
Читайте также:
|
Water consumptionis the water objects use for population and subjects of economic activity necessities satisfaction.
In accordance with State Standard 17.1.1.03-86. water consumption is classified for such signs:
§ on the aims of water consumption −, public supply water use, industrial, agricultural, for energy necessities, for fish economy, for a water-carriage and timber-rafting, for medical and resort necessities and others;
§ and on water use subjects − superficial, underground, internal and territorial marine waters;
§ and on the method of consumption − with the water exception and its returning, with water exception without returning, without water exception;
§ and on the waterconsumption technical conditions − with application of technical buildings, without application of buildings.
Depending on the water consumption purposes water-supply sources are divided into two categories.
To the I category belong water objects, utilized as centralized or uncentralized household water-supply sources, and also for the water-supply of food-processing industry enterprises.
To the II category belong water objects for cultural and welfare purposes and which are located within the settlements limits.
Requirements according to water composition and properties are regulated depending on the water objects category.
There iswater use, which can be irretrievable, repeated, circulating in the presence of w ater consumption. With the purpose of the water rational use the water consumption norms are inculcated on one inhabitant and on conditional product unit, which is characteristic for enterprises of each branch of industry. In limited water resources districts the waterworks balance, which foresees water use comparison with the potential resources of water pools, should be adhered.
Table 3.1 – Qualitative indexes of water objects I and II pollutions
| Pollution level | Organoleptic mode | Toxico-logical mode | Sanitary mode | Bacterio-logical mode | Pollution index | |||
| Smell, flavor, marks | 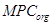 , excess degree , excess degree
| 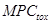 , excess degree , excess degree
| 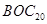
| Dissolved oxygen, 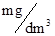
| Quantity of lactose- positive colibacillus in 1 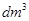
| |||
| I | II | |||||||
| Admissible | less than 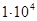
| |||||||
| Moderate | 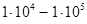
| |||||||
| High | 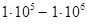
| |||||||
| Extraordi-narily high | >4 | >8 | >10 | >8 | >10 | more than 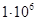
|
Note: 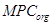 − maximum possible substances concentrations, established according to harmfulness organoleptic sign;
− maximum possible substances concentrations, established according to harmfulness organoleptic sign; 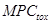 − maximum possible substances concentrations, established according to harmfulness toxicological sign;
− maximum possible substances concentrations, established according to harmfulness toxicological sign; 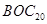 − biological oxygen consumption for 20 days for water use reservoirs I and II categories.
− biological oxygen consumption for 20 days for water use reservoirs I and II categories.
On character of water use the water-supply systems are divided into straight current, successive, circulating, ijected.
Straight current water is utilized once during the production process, whereupon threw off in reservoirs or sewage system.
Consistently used water is consumed in a few technological processes.
Circulating water is used repeatedly in production, with its periodic or continuous clearing. On the well equipped enterprises an index of circulating and successive water-supply degree is 30...90 %. Thus it should be taken into account that buildings of water circulating systems is tenfold cheaper, than corresponding power purifying buildings.
Areas of sanitary guard, in which the special mode of waters guard is set from chemical matters, harmful biological organisms and sewage pollution, settle down round water supply point or another water-supply resource. The area of sanitary guard is divided into two or three subareas.
First subarea − high security subarea, sometimes with the special guard. This area is planted around the forest planting, here are forbidden to build, to pasture cattle, any type of activities, which can entail water pollution.
Second subarea has limitation on the types of activities, which cause pollution and capable to penetrate to water supply point; here are forbidden to dispose storehouses of fuels and lubricants (FL), stock-raising farms, apply fertilizers.
Third subarea is preventive. The types of activities, which draw water pollution, are also limited here.
General water use of enterprise is determined after a formula:
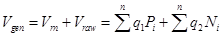 ,
,
where 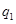 ,
, 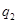 − specific norms of water use on economic and production necessities;
− specific norms of water use on economic and production necessities;
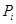 − amount of shift workers;
− amount of shift workers;
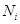 − amount of production users;
− amount of production users;
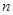 − amount of workers groups and equipment.
− amount of workers groups and equipment.
Level of water resources use in industry, and also technical equipment of buildings and in applied sewage clearing technologies is characterized by such coefficients:
1) use of circulating water in general volume of water use
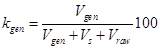 ,
,
where 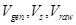 − water volume, used accordingly in a turn, which perches from a source, and arrived with raw material;
− water volume, used accordingly in a turn, which perches from a source, and arrived with raw material;
2) irretrievable consumption and fresh water losses
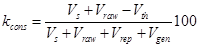 ,
,
where 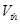 ,
, 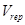 − water volume, which accordingly thow off to the reservoir, and utillized repeatedly;
− water volume, which accordingly thow off to the reservoir, and utillized repeatedly;
3) water use which perches from the water-supply source
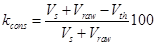 ,
,
overflow-pipe
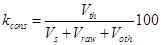 ,
,
where  − water volume which arrives from other users;
− water volume which arrives from other users;
5) normative loading of pollution reservoir by sewages
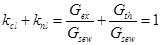 ,
,
where 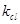 − clearing coefficient;
− clearing coefficient;
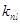 − coefficient of the normal loading of pollution reservoir by sewages;
− coefficient of the normal loading of pollution reservoir by sewages;
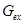 − mass of pollutions, which are subject to extraction from sewages,
− mass of pollutions, which are subject to extraction from sewages,
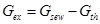 ;
;
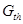 − mass of pollutions, which is admitted to throw off in reservoirs (GDS);
− mass of pollutions, which is admitted to throw off in reservoirs (GDS);
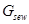 − mass of contaminating matters in sewages.
− mass of contaminating matters in sewages.
Water-supply is carried out from conduits which are divided into drinkable and technical. From city water conduit water can be utilized for economic-drinkable necessities and fires extinguishing. Assumed to satisfy up to 15 % water production requirements from city water conduit, other requirements should be covered by technical conduits.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 130 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Rational use and guard of water resources | | | Sources of water pollution |