
|
Читайте также: |
The business cycle or trade cycle is the periodic but irregular up-and-down movements in economic activity. It is measured by fluctuations in real GDP and other macroeconomic variables such as employment, industrial productivity, and interest rates. It is a permanent feature of market economies: gross domestic product (GDP) fluctuates as booms and recessions succeed each other. Since the World War II, most business cycles have lasted three to five years from peak to peak. The average duration of an expansion is 44.8 months and the average duration of a recession is 11 months. As a comparison, the Great Depression – which saw a decline in economic activity from 1929 to 1933 – lasted 43 months.
During a boom, or a period of prosperity, an economy (or at least parts of it) expands to the point where it is working at full capacity, so that production, employment, prices, profits, investment and interest rates all tend to rise. During a recession, the demand for goods and services declines and the economy begins to work at below its potential. They start speaking of a recession if there are two consecutive quarters of real GDP decline. In this period of business cycle investment, output, employment, profits, commodity share prices, and interest rates generally fall. But the price level is likely to fall only if the recession is severe and prolonged – that is, if a depression occurs.
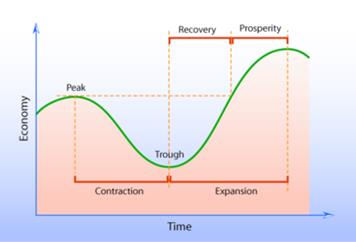
The highest point on the business cycle is called a peak, which is followed by a downturn or downswing or a period of contraction. Economists sometimes describe contraction as ‘negative growth’. Recession is a severe contraction which is called a slump or a depression. The lowest point on the business cycle is called a trough, which is followed by a recovery or an upturn or upswing or a period of expansion and prosperity. The trough phase of the cycle may be short-lived or quite long.In the recoveryphase, output and employment expand toward full employment. As recovery intensifies, the price level may begin to rise before there is full employment and full capacity production. The graph below shows the several phases of stylized business cycle.
There are various theories as to the cause of the business cycles. Internal (or endogenous) theories consider it to be self-generating, regular, and indefinitely repeating. A peak is reached when (or just before) people begin to consume less, for whatever reason. As far back as the mid-nineteenth century, it was suggested that the business cycle results from people infecting one another with optimistic or pessimistic expectations. When economic times are good or when people feel good about the future, they spend, and run up debts and vice-versa.
External (or exogenous) theories, on the contrary, look for causes outside economic activity: scientific advances, natural disasters, elections or political shocks, demographic changes, and so on. Joseph Schumpeter believed that the business cycle is caused by major technological inventions (the steam engine, railways, automobiles, electricity, microchips, and so on), which lead to periods of ‘creative destruction’. He suggested that there was a 56-year Kondratieff cycle, named after a Russian economist. A simpler theory is that, where there is no independent central bank, the business cycle is caused by governments beginning their periods of office with a couple of years of austerity programmes followed by tax cuts and monetary expansion in the two years before the next election.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 118 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Gross Domestic Product | | | Vocabulary Focus |