
Читайте также:
|
The overwhelming majority of the enterprises has park of cars of different types in this connection there is a necessity of calculation of annual exhausts of harmful substances motor transport and inclusion of these data to planned forms for the purpose of realisation of the state account of these exhausts and working out of actions for their decrease at all levels planning, the control and the account.
In a basis of a technique of calculations of exhausts of harmful substances motor transport it is necessary centre specific exhaust of cars of separate groups (cargo, buses, automobile). Thus exhaust of harmful substances is corrected depending on a technical condition of cars, their middle age, and also from influence of natural climatic parametres.
For cars of park of the enterprise the mass of exhausts for the settlement period and time j - substances (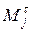 ) at presence in group of cars of different types combustion engines (ДВЗ) - petrol, diesel, gas, etc. - is defined under the formula.
) at presence in group of cars of different types combustion engines (ДВЗ) - petrol, diesel, gas, etc. - is defined under the formula.
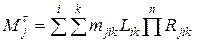 , (2.3)
, (2.3)
де і – quantity of groups of cars;
mjik – Relative density of blowout j - harmful substance the car, and - groups of the engine k - го type the settlement period (including prorunning blowout with the account carter type blowouts and fuel evaporations), g/kg;
Lik – Run of cars and - ї groups of the engine k - го type for the settlement period, million in km;
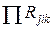 - Product of factors of influence n factors on blowout j - ї harmful substance cars and - ї groups of the engine k - type.
- Product of factors of influence n factors on blowout j - ї harmful substance cars and - ї groups of the engine k - type.
The influence factor is defined on tab. 2.6
Table 2.6 Factor of influence for different groups of cars
| Groups of cars | Factor of influence of blowouts | |||||
| Monoxide carbon | Hydrocarbons | Nitric oxides | ||||
| СВП | РТС | СВП | РТС | СВП | РТС | |
| Cargo and cargo special with petrol engine | 1,33 | 1,69 | 1,20 | 1,86 | 1,0 | 0,8 |
| Cargo and cargo special with diesel engine | 1,33 | 1,80 | 1,20 | 2,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 |
| Buses with petrol engine | 1,32 | 1,69 | 1,20 | 1,86 | 1,0 | 0,8 |
| Buses with diesel engine | 1,27 | 1,80 | 1,17 | 2,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 |
| Passenger office and special | 1,28 | 1,63 | 1,17 | 1,83 | 1,0 | 0,85 |
| Passenger individual using | 1,28 | 1,62 | 1,17 | 1,78 | 1,0 | 0,9 |
The note: СВП - park middle age, RTS - level of a technical condition.
The compound of harmful substances resulted in tab. 2.7 does not reflect to the full a quantitative compound of harmful impurities in spent gases of cars with engine diesel type (tab. 2.7).
Table 2.7 the Quantitative compound of harmful impurities, mg/m3 in spent gases
| Components | Duple a diesel engine | Four-cycle a diesel engine | ||
| Idling | 100 % Loadings | Idling | 100 % Loadings | |
| Carbon dioxide | 1,70 | 2,20 | 1,20 | 2,10 |
| Monowhite damp | 1100,00 | 1100,00 | 700,00 | 1300,00 |
| Acrolein | 24,00 | 31,20 | 2,90 | 0,86 |
| Nitrogen oxide | 650,00 | 900,00 | 90,00 | 87,00 |
| Sulphur dioxide | 1600,00 | 1700,00 | 1800,00 | 1800,00 |
| Carbon black | 0,18 | 0,09 | 0,12 | 0,07 |
| Fuel pairs | 3,00 | 25,00 | 3,00 | 25,00 |
The note: for carbon dioxide the qualitative compound is resulted in percentage.
Particle of harmful impurities which are implanted on air mediuim through a thinness of the engine and its air-gas path, position by means of gaugings in real conditions or a settlement method.
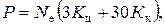 (2.4)
(2.4)
де Р – quantity of gase, mg/year;
N е – Effective power of a diesel engine for a minimum quantity of turns, mg/H;
К ц, К к – Contents of separate making (gases) in cylinder and crankcase spent gases, mg/l (tab. 2.8).
Table 2.8 Contents of separate components, mg/l in spent gases and in a crankcase
| Harmful impurities | Spent gas | Carter |
| Monowhite damp | 0,80 | 1,3 |
| Akrolein | 0,90 | 0,04 |
| Hydrocarbons | 0,71 | 0,03* |
| Nitrogen oxide | 0,61 | - |
* Total concentration is resulted.
2.5 Calculations aerosol to removal of an electrolyte from accumulators
Lead-acid accumulators belong to the most widespread chemical current sources, are widely applied in different areas of technics, including in electropenalties which are one of the basic intershop vehicles.
For exploitation of acid accumulator batteries hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur dioxide, antimonous and arsenic hydrogen, carbonic gas, and also a sulfuric acid aerosol (accumulator gases) in the form of a fog precipitate out. Hydrogen and oxygen precipitate out owing to water electrolysis.
Stibine (stibin) is received at interaction of singlet hydrogen with antimony which add for granting of strength to plates. The stibine part dissolves in an electrolyte, in active mass and in separators, and the most part together with hydrogen enters in air. Stibine allocation considerably increases with increase in gas releases from the accumulator.
Arsine hydrogen (arsine) is formed in small amounts owing to passing of reactions between arsenic and sulfuric acid. Arsenic in the form of dashes contains in lead and in sulfuric acid. Arsine - joint nonresistant which is easily displayed on arsenic and hydrogen. Carbonic gas precipitates out from accumulators in insignificant quantity at use in them of separators from a tree. The quantity of hydrogen (д/г), that precipitates out at charging of acid accumulators, is estimated on expression:
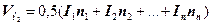 , (2.5)
, (2.5)
where 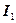 ,
, 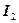 ,
,  – Magnitude of a current(it is underlined in the accumulator passport), А;
– Magnitude of a current(it is underlined in the accumulator passport), А;
n – Quantity of accumulators in the battery which is charged.
Knowing, it is possible to position, how many sulfuric acid has got to air taking into account that with 1л hydrogen 0,3 mg/l H2SO4 - for tight accumulators with a respiratory hole precipitate out; 0,9 mg/l - for open accumulators with a protective glass; 3,0 mg/l - for open accumulators without a protective glass.
In an event charging alkaline accumulators
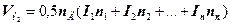 , (2.6)
, (2.6)
where 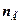 – The factor which considers magnitude of a warhead current, is equaled 0,85 at charging the accumulator by a direct current and 0,25 - at charging a current descending behind magnitude.
– The factor which considers magnitude of a warhead current, is equaled 0,85 at charging the accumulator by a direct current and 0,25 - at charging a current descending behind magnitude.
Quantity of alkali which precipitates out, defined on dependence:
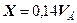 ,
, 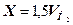 , (2.7)
, (2.7)
where 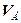 ,
, 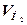 – Quantities of gases and hydrogen (accordingly) which precipitate out from the accumulator, l/h.
– Quantities of gases and hydrogen (accordingly) which precipitate out from the accumulator, l/h.
Feature of alkaline accumulators is active interaction of a water solution with carbonic gas, air with formation of carbonates. Their presence causes increase of internal resistance of accumulators. Growth of carbonates in 2,5... 3 times compared with norm are reduced by container of accumulators on 35... 40 %.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 144 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| What is Air Pollution? | | | Methods and means of weeding of atmospheric emissions |