious and philosophical literature since ancient times. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| SOCIAL SYSTEM / CULTURE | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| Music | Hop, jazz, pop, popular, rock, soul. Classical music, Early music, Folk, Hip. | Rock and roll, blues, country, rhythm and blues, jazz, pop, techno, and hip hop. | From the17th century onward Canada has developed a music infrastructure that includes church halls, chamber halls, conservatories, academies, performing arts centers, record companies, radio stations. | Some modern trends in Australian music is based on, or concurrent with, similar trends from the United States or United Kingdom and elsewhere. | The most popular styles were rock and hip hop. | The music of India includes multiple varieties of folk, popular, pop, classical music and R - B. Religious, Hinduism music is very popular. |
| Religion | Protestant, Catholic and Orthodox Christians, Muslims, Sikh, Hindu. | Protestant 52%, Roman Catholic 24%, Mormon 2%, Jewish 1%, Muslim 1%, other religion 10%, no religion 10% (2002 est.) | Religion in Canada encompasses a wide range of groups, and Canada has no official religion. Protestants, Catholics and other. | Religion in Australia remains dominated demographically by Christianity. | Christianity is the predominant religion in New Zealand. | The two main religions are Hinduism (80%) and the Muslim religion (10%) but there are also small numbers of Buddhists, Christians, Sikhs, Parsees and others. |
Продолжение таблицы.
| SIGHTS | United Kingdom | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| In the capital; Central buildings; Museums; In the country; Cities; Waterfalls | The National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery, Tate Modern; Westminster Abbey, Westminster Cathedral, Houses of Parliament, Buckingham Palace; Imperial War Museum, British Museum; London, Birmingham, Leeds, Glasgow, Liverpool, Cardiff, Belfast; Eas a’ Chual Aluinn is located near Glen Coul, Sutherland in the Scottish Highlands. | United States Capitol; Bridge Museum, Museum Interior; New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, Philadelphia, San Diego; Ahern Glacier Falls, Aimoo Falls, Angel Falls. | First Canadian Place, Scotia Plaza; Nova Scotia Museum of Natural History, School Days Museum, Acadian House Museum; Airdrie, Abbotsford, Brandon Athabasca Falls, Panther Falls. | Provisional Parliament House building, Parliament House, Canberra; Museums Australia National Conference, Museums Australia Magazine Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane; Apsley Falls, Bangalore Falls, Beauchamp Falls. | Government House, the official residence of the Governor-General; City Gallery, the oldest building in Wellington is the late Georgian Colonial Cottage, St. James Theatre; The Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa; Auckland, Christchurch, Hamilton; Kitekite Falls, Karekare Falls, Piroa Falls and Whangarei Falls. | Parliament of India building in New Delhi; National Museum, the National Museum Institute of History of Art, Conservation and Museology; Mumbai, Bangalore, Kolkata Kailasakona Falls, Kuntala Falls, Pochera Falls. |
Таблица 3
История англоязычных стран
| United Kingdom | The USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | |
| History of countries | Iberian tribes, about 3000 BC
 Stonehenge, thought to have been erected in.2500-2000BC
Celtic tribes (Britons)
Invade by the Romans in 55-54 BC
Second Invade in 43 AC
Stonehenge, thought to have been erected in.2500-2000BC
Celtic tribes (Britons)
Invade by the Romans in 55-54 BC
Second Invade in 43 AC
 Vikings attack till 793
Scandinavian attacks
Normans conquest in 10th c.
Vikings attack till 793
Scandinavian attacks
Normans conquest in 10th c.
| First inhabitants
15-50000 years ago
 A traditional Iroquois longhouse.
Native Americans (Indians)
14000 years ago
Well known groups:
Apache, Tribe, Cherokee, Sioux, Delaware,
Algonquin, Choctaw, Mohegan, Iroquois
A traditional Iroquois longhouse.
Native Americans (Indians)
14000 years ago
Well known groups:
Apache, Tribe, Cherokee, Sioux, Delaware,
Algonquin, Choctaw, Mohegan, Iroquois
 The Mayflower, which transported Pilgrims to the New World
The Mayflower, which transported Pilgrims to the New World
| From Asia across the Bering Strait
25000 years ago
The Eskimos
6000 years ago
The Vikings from Iceland - Greenland
English seaman John Cabot reach the Newfoundland
 French explorer company
1608-1642
British Trade Company
French-Indian War
French explorer company
1608-1642
British Trade Company
French-Indian War
| Indigenous Australia
 A pioneer settler family
British Settlement and Colonization
26 January 1788
The Discovery of Gold
Colonial self-government
A pioneer settler family
British Settlement and Colonization
26 January 1788
The Discovery of Gold
Colonial self-government
 Australian soldiers in Egypt
Australian soldiers in Egypt
| Settled by Polynesians
700 years ago
First European explorer
European settlements
British sovereignty
Treaty of Waitangi,
European colonies in island
Colonial period
Since 1840
 Establishing first Liberal Government
Establishing first Liberal Government
|
Продолжение таблицы.
| United Kingdom | The USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | |
Norman English
Free from French
Grammar unification
Capitalism in England.
 Painting of England Port
Criticism – Mercantilism
XVI-XVIII
Fight with the Spanish Armada
Beginning of English colonization
English Civil War
Independence of Colonies
1760s
Industrial Revolution
XVIII-XIX
Painting of England Port
Criticism – Mercantilism
XVI-XVIII
Fight with the Spanish Armada
Beginning of English colonization
English Civil War
Independence of Colonies
1760s
Industrial Revolution
XVIII-XIX
| Colonial Period
Since XV
- Spanish
- Dutch
- French
- British
 Cartoon by Benjamin Franklin
Political integration and autonomy
1750-1775
Cartoon by Benjamin Franklin
Political integration and autonomy
1750-1775
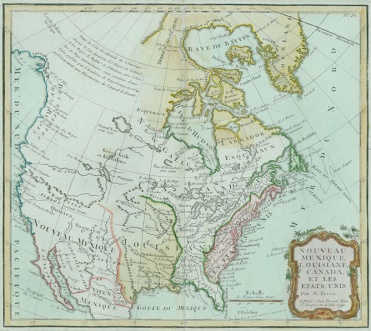 Map of the USA, 1790
Formation of the United States of America
1776-1789
Map of the USA, 1790
Formation of the United States of America
1776-1789
| Creation of British North America
1764-1837
British Lord Durham – political agitation
1837-1839
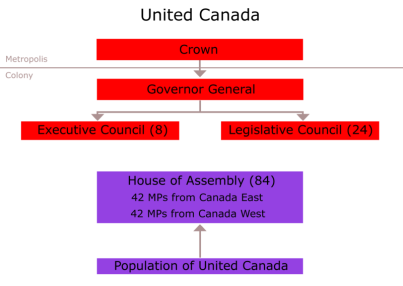 Political organization under Act of 1840
Act of Union
Got internal self-government
Dominion of Canada:
Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick
1st July 1867
All provinces had become part of the central government
A member of United Nation Organization
Political organization under Act of 1840
Act of Union
Got internal self-government
Dominion of Canada:
Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick
1st July 1867
All provinces had become part of the central government
A member of United Nation Organization
| World War I - II 1914-1917 1940-1945 Great Depression 1930s | Separate from Australia Depression 1930s Second World War Support of GB and the USA |
Продолжение таблицы.
| United Kingdom | The USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | |
 English troops in Africa
I – II World Wars
1914-1917
1939-1945
Cold War with Soviet Union
Support the USA in a most ways
- Antiterrorism
- Economic
- Political
English troops in Africa
I – II World Wars
1914-1917
1939-1945
Cold War with Soviet Union
Support the USA in a most ways
- Antiterrorism
- Economic
- Political
| Foundation of American government
Western Expansion
1789-1849
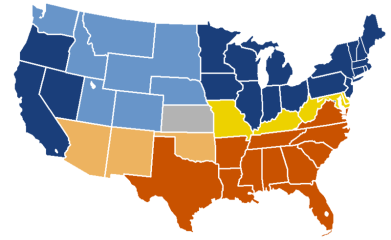 The Union: blue, yellow, gray;
The Confederacy: brown
Civil War era
1849-1865
Rise of Industrialization
1865-1890
Great Depression
1929-1935
The Union: blue, yellow, gray;
The Confederacy: brown
Civil War era
1849-1865
Rise of Industrialization
1865-1890
Great Depression
1929-1935
 Douglas MacArthur lands at the Battle of Leyte
Douglas MacArthur lands at the Battle of Leyte
|  Post-war
A member of NATO
Canada’s first Bill of Rights is signed
Canada maintains its position in NATO and is one of the so-called G-7 countries. (The G-7 group of Germany, France, the USA, the UK, Japan, Italy and Canada meet regularly to develop major economy)
Post-war
A member of NATO
Canada’s first Bill of Rights is signed
Canada maintains its position in NATO and is one of the so-called G-7 countries. (The G-7 group of Germany, France, the USA, the UK, Japan, Italy and Canada meet regularly to develop major economy)
|
Продолжение таблицы.
| United Kingdom | The USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | |
World War II
1941-1945
The Cold War
1945-1991
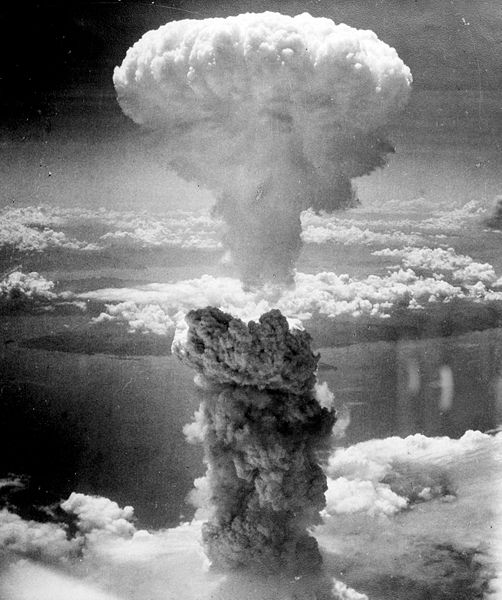 Atomic bombing of Nagasaki
Nuclear Weapon
Terror Acts of 11th of September 2001
Fight against World Terrorism
Since 2001
First black president – Barak Obama
May 2009
Atomic bombing of Nagasaki
Nuclear Weapon
Terror Acts of 11th of September 2001
Fight against World Terrorism
Since 2001
First black president – Barak Obama
May 2009
|
Дата добавления: 2015-10-16; просмотров: 99 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Раздел 1. АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК – ЯЗЫК МЕЖДУНАРОДНОГО ОБЩЕНИЯ | | | Раздел 3. направления магистерской подготовки |