
|
Читайте также: |
| 3.1 Using … law, one finds the magnetic fields. A) Ampere’s B) Maxwell’s C) Lorentz’s D) Faraday’s E) Hertz’s | 3.2 When a body moves in a circle with changing speed, the velocity vector A) changes in both magnitude and direction with time B) changes in magnitude only and constant in direction C) zero D) is constant in both magnitude and direction with time E) is constant in magnitude and changes in direction with time |
1. 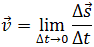 instantaneous speed is the ratio of the displacement body to the interval of time over which the movement occurred, if the time interval tends to zero. The instantaneous velocity, i.e. the velocity at a given time is a physical quantity equal to the limit, which seeks medium speed with an infinite reduction of the time interval Δt: this ratio is very small displacement to a very small period of time over which the movement occurred.
instantaneous speed is the ratio of the displacement body to the interval of time over which the movement occurred, if the time interval tends to zero. The instantaneous velocity, i.e. the velocity at a given time is a physical quantity equal to the limit, which seeks medium speed with an infinite reduction of the time interval Δt: this ratio is very small displacement to a very small period of time over which the movement occurred.
2. Inside the liquid at any point there is a pressure due to the weight of the upper layers of the liquid on the bottom. to determine the fluid pressure at any point, and also on the bottom and sides of the vessel:  the density of the fluid, the height of the liquid column, acceleration of gravity
the density of the fluid, the height of the liquid column, acceleration of gravity
Archimedes ' principle is formulated as follows[1]: on a body immersed in a fluid (or gas), the buoyancy force equal to the weight of the liquid (or gas) in the body. Force is called force of Archimedes: 
3. Snell's law (also Snella or Snell) describes the refraction of light at the boundary of two transparent media. The angle of incidence of light on the surface is associated with the angle of refraction ratio 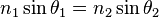
Here:
n_1 is the refractive index of the medium from which light is incident on the boundary;
\theta_1 - angle of incidence - the angle between the incident surface of the beam and the normal to the surface;
n_2 is the refractive index of the medium in which light enters, after passing the boundary of the section;
\theta_2 - angle of light refraction - the angle between passed through the surface of the beam and the normal to the surface.
Refraction (refraction) - changes the direction of propagation of waves (rays) electromagnetic radiation at the interface of two transparent media.
Reflection - the physical process of interaction of waves or particles to the surface, changing the direction of the wave front at the boundary of two media with different properties, in which the wave front returns into the medium from which it came.
4. In nature, substances are found in three States: solid, liquid and gaseous. For example, water can be solid (ice), liquid (water) and gaseous (water vapor) conditions. A solid has its own shape and volume. Unlike solids, liquids easily change their shape. They take the form of the vessel in which it is located. Liquid to easily change its shape, but keep the volume. Gases unlike liquids easily change its volume. Gases have no shape and constant volume. They take the form of a vessel provided and completely fill up the volume

5.
Е
Дата добавления: 2015-10-16; просмотров: 78 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Задание 3. (10 баллов) | | | Задание 3. (10 баллов) |