
Читайте также:
|
The main concepts of Chapter three:
Concept of Respiration
1- A T P molecule is built up of three subunits which are Adenine, Ribose and three phosphate groups.
2- One A T P molecule is hydrolyzed into A D P and about 7 - 12 k cal.
3- Oxidation of glucose can be summarized by the following equation:
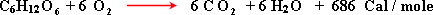
4- Oxidation of glucose takes place into two stages:
A- Glycolysis in the Cytosol
B - Respiration which divided into:
- krebs cycle, - electron transport.
5- The mitochondria are the centers of respiration in the cell.
6- Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is the gain of electrons.
7- NAD+ is a co-enzyme which can receive a proton and two electrons to be reduced to NADH2.
8- Co-enzyme FAD+ can receive two protons and two electrons to be FADH2
9- Cytochromes are electron acceptors which are similar in structure and carry electrons at different energy levels.
10- Through krebs cycle acetyl COA joins krebs cycle where its coA-enzyme splits off to repeat its role, at the same time the acetyl group combines with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid.
11- Krebs cycle does not need oxygen because all the electrons and protons are received by NAD+ and FAD+
12- Oxidative phosphorylation is a conversion process from ADP and phosphorus into ATP.
13- Through electron transport, 3 molecules of ATP are formed every time a pair of electrons is transferred through the entire carrier system.
14- Anaerobic respiration or fermentation is a process through which living organisms break down food molecule to release energy in the absence of oxygen or in low quantity.
15- Anaerobic respiration starts with glycolysis to form pyruvic acid which may be changed into ethyl alcohol in case of yeast fungus or lactic acid in case of animal muscles or several kinds of bacteria.
16- The released energy from aerobic respiration is 38 ATP while that of anaerobic respiration is only 2 ATP.
17- The respiration system in man consists of:
- Nose
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Bronchioli
- Air sacs.
18- It is better to breath through the nose because it contains hairs, blood capillaries and secretes mucus.
19- Alveoli have very thin walls surrounded with a network of blood capillaries to make gas exchange easier.
20- Alveoli bronchioli and capillaries together form the lung.
21- Diaphragm is a respiratory muscle that participates in the mechanism of respiration.
22- During inspiration, the rib muscles and diaphragm muscle contract, so the size of the chest cavity increases and the internal air pressure decreases so the outside air flows into the lungs.
23- During expiration, the rib muscles and diaphragm relax decreasing the chest cavity and increasing the internal pressure so the air is forced outside the lungs.
24- A part of air is always left inside the lung to warm the new coming air to make adhesion of the alveoli membranes with the walls of blood capillaries to ease gas exchange.
25- During each respiratory cycle the aeration of lungs not usually exceed 10% of its capacity, this ratio varies according to the rate of individual activity and depth of inspiration.
26- The respiratory system in man plays an important role in the excretion of water in the form of water vapour.
27- Man usually loses daily about 500 mL of water through his lungs out of 2500 mL of water that he lost daily.
28- Water inside alveoli helps to moisten the alveoli membrane and also necessary for dissolving oxygen and carbon dioxide, so the gas exchange occurs easily.
29- Respiration in plants may be aerobic respiration or anaerobic respiration.
30- In case of vascular plants, oxygen reaches the cell through various passage ways such as:
A- stomata of the leaf.
B- Through the phloem.
C_ Oxygen may enter the plant through the root.
D- green plant stem has stomata so oxygen may enter through them.
E - woody plant stem has lenticels or cracks through which oxygen may pass.
31- CO2 which is resulted from respiration of the plant may be expelled out through:
A- Diffusion if plant cells are directly in contact with air.
B - Deep cells pass CO2 to xylem and phloem to carry it to stomata
C- A part of CO2 is used in photosynthesis.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 109 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Chapter Two : Transport | | | Chapter Four : Excretion |