
|
Читайте также: |
| 3.1 The elastic properties of a body are described by … law A) Hooke’s B) Pascal’s C) Kepler’s D) Cavendish’s E) Newton’s | 3.2 A quantity that needs both a magnitude and direction to completely describe it is … A) Vector B) Scalar C) Resultant D) Scalar Product E) Vector Product |
1. The body may be at rest relative to one body and at the same time in a state of motion relative to another body. For example, the person sitting in the seat of an airplane, is at rest with respect to the aircraft, but at the same time - in a state of motion relative to the earth. And "blame" in this case, different reference frames! This is the relativity of motion. The relativity of motion is manifested in the fact that the speed, trajectory, path and some other characteristics of the relative movement, i.e. they can be different in different reference frames.
2. Sound is a mechanical elastic waves propagating in gases, liquids, solids. Waves that cause the sensation of sound, with a frequency of 16 Hz to 20 000 Hz are called
sound waves (mainly longitudinal). Sound is a mechanical elastic waves propagating in gases, liquids, solids. Waves that cause the sensation of sound, with a frequency of 16 Hz to 20 000 Hz are called
sound waves (mainly longitudinal).A normal person can hear sound vibrations in the frequency range from 16-20 Hz to 15 to 20 kHz[2]. The sound below the range of human hearing are called infrasound; above: up to 1 GHz, - ultrasound, 1 GHz - acoustic. The volume is a complicated function of the effective sound pressure, frequency and mode shapes, and the pitch - not only on frequency but also on the size of the sound pressure.
3. An ideal gas is a model of rarefied gas, which neglects the interaction between the molecules. The forces of interaction between molecules is quite complicated. At very small distances, when the molecules fly up close to each other, between them there is a large magnitude of repulsive forces. Properties of an ideal gas described by the equation of Clapeyron - Mendeleev: 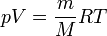 where R is the universal gas constant,m is the mass, M - molar mass,
where R is the universal gas constant,m is the mass, M - molar mass,
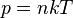 , where,n is the concentration of particles,k is Boltzmann constant.
, where,n is the concentration of particles,k is Boltzmann constant.
For any fairly ideal gas the ratio Mayer: 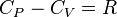 ,
,
where,R is the universal gas constant,C_P is the molar heat capacity at constant pressure,C_V is the molar heat capacity at constant volume.
Natural cooling is called cooled by heat exchange between body and environment - the ambient air and natural water reservoirs. However, when such a cooling temperature of the cooled body can be lowered only to the ambient temperature. Cooling using refrigeration machines is called computer cooling.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-16; просмотров: 79 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Задание 3. (10 баллов) | | | Задание 3. (10 баллов) |