
Читайте также:
|
Every facility involved in the production of petroleum and related products requires some type of storage. Manufacturers also should be consulted for specific design information on a particular type of storage. During the early days of oil production, the method of storing was almost exclusively white-pine wooden tanks, which were followed by cypress tanks, and then redwood tanks. However, because of the constant and steep rise in the cost of redwood lumber and the diminution of skilled erectors required, the installation of new wooden tanks is nearly non-existent. The bolted-steel tank was developed next and replaced the wooden tank.
Bolted-steel tanks
Bolted tanks are designed and furnished as segmental elements assembled on location to provide complete vertical, cylindrical, above-ground, closed and open-top steel storage tanks. Standard API bolted tanks are available in nominal capacities of 100to 10.000bbl, and are designed for approximately atmospheric internal pressures. Bolted tanks offer the advantage of being easily transported to desired locations and erected by hand. To meet changing requirements for capacity of storage, bolted tanks can be easily dismantled and re-erected at new locations. If a tank develops a hole from corrosion or becomes damaged, a single sheet or more may be replaced. A complete tank bottom may be replaced in the field without dismantling the tank. Also, a section may be removed from the tank, a new connection installed in the sheet and the section replaced without danger. No special equipment is required for the erection of bolted tanks. These tanks are erected by non-specialized crews using hand tools and usually an impact wrench. Bolted tanks are available with painted, galvanized and special coatings, including factory-baked coatings. Painting on both sides of the sheets during fabrication gives the inside of the tank some corrosion protection. Galvanizing the sheets and all tank parts by the “hot-dip” process or applying a factory-baked coating affords high corrosion protection. Generally, bolted tanks are fabricated from 12- or 10-gauge steel, and if not galvanized or furnished with a protective coating for corrosion protection, they do not have the expected life of the welded – steel tanks, which are usually constructed of heavier steel. The component parts of a typical bolted tank are shown in Fig. 1.
|

Fig.1 Typical bolted tank
Welded – steel Tanks. Shop-fabricated welded, cylindrical-shape tanks are available in a large variety of sizes as shop-fabricated items. Shop-welded tanks fabricated to API specifications provide the oil production industry with tanks of adequate safety and reasonable economy for use in the storage of crude petroleum and other liquids commonly handled and stored by the production segment of the industry. Shop-welded tanks are usually fabricated from 3/16-in. or heavier steel and will permit internal pressure up to 16oz. Shop fabrication permits testing in the shop for leaks and also provides immediate storage. Tanks are merely up-ended from a truck on the location.
Field-welded Tanks provide large storage capacities in a single unit. Large field-welded tanks providing storage capacities of 150.000 bbl or more have become prevalent for use in the storage of oil and petroleum products. Field-welded tanks are designed and erected in accordance with API Standard, which covers material, design, fabrication, erection and testing requirements for welded-steel storage tanks. It also includes an alternative basis for shell design, as well as one for calculating tank-shell thickness.
Fixed Roof are permanently attached to the tank shell. Welded tanks of 50 bbl capacity and larger may be provided with a frangible roof (designed for safety release of the welded deck-to-shell joint in the event excess internal pressure occurs). In this case, the design pressure should not exceed the equivalent pressure of the dead weight of the roof including rafters, if external.
Floating Roof storage tanks may be tank type is used primarily for storage near atmosphere pressure. Floating roofs are designed to move vertically within the tank shell to provide a constant minimum void between the surface of the stored product and the roof. Floating roofs normally are designed to provide a constant seal between the periphery of the floating roof and the tank shell. They can be fabricated in a type that is exposed to the weather or a type that is under a fixed roof. Internal floating-roof tanks, with an external fixed roof, are used in areas of heavy snowfall since accumulations of snow or water on the floating roof affect the operating buoyancy. These can be installed in existing tanks as well as new tanks. Both floating roofs and internal floating roofs are used to reduce vapour losses and to aid in conservation programs. Fig. 2 is a schematic of a typical internal floating roof tank.
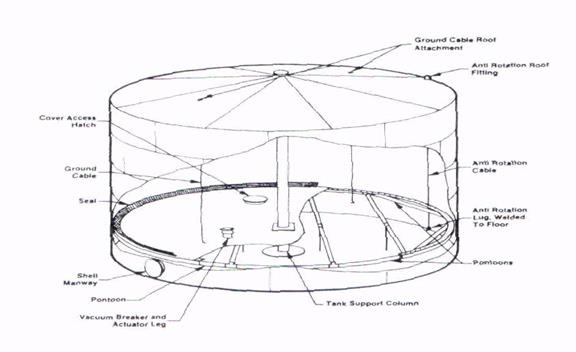
Fig.2.Typical arrangement of internal floating roof
|
Cone - Bottom Tanks. The cone-bottom in either the bolted or the welded tank offer a means of draining and removing water or water-cut oil, from only the bottom of the tank, leaving the marketable oil above. The drain line from a sump-equipped cone bottom must be equipped with a vortex breaker to drain off most of the water without coning oil into the drain. With a flat-bottom tank, some of the marketable oil must be removed if all the water is removed from the tank. Corrosion on the tank bottom is kept to a minimum by keeping all water removed. A cone bottom can be kept clean without having to open the tank if 1 or 2 bbl are drained off once or twice weekly and pumped back through the treating system. If this is not done and the bottom solidifies, the tank must be opened. The cone-bottom tank can be cleaned without entering. A water hose, handled just outside the cleanout opening, can be used to flush the solids to the centre of the cone and drain connection.
(Petroleum Engineering Handbook, Society of Petroleum engineers, Richardson, TX. USA. 1992)
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 113 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Answer the following questions. | | | The pictures show the installation process of tanks. Read the information and number the steps. |