
Читайте также:
|
List of abbreviations and their Russian equivalents
| Abbrevi-ation | Decoding | Abbrevi-ation | Equivalent in Rusian |
| ABV | air by-pass valve | КПВ | клапан перепуска воздуха |
| ACS | automatic control system | САУ | система автоматического управления |
| ACU | acceleration control unit | АП | автомат приёмистости |
| AD | automatic device | АУ | автоматическое устройство |
| CD | control device | УО | управляющий орган |
| CE (ED) | comparison element | ЭС | элемент сравнения |
| CF | controlling factors | УФ | управляющий фактор |
| CO | control object | ОУ | объект управления |
| CP | controlled parameters | УП | управляемый параметр |
| CU | control unit | УО | управляющий орган |
| ED (CE) | error detector | ЭС | элемент cравнения |
| FFB | flexible (elastic) feedback | ИОС | изодромная (гибкая) обратная связь |
| GTE GTP | gas-turbine engine gas-turbine plant | ГТД ГТУ | газотурбинный двигатель газотурбинная установка |
| HM | hydraulic moderator | ГЗ | гидравлический замедлитель |
| HP | high pressure (rotor) | ВД | высокого давления (ротор) |
| HPC | high pressure compressor | КВД | компрессор высокого давления |
| ICG | integral control gear | МОУ | механизм объединённого управления |
| Abbrevi-ation | Decoding | Abbrevi-ation | Equivalent in Rusian |
| LP | limited parameters | ОП | ограничиваемые параметры |
| LP | low pressure (rotor) | НД | низкого давления (ротор) |
| LPC | low pressure compressor | КНД | компрессор низкого давления |
| PRL | pressure rise limiter | ОНД | ограничитель нарастания давления |
| RFB | rigid (proportional) feedback | ЖОС | жесткая обратная связь |
| SD | set up device | ЗУ | задающее устройство |
| SE | sensitive element | ЧЭ | чувствительный элемент |
| SFCU | starting fuel control unit | ТАЗ | топливный автомат запуска |
| SM | servomechanism | СМ | сервомеханизм |
| TCL | throttle control lever | РУД | рычаг управления двигателя |
| TFE | turbofan (bypass) engine | ТРДД | турбореактивный двухконтурный двигатель |
| TM | tuning mechanism | МН | механизм настройки |
| TPE | turbo-prop engine | ТВД | турбовинтовой двигатель |
| VBV | variable bleed valves | КПВ | клапаны перепуска воздуха |
| VSV | variable stator vanes | РНА | регулируемый направляющий аппарат |


Automatic control system block diagram
For the realization of the chosen engine control law in maximum mode, and also for engine operation in other steady and transient modes, an engine ACS is required.
In general case, engine ACS is the combination of the gas turbine plant (ACS of GTP) as CO and the set of the AD – regulators, governors, limiters, automatic control units, which are coordinated (matched) with the GTP by their own parameters and providing their control, that is influence the engine operating process so that to get desired operation characteristics of GTP under all ambient conditions and all operation modes.
ACS of GTP can be represented using: Block diagram, Functional diagram and Schematic diagram.
The block diagram is the system of agreed image of the ACS structure and the way of connection between CO and automatic devices, included in a system.
Each system element in the block diagram is represented as a rectangular inside of which its name is indicated; to the left and to the right there are arrows which show the input and output signals describing its operation (fig.2.1),
Feature of the engine image as CO on the block diagram is such that the input signals acting on it are divided into two big groups: external disturbing effects and controlling influence.
Parameters, describing external disturbing effects, shown in fig.2.1 with general symbol Х1,i are designated on block diagrams by the arrows located above rectangular CO, with the indication at each arrow the type of disturbing effect (nhp, nlp, Tamb, etc). Parameters describing controlling effects on CO from regulators, limiters and other elements of the ACS, are designated in fig.2.1 by symbols Х5,1, Х5,2 … Х5,і are represented by the arrows to the left of CO and there are the inscriptions corresponding to the CF type (Wf - fuel flow rate, j prop - a propeller blades setting angle, α IGV - set angle of inlet guide vanes, etc.)
CO output signals are represented by arrows to the right of CO, indicating the type of a signal. In fig. 2.1 all CO output signals are conditionally joint into the following groups: X2,i - group of the engine controlled parameters, X3,i - group of limited parameters by which the limitation of engine fuel supply is provided; X4,i - group of additional parameters, describing the working process or operational mode of a GTE
and necessary for functioning of automatic devices of variable stator vanes (VSV) control, air bypass valves (VBV) control, and also for engine starting system and fuel starting devices operation, etc.

Fig. 2.1. Examples of the main devices representation,
included into the GTE ACS.
Controlling effects from H6 limiters, і and setting signals from Х8, і adjusting mechanisms can also be input signals of the main regulators alongside with the controlled parameters, conditionally joint in fig.2.1 in the group of parameters X2,i.

Fig. 2.2. Simplified block-diagram of connection of main automatic
devices with control object
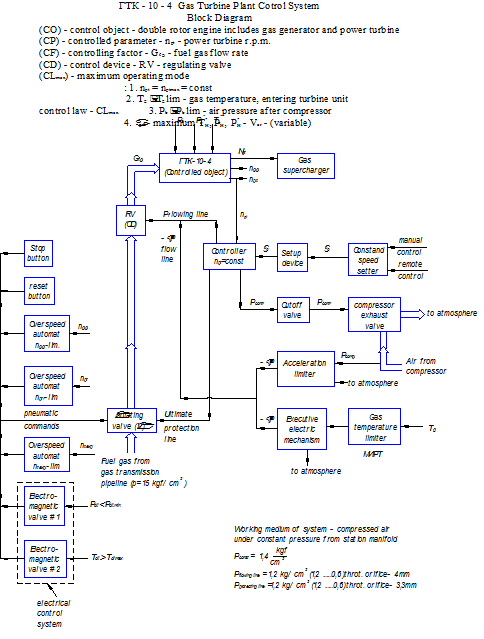
Структурная схема САУ газотурбинной установки ГТК-10-4
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 176 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| РОЗДІЛ 3. ПЕРШОЧЕРГОВІ ЗАХОДИ ПО ВДОСКОНАЛЕННЮ ГРОШОВОЇ СИСТЕМИ В УКРАЇНИ | | | ACS functional diagram development |