
|
Читайте также: |
Medved A.V.
A.A. Trofimuk Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Andreymedved89@mail.ru
In the south-eastern regions of West Siberia most oil and gas fields are concentrated in the Upper Jurassic anticlinal traps. When searching for oil and gas one of the major challenges facing the seismic survey is the selection of promising structures.
The work performed on the basis of complex interpretation of seismic data and exploratory drilling is devoted to the analysis of structural framework and tectonic history of northern part of Kaymysovsky vault.
Study area is located in the Tomsk region and it is the part of the Mezhovskaya oil and gas area in Kaymysovsky oil and gas region. 46 wells were drilled in the study area. 58 CDP seismic profiles were made, the total length of 1209, 32 km. The density of seismic observations on average is 1.24 km/km2.
Seismological project was created in interpretation soft W-Seis, the reflection horizons which control the basic seismological sedimentary complexes were correlated. Seismological complexes are intervals of cross sections, characterized by different depositional environments. Roofs and bases of complexes are seismic and geological boundaries, changed by the conditions of sedimentation - the surface of the regional unconformities, breaks, or regional planation surfaces, which are confined to the most stable reflectors - seismic frames.
During the held studies constructing of structural maps has been carried out: F2 - a base surface of a sedimentary cover, ∙IIа - top of Jurassic sedimentary complex (a base surface Bazhenovskaya formation), III - Koshayskaya unit of Alymskaya formation (the Lower Cretaceous, aptian), IV - Kuznetsovskaya formation (the Upper Cretaceous, turonian), V – Talitskskaya formation (the Paleocene).
According to the map of Jurassic sedimentary cover of the Tomsk region (Fig.) [1] the study area is located mainly within Kaymysovsky vault, Nyurolka megadepression and Novovasyugansky swell partially captures North Demyanskaya megamonoklinal, Verhnedemyansky megaswell, Ledyanskaya mezosaddle and Cheremshanskaya mezosaddle.
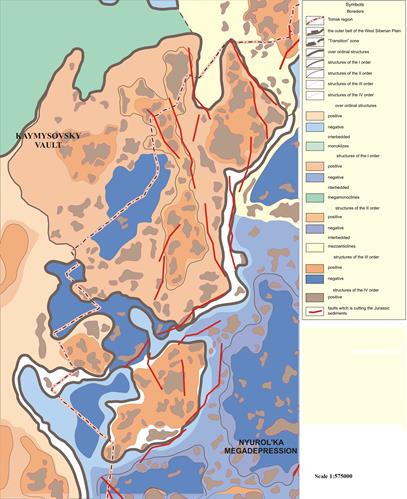
Fig. Fragment of "Tectonic Map of the sedimentary cover (Tomsk Region)" (Edited by A. Kontorovich)
Kaymysovsky vault is isometric tectonic element located in the northeastern part of the Nizhnevasyuganskaya antekliz. Mezosaddle is formed by two systems of elevations, having north-west and north-easterly direction, for which the central (axial) part of the structure of the order a few omitted. Such a structure is set, is not typical for positive tectonic elements, as recorded in the relief of the Bazhenovskaya Formation and pre-Jurassic basement.
The analysis of izopachous maps has allowed to draw following conclusions.
Allowing, that in Aptian paleorelief of Bazhenovskaya formation (an izopachous map of Volga-Aptian sediments) the Larlomkinsky swell has been laied out hypsometric fundamentaly above, than Pervomaj-Vesenny swell, it is possible to draw a conclusion that at this stage it developed essentially more intensively.
The South Turjahsky depression and a depression zone in the north-west territory were active shaped at the Volga-Aptian time.
As a whole, the analysis of Bazhenovskaya formation paleorelief, taking place in Aptian century, allows to notice that by the forming moment of Koshayskaya unit the modern relief of investigated territory has been appreciably generated. At this stage all local structures of II order have been formed practically. For example, though the Pervomaj-Vesenny swell was hypsometric below the Larlomkinsky swell, both these tectonic elements at this stage of progressing had the delineations close to the modern.
At the Alb-Turonian time directivity of tectonic processes was fundamentally changed. At this time the Pervomaj-Vesenny swell intensively grew, while the Larlomkinsky swell and all western part of esteemed area plunged.
As a result of these opposite processes which were originating in Volga-Aptian and Albian-Turonian times, Pervomaj-Vesenny and Larlomkinsky swells in a modern relief of Bazhenovskaya formation are laied out approximately at one hypsometric level.
In Lower Paleogenic-Neogenic time intensive regional submergence of a northwest part of territory took place, against which local structures practically were not shaped. It is suspected that the modern shape of the Jugansk megadepression has been generated at this stage of developing of the West-Siberian syneclise, because the northwest part of the studying area was most active plunged in Cenosoic age.
References:
1. Tectonics and oil and gas potential of Mesozoic and Cenozoicsediments of the south-eastern regions of West Siberia. / Kontorovich, V.A. Novosibirsk: Publishing House of SB RAS, Branch of "Marketing", 2002. 253 p.
2. Stratigraphy and oil and gas basins of Siberia. Jurassic System. / Ed. Shurygin B.N., B.L. Nikitenko, V.P. Devyatov and other. Novosibirsk:Publishing House of the Siberian Academy of Sciences, 2000. 480 p.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-29; просмотров: 108 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| MODERN METHODS OF HYDROCARBON FUEL PROSPECTS AND EXPLORATION | | | Seismic reflection synthetics and petrophysical properties. |