
Читайте также:
|
The main concepts
Chapter 1: Nutrition
1- Nutrition is the study of food and various modes of feeding in living organisms.
2- Living organisms may be:-
- Autotrophic [photoautotrophs or chemoautotroph.
- Heterotrophic
3- Autotrophic nutrition in green plants includes:-
- Absorption of water and salts.
- Photosynthesis.
4- The different tissues of the root are:-
- Epidermis
- Cortex
- Endodermis
- Vascular cylinder which consists of pericycle- xylem - phloem - pith.
5- The root hairs are well adapted to their function that: -
- They have thin walls
- They are large in number
- The solution in their vacuoles is more concentrated.,BR> - They secrete a viscous substance.
6- Diffusion:
It is the movement of a substance from highly concentrated medium to a lower concentrated one.
7- Osmosis:
It is the diffusion of water from a diluted medium of high water concentration to another of lower water concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
8- Permeability:-
It is the ability of cell walls and cell membranes to pass substances through them.
9- Imbibition:
It is the ability of solid particles especially colloidal ones to absorb liquids and increase in volume.
10- The absorbed water passes through the root cells until it reaches xylem vessels in three pathways:
A- Cell walls by imbibition.
B- Through the cytoplasm and plasmodesmata.
C- Cell sap by osmosis.
11- The root hairs of desert plants (xerophytes) reaches 50 - 200 atmospheres while that of the ordinary plants (mesophytes) ranges from 5 to 20 atmospheres.
12- The endodermis has a major role in controlling the passage of both water and solutes to the xylem vessels that the cells that face the phloem are completely thickened with suberin, while those facing the xylem which we call passage cells have impermeable ribbon of suberin called casparian strip.
13- Essential elements for green plants are divided into:
A- Macro - nutrients N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S, Fe
B- Micro-nutrients:
Mn, Zn, B, Cl, Cu, Mo, I, Al which act as co-enzymes that they activate enzymes.
14- Active transport:
It is the passage of any substance through the cell membrane against concentration gradients, with the help fo chemical energy released during aerobic respiration.
15- Cation exchange.
The root cells may get rid of some positive ions like Na+ and replace them by K+ ions this is done according to the cell needs.
16- Photosynthesis is important because it provides food for all living organisms, gives oxygen, some plant fibers are used in some industries as well as fossil fuels were originated from plants.
17- The raw materials required for photosynthesis:
a- water as a source of Hydrogen.
b- nitrates, sulphates, phosphates are needed to convert carbohydrates into proteins.
c- phosphorus to build A T P.
d- Magnesium for chlorophyll synthesis.
e- Iron as co-enzyme.
18- Products of photosynthesis:
a- monosaccharide "glucose"
b- Oxygen.
19- The rate of photosynthesis can be determined by two ways.
a- By measuring the amount of starch built in a unite time.
b- By counting the number of oxygen bubbles evolved.
20- The normal rate of photosynthesis is gram / hour / meter square of the green leaf.
21- The chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis.
22- Each chloroplast is enclosed by a thin double membrane, disc-shaped structures called grana are embedded in the stoma.
23- There are 4 main Pigments inside the hollow of the grana, these are chlorophyll A and B, Xanthophyll and Carotine.
24- The chemical structure of the chlorophyll is N4 MG
25- Plant leaves are well adapted for their function, that, they are arranged in a parallel way, the blade is thin and flattened, the blade is supported by a mid rube as well as protective hairs may grow on the surface of some plant leaves and their tips.
26- The plant leaf consists of three main tissues:
a- The epidermis "upper and lower"
b- The mesophyll "palisade and spongy"
c- The vascular tissue "xylem and phloem"
27- Van Neil studied photosynthesis is both green and purple bacteria.
28- Green and purple bacteria use H2S


31- Water is the source of oxygen released from photosynthesis


34- Photosynthesis includes two main stages.
A- Light reactions in which the light is the limiting factor, through which light is absorbed by
A- Chlorophyll A and energy which is released from its electrons are used to split water into oxygen and hydrogen and the rest is used to convert
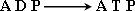 to store energy.
to store energy.
B - Dark reactions:
In which CO2 is reduced by hydrogen (NADPH2) with the help of energy stored in A T P to form monosaccharide glucose these reactions are controlled by temperature and enzymes.
35- Digestion is the change of large molecules polymers into smaller one monomers by hydrolysis.
36- Enzymes are protenic substances that act as catalyst which activate a particular chemical reaction.
37- Enzymes are highly specific, some have a reversible action, some are secreted in inactive form, and each enzyme has a certain pH to work or to be active.
38- The digestive system in man consists of two main parts:
A - The alimentary canal which starts with the mouth and ends with anus.
B - Associated or accessory glands which produce digestive juices that help in digestion.
39- The different organs of the alimentary canal are:
- The mouth
- The pharynex
- The oesophagus
- The stomach
- The small intestine
- The large intestine which ends with anus.
40- Digestion takes place in three organs:
A- Mouth [Buccal digestion]
B- Stomach [gastric digestion]
C- small intestine [intestinal digestion ].

42- There are two main types of glandular cells in the stomach:
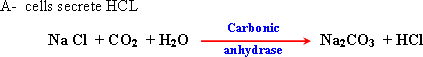
HCl creates an acidic medium which stop the action of ptyalin, activates gastric enzymes as well as kills harmful bacteria.
B - Cells secrete gastric enzymes (Pepsin).
43- 
44- Secretin hormone stimulates the pancreas to secrete sodium bicarbonate also it activates the liver cells to secrete the bile.
45- 
46- 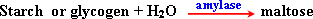
47- 
48- 
49- 
50- Peptidases are a group of enzymes which catalyze the hydrolysis of polypeptides into amino acids.
51- 
52- 
53- 
54- Absorption is the transfer of digested food to the blood and lymph by diffusion or active transport.
55- The inner lining of the ileum of the small intestine has tiny finger like projections called villi, through them absorption happens.
56- The absorbed food passes through two main routs:
A- fatty acids, glycerol together with vitamins A, D, K pass through lymphatic route.
B - Water, mineral salts, glucose, amino acids together with vitamin B, pass through blood route.
57- Wastes are finally expelled out as feaces through the anus by means of strong muscular contraction of the rectum together with the relaxation of the anal sphincter.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 132 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| There are some structures which carry a passive meaning in spite of the verb being active. | | | Chapter Two : Transport |