
|
Читайте также: |
The Senses and Sense Organs
One group of sensory receptors is distributed widely within the skin and deeper tissues and is responsible for the somatic senses of touch, pressure, temperature, and pain. A second group of sensory receptors functions as components of highly complex, intricately designed sense organs that provide us with the special senses of sight, hearing, smell, taste, and balance.
The Sensations of the Skin
Skin has different kinds of sensory receptors(pain receptors, m echanoreceptors, thermoreceptors) each of which is associated with one of the somatic senses. Some receptors consist of many cells, others of a single cell, and still others are only bare nerve endings. Each receptor is designed to respond to only one type of stimulus and relay the proper information to the central nervous system.
The Chemical Senses
The senses of taste and smell, which are chemical senses, result from the stimulation of chemoreceptors [kem'o-re-sep'terz]. Chemical substances in solution provide the stimulation of chemoreceptors on the tongue and in the nose.
The sense of taste. The tongue possesses the organs of taste, called taste buds ( вкусовые луковицы).Taste buds are chemoreceptors on the back, sides, and front of the tongue that detect dissolved substances. Like the other senses, taste occurs in the brain, where the substance in the mouth is indentified as sweet, sour, salty, or bitter. Taste buds are arranged in projections called papillae (сосочки) Adults have some nine thousand taste buds, located mainly on the tongue's surface. Babies have many more. Taste buds are replaced every ten to thirty hours.
The sense of smell. The nose's sensory receptors are located in the upper part of the nasal cavity and are connected to the brain by the olfactory nerve. Because the smell receptors are located rather high in the nasal passage way, ordinary breathing does not cause much stimulation. Also, olfactory receptors that are exposed to a certain odor over a prolonged period of time become insensitive to that odor.
The Sense of Hearing
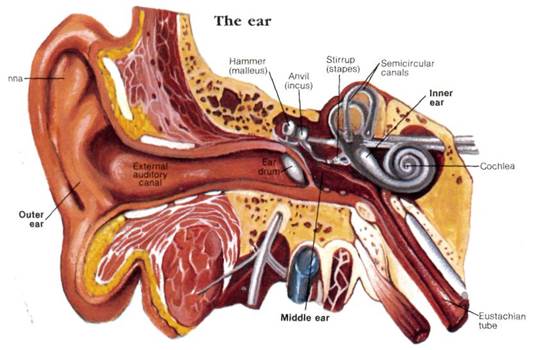
The ear is the organ of hearing, and it has external, middle, and inner parts. The sense of hearing brings us into contact with our world by means of sound waves transmitted by air. Through hearing we communicate with other people, and others communicate with us. Our ears are among the most wonderfully complex and intricately designed organs in the human body.
|
The mechanism of hearing
Sounds are collected into the external auditory canal by the pinna → eardrum (cause vibration) → vibration is transmitted through hammer, anvil. stirrup →on the oval window (cause vibration of membranes of the oval window) → vibrations are transmitted to the fluid within the cochlea (perilymph →endolymph) →to organ of Corti, which produces nerve impulses at the cochlear nerve endings -→ nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain by auditory nerve→→
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 114 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| THE PRINCIPLES OF EUROPEAN CONTRACT LAW - completed and revised version 1998 | | | Inside an English house |