
|
Читайте также: |
A shaft is a running part of the unit on which the parts (toothed gears ets.) to transmit torque are fitted.
During design stage the diameter of output (input) section of the shaft can be defined from conventional calculation of rotation per maximum long-lasting torque acting at reduced value of permissible tangential stresses  . Value
. Value  is taken reduced, because this calculation does not take into account shaft bending resistance.
is taken reduced, because this calculation does not take into account shaft bending resistance.
The shaft diameters are defined subject to strength conditions (see Figure 3):
- input shaft diameter
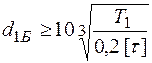 , mm;
, mm;
- output shaft diameter
 , mm
, mm
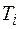 – torque on shaft under assessment, N m;
– torque on shaft under assessment, N m;
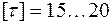 МPa – permissible stresses.
МPa – permissible stresses.
Minimum diameter values obtained for both input and output shafts are rounded to the closest large one from normal rows according to GOST. These diameter values should be applied as benchmark ones for further design of the shafts.
Diameters of other reduction shaft sections as well as lengths of these sections are defined in approximation during development of the design.
Then the diameter value of the shaft is defined as per rolling bearing as follows:
- for input shaft
 ;
;
- for output shaft
 ,
,
in such a manner that calculated value is expressed with whole integer in mm and ending with 0 or 5 (see item 2.5)
The pinion is to be integral part of the shaft, therefore the next section of the input shaft shall have the following diameter (see Figure 3 a)
 .
.
Hence,  – size of the bearing facet selected as per item 2.5. recommendation.
– size of the bearing facet selected as per item 2.5. recommendation.
Then shaft diameter under the wheel is defined as follows:
 .
.
The wheel nave diameter is defined:
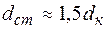 .
.
Then diameter and length of the collar – it’s such a section of the shaft (narrow thickening) that serves as a limitation to wheel moves along shaft axle are assessed:
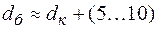 mm;
mm; 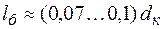 mm.
mm.
The dimensions calculated are to be referenced with target dimensions under GOST 6636-69.
The dimensions and shape of end section of the shaft  ,
, 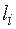 (
(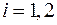 ) shall match the target values as per GOST 6636-69.
) shall match the target values as per GOST 6636-69.
Cylindrical ends of the shaft can have two versions: 1 – long end 2 – short one.

Key dimensions of shaft cylindrical ends, mm
(as per GOST 12080-66*)
| Diameter d | Length l | r | с | ||
| Row1 | Row 2 | Version | |||
| 10; 11 12; 14 16; 18 20; 22 25; 28 – | – – – | 0,6 1,0 1,0 1,6 1,6 2,0 | 0,4 0,6 0,6 1,0 1,0 1,6 | ||
| 32; 36 40; 45; | 42; 48 – | 2,0 2,0 | 1,6 1,6 | ||
| 60; 70 – | 63; 65; | 2,5 2,5 2,5 | 2,0 2,0 2,0 | ||
| 80; 90 | 85; 95 | 3,0 | 2,5 |
Note. Row 1 diameter is preferable
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 115 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Reduction unit wheels layout method | | | Selection of rolling bearings |