
|
Читайте также: |
| 3.1 The law of electric charges interacting was discovered by … A) Coulomb B) Gauss C) Ohm D) Kirchhoff E) Volta | 3.2 A unit that is used to measure an angle. A) Radian B) Uniform circular motion C) Nonuniform circular motion D) Range of a projectile E) Steradian |
1. The average velocity of a particle during some time interval is equal to the ratio of the displacement, ∆x, and the time interval, ∆t:
The speed of a particle is equal to the absolute value of the velocity. The average speed during the course of a motion is often computed using the following formula:
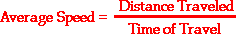
In contrast, the average velocity is often computed using this formula

2. In a closed mechanical system, the sum of the mechanical energy (potential and kinetic energy, including the energy of rotational motion) remains unchanged. Wп + Wк + Wвр = Wполн = const
Here:
WP - Potential energy of the body, the energy of position (Joule),
Wk is the Kinetic energy of the body, the kinetic energy (Joule),
Wвр - Energy of rotation of the body (Joule),
3. Lens called transparent body, restricted to the two curved (usually spherical) or curved and flat surfaces. Lenses are divided into convex and concave. Lenses whose middle thicker than the edges, are called convex. Lenses whose middle is thinner than the edges, are called concave. If the refractive index of the lens is greater than the refractive index of the environment, in the convex lens parallel beam of rays after refraction is converted into a convergent beam. Such lenses are called converging. If the lens is a parallel beam is converted into a divergent beam, these lenses are called scattering. Concave lens, in which the external environment is the air, are scattering.
4. The electric circuit is a collection of devices, elements, intended for the flow of electric current, electromagnetic processes which can be described by using the concepts of current and voltage.
Serial and parallel connections in electrical engineering - two basic ways of combining the elements of an electric circuit. A series connection of conductors current in all conductors of the same. Total voltage in the circuit in series connection, or the voltage at the poles of the current source, is equal to the sum of the voltages of different sections of the circuit: U\mathrm = U_1 + U_2 When connected in parallel the voltage drop between two nodes, integrating elements of the circuit, the same for all elements. The current in the unbranched part of the circuit is equal to the sum of the forces of currents in separate parallel connected conductors: I\mathrm = I_1 + I_2
The voltage at the circuit sections AB and at the ends of all parallel connected conductors is the same: U\mathrm = U_1 = U_2
5. Кулон
6. радиан
Дата добавления: 2015-10-16; просмотров: 61 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Задание 3. (10 баллов) | | | Задание 3. (10 баллов) |