
Читайте также:
|
6.1. Characteristics of the dynamics intensity
Time series is a sequence of values of statistic indicators that characterize the time variation of social and economic phenomena or processes.
A specific value of a dynamic series - series level (Yt).
The typ e of time series: moment, interval
Time (or dynamic) series study involves the following research:
- tendency of development or trend,
- seasonal variations
- random variations
Methodological basis for evaluating the dynamics intensity is the comparison of series levels.
Basis and chain indicators are the generalizing characteristics of time series intensity.
The chain interconnection of a time series level takes place when each of the following levels is compared to the previous one.
The basis interconnection of a time series level takes place when each of the following levels is compared to a definite level, which is referred to as a base for comparison.
Time (dynamic) series indicators.
1. Average series level(¯Y):
- for a moment time series:
* with equal intervals of time between dates:(
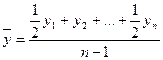 ;
;
*with unequal intervals between dates:
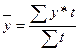 ;
;
where y is a series level, t is a time interval between dates
- for the interval time series:
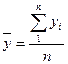 , where n is a number of time series levels.
, where n is a number of time series levels.
2. Absolute increase or decrease (Δy):
* for the chain interconnection (ch.): ∆  ;
;
*for the basis interconnection(b.):  ∆
∆ 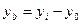 ;
;
3. Growth rate (or decrease rate):
· for the chain interconnection (ch.): 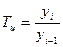
Yi – is the current time series level
Yi-1 –is the previous time series level
· for the basis interconnection (b.): 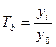
Y0 – is the basis time series level
4. The increase rate has the same formula both for a chain interconnection and a basic interconnection (ΔT).
ΔT = T(ch. or b.) – 1 (100).
5. Absolute value of 1% increase rate has the following formula: A = 0,001* Yi-1
The average absolute and relative dynamics rate:
* average absolute increase (decrease) indicator:
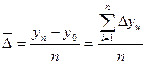 ;
;
where Δy ch. ¯ - the chain absolute increases,
n – the number of chain absolute increases
• the average annual growth rate (decrease rate):
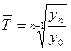
This formula is used when:
- there are only the initial and final values of the time series levels available,
- within a dynamic series there is a time gap between the time series levels.
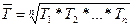
where Ti- is the chain growth rates,
n – the number of chain growth rates.
• the average annual increase rate:
ΔT¯ = T¯(ch. or b.) – 1 (100).
Estimation of changes in the dynamics rate s:
- Absolute acceleration (deceleration)
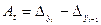 ;
;
If At >0 we have its acceleration, if At <0 we have its deceleration.
- The relative acceleration (deceleration)
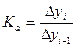
If Kt >0 we have its acceleration, if Kt <0 we have its deceleration.
Comparative analysis of the dynamics of interrelated indicators x and y reflect the empirical coefficient of elasticity 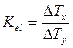
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 107 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Meaning in Morphemes | | | I. Специальные события |