
Читайте также:
|
The principle of an ultrasonic method of visualization of the diagnostic image consists in an opportunity of reception of a focused beam of ultrasonic mechanical vibrations by frequency of 1-20 MHz, its introductions in investigated substance through an acoustic window and registration of the waves reflected from borders of different mediums. A fascicle of ultrasonic fluctuations enter into an investigated part of a body through a skin by means of the ultrasonic generator - пъезопреобразователя. Diffusion of ultrasound depends on the form пъезопреобразователя, properties of a ultrasonic beam and medium through which it passes, diffusion of ultrasound submits to laws of its reflection and a diffraction on border of different mediums, and also to laws of diffraction and dispersion. The reflected waves are perceived by the same converter, processed by the electron device and transformed to the one-dimensional or two dimensional image (an echogram or a ultrasonic scanning image). According to an echogram, it is possible to define topography, the form, size and structure of an investigated organ that allows to find out diffusive inspissation of a parenchyma of an organ, эхоплотные the centers in itself, and also cavities with a liquid or air.
There is an one-dimensional technique of BRIDLES: And-method (And - the amplitude) allows to record on the screen of an oscillograph ultrasonic impulses which look like vertical Figes on the direct line, different mediums reflected from border and tissues. Apply two variants of two dimensional echography: In (brightness) and M (movement). In case of use In a variant the beaten off impulses are recorded on the screen in the form of light points which brightness is directly proportional to intensity of reflection of ultrasound. The m-variant allows to receive the information on mobile structures in real time.
There are also three-dimensional (ultrasonic reconstruction see fig.10.11.) and four-dimensional (observation of the three-dimensional image in a regimen of real time) techniques.
The sound is a mechanical fluctuation which causes a compression and decompression of particles of a matter. By the physical nature, sound fluctuations are resilient waves. Their diffusion depends on resilient properties of particles of a matter. Sound waves cause fluctuation of these particles and transfer energy, instead of a matter. Molecules wave forward and back, they are compressed and stretched in medium according to a direction of a wave
In diagnostic devices use ultrasound which frequency makes 1 MHz and оmore.
Ultrasonic apparatus (see fig.10.25) define distance to reflecting structures, measure time during which ultrasonic wave passes to the certain structures and comes back to the converter.
Echogenisity is an ability of investigated object to reflect ultrasonic waves.
Action of the ultrasonic diagnostic device is based on introduction in a tissue of the patient of a ultrasonic beam and the subsequent registration эхосигналов, two mediums reflected from border with different acoustic density.
By a principle of action devices divide on echoimpulse scanners by means of which define anatomic structures, devices for definition of cinematic characteristics in which use Doppler's effect, and also the combined devices impulse-Doppler type.

Fig. 10.25.Ultrasonic impulse-Doppler apparatus Philips U22


Fig. 10.26. a)three -dimensional images of the face of a fetus; b) spectral допплеровская a curve of a normal hepatic artery.
Ultrasonic sings. During ultrasonic diagnostics of pathological process it is necessary to define: 1) a primary place of development of pathological process and its attitude to organs (органное, внеорганное); 2) localization of pathological formation in an organ; 3) shift, an elastance of an organ or pathological formation (if it can be defined); 4) the form of a tumour or cystic formation (they can be round, oval or wrong); 5) the sizes (only maximal) both a healthy organ, and pathological formation; 6) contours of organs and pathological formations; 7) ehogenisity (non-ehogenic, lowered, average, raised, high) see fig.. 2.20.; 8) the internal structure can be homogeneous and non-uniform (presence and localization of membranes, calcifications, localization of pathological includings inside of formation); 9) sound transmission (lowered, normal, raised, high); 10) definition of a stria with lowered ehogenisity on periphery of tumour unit, so-called гало which presence often testifies to development of malignant process, especially in a liver.
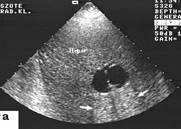

Fig. 10.27 Echograms of a liver. A cyst of a liver; a hemangioma of a liver
Ultrasonic contrast agents are grouped: vascular (Альбунекс, Левовист, Еховист) and peroral contrasts for evaluation of hollow organs (water, SonoRx).
UltrasonicDoppler. Doppler's effect consists that during reflection from mobile object frequency of a ultrasonic signal (beam) changes proportionally rates of movement of object. In case of reflection from object which keeps away, frequency of display of a ultrasonic signal decreases, and in case of its reflection from a coming nearer object - is enlarged.
Doppler use for studying the form, contours, definitions of diameter of vessels, rates of movement of a blood on vessels or the object located on certain depth from the converter.
Duplex sonography allows to receive the image of vessels (the anatomic information), record of a curve of a blood flow in them (the physiological information) and to diagnose a lesion of different vessels with a simultaneous estimation of a blood flow in them.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 157 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Physical bases of MRI | | | Drug Smuggler* as Pilot |