
|
Читайте также: |
The phenomenon of a magnetic resonance was found in 1946 by F.Blochem, E.Parmelem, in 1952 they have been awarded the Nobel Prize in 1973 by P.Rautenburg for the first time showed the opportunity of reception of the image by means of magnetic resonance radio signals, and in 1982 magnetic resonance tomograms for internal organs of the person were in access.
The principle of the method consists of the change in position and rotation of protons which are magnetic dipoles under influence of a strong external magnetic field. AFiging electromagnetic impulses, and the induced electromotive power is recorded and processed by a computer, on its basis the visual image is constructed.
The resonance tomograph consists of the following: superstrong magnet, radioconverter, reception radio-frequency coil, computer (COMPUTER) and consoles of management. Superconductivity of coils is assumed through the system of cooling inert gases (nitrogen, helium) up to the temperature of-269°С (4°К).
Force of a magnetic field is defined in Tecl or Gaus (1 Т = 10.000 gaus). In clinical diagnosis use a magnetic field of 0,1 to 1,5 T.magnatic resonance tomography (МРТ) more often exceeds on the opportunities of x-ray computer tomography. It is caused by that CT which is based upon the definition of only electron density, and МРI - on four separate components: proton density, two times weakening - Т1 and Т2 and rates of movement of a liquid.
The majority of tissues of a human body appreciably contain water which includes oxygen and Hydrogen. Kernels of Hydrogen have one proton which is a magnetic dipole with southern and northern poles. The proton rotates about the axis, framing the weak magnetic moment which has received the name of backs. Dipoles are randomly focused in space. If the person is placed in a constant magnetic field of MRI, protons of kernels of atoms of Hydrogen are like small magnets, are guided along the direction of power lines of a magnetic field. The axis of a proton describes a figure of a cone similarly to the top. This original rotation refers to a procession. The Most part of the protons with low power level, a basis of a cone (procession) is turned on the north, and a smaller part of protons with higher power level - into the opposite part, that is on the south. On this basis they are accordingly named parallel and antiparallel protons. Thus in an organism the total tissue magnetic moment - M which is referred in parallel to power lines of a magnetic field (see fig 10.22 - 1,2,3,4).


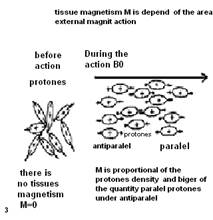
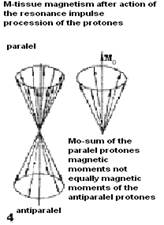
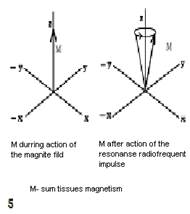
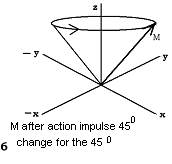

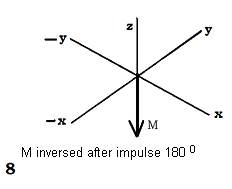
Fig.10.22 Chart Formation of the tissue magnetic moment (1,2,3,4) and its deviation under influence of external magnetic impulse (5,6,7,8).
It is necessary for exaltation resonance of protons of Hydrogen except for a strong magnetic field, to frame a weak variable field which frequency will correspond to the frequency of their processions. For this purpose from radio-frequency generator of MRI impulse submit on the coil which surrounds an investigated site of a body. Entering of corresponding radio-frequency impulse causes a resonance of protons. As a result of a resonance the magnetic moments of all parallel protons start to rotate clockwise. Thus the total axis of tissue magnetism-Mz deviates on the certain angle to the direction of power lines of a magnetic field. The degree of deviation depends upon the force and time of action of radio-frequency impulse, therefore last define angle of deviation Mz from a direction of power lines of a magnetic field. During a pause between repeated radio-frequency impulses protons, and accordingly axis - Mz, will start to come back to a starting position, with different rate, sending МR impulses of different force which are perceived by the coil with prompting electromotive power and induction of an electric current (see fig. 10.22. - 5,6,7,8).
For reconstruction of the image consecutive entering certain quantity of МR signals are necessary. By means of calculation of force of impulses the visual image of corresponding area of investigated object is under construction. Appearance МRT see fig.10.23. Magnetic-resonance tomogram of head and the spinal cord see fig. 10.24.
Fig.10.23 МRI. EXELART with Pianissimo, 1,5 T, Toshiba Corporation, Tokyo.
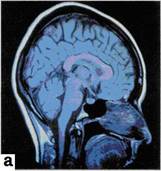
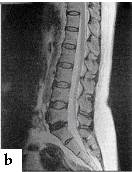
Fig. 10.24magneticaly-resonant tomograms:heads (Т1); lumbar spine (Т2).
In complex cases of diagnosis apply artificial contrasting which structure includes a paramagnetic ion from metal called gadoline. These contrast agents are entered intravenously. They collect in the centers of the inflammation and tumours. These substances owe magnetic properties which promotes change in the contrast..
Clinical action of a magnetic resonance on patients and the personnel who are engaged in the invstigation are minimal as clinical displays are absent, therefore contraindications to evaluation are limited only the presence of ferromagnetic object in an organism which in case of carrying out МRI are exposed to influence the magnetic forces with an induction of a current and thermal effect.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 184 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Auxiliary techniques of investigation | | | Physical bases of ultrasonic diagnostics and ultrasonic diagnostic devices |