Pic.1. Diffraction pattern of a cell nucleus
Occupation No. 5
The theme of the lesson: Temporary organization of a cell.
The aim of the lesson: study a microscopic and submicroscopic structure of a nucleus of a cell; cellular cycle and essence interphase, ways of cell fission; to be able to make entry of the maintenance of a genetic material during the different periods of interphase and at different levels of a mitosis and meiosis.
I. Questions for self-preparation (60 min.).
- Structure and functions of a nucleus of a cell.
- Types of chromosomes. Structure of a metaphase chromosome; Rules of chromosomes
- Cellular and mitotic cycles.
- Interphase, characteristic of the periods. Mitosis reasons.
- Comparative characteristic of a mitosis and meiosis. The maintenance of a genetic material in various phases of division. The importance of a mitosis and meiosis.
- Amitotic division and mitosis versions (endomitosis, pollinate), their characteristic and value.
II. Main terms and concepts
- Bivalents – two homologous chromosomes conjugating in a pro-phase of meiosis I. Their number equals to a haploid set of chromosomes.
- Karyolimph – nuclear juice.
- The cellular cycle is the period of time from emergence of a cell to its death or until the end of the following cellular division.
- Conjugation fof chromosomes – connection of homologous chromosomes on length.
- Crossing-over – an exchange of identical sites of chromatids of homologous chromosomes in pachiten of prophase of meiosis 1.
- Meiosis is a division of somatic cells of sexual glands at which sexual cells are formed.
- The mitotic cycle is the period of preparation of a cell to division (interphase) and division itself (mitosis).
- Telomera of chromosomes is the ending sites of shoulders of chromosomes.
- Hiazma – a recross of chromatids of homologous chromosomes at conjugation.
- chromatid – a complex consisting of DNA and histonic proteins.
- The nuclear and cytoplasmatic relation is physiologically and morphologically natural relation of the weight (volume) of a nucleus to the mass (volume) of cytoplasm in each cell.
III. Independent work of the student at home.
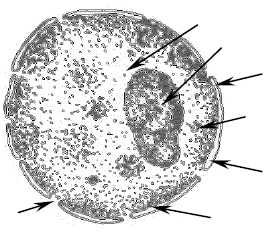
Pic.1. Diffraction pattern of a cell nucleus
1 – the external nuclear membrane, 2 – an internal nuclear membrane, 3 – perinuclearic space, 4 – slice, 5 – karyoplasma, 6 – chromatid, 7 – a nucleus.
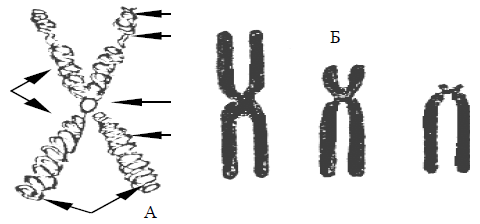
Pic. 2. Scheme of a metaphase chromosome (A) and types of chromosomes (B): 1 – shoulder, 2 – a cenrtromere, 3 – a secondary banner, 4 – the satellite, 5 – chromatid, 6 – telomer, 7 – metacentric, 8 – submetacentric, 9 – acrocentric chromosomes.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 124 | Нарушение авторских прав
Читайте в этой же книге: Health profession | Diagnosis for Laryngitis | Treatment for Laryngitis | Mechanism of injury | Complications |
mybiblioteka.su - 2015-2025 год. (0.005 сек.)


