
Читайте также:
|
9. Are the following statements about the text true or false?
10. Match the first part of the sentence (1 –6) with the second part (a-f).
| 1. Mass is an inherent property of all matter. |
| 2. The mass of this lump is certainly much greater than the ashes. |
| 3. The energy makes its appearance in a number of forms. |
| 4. Experiments carried out over a long period of time. |
| 5. The energy can be freely transformed from one variety to another. |
| 6. These are the same as the results obtained when d= 0. |
| athan the ashes. |
| b a long period of time. |
| cone variety to another. |
| dof all matter. |
| e obtained when d= 0. |
| f in a number of forms. |
Complete the sentences with words from the box.
| conservation - study – approach - amount - system - experience |
1. The quantity of heat is the actual amount of kinetic energy.
2. Thermodynamics is a study of processes in which energy is transformed as heat.
3. There are several kinds of system.
4. The first law of the thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy.
5. All the experience accumulated in the study of every change in matter.
6. I like her approach to the problem.
UNIT FOUR
Grammar:
1. Modal verbs (Obligation and permission). Модальні дієслова.
2. Question Types. Subject questions. Tag questions (Типи питальних речень).
Reading tasks:
Read the words, pay attention to the different types of syllables.
| Літера | Відкритий склад | Закритий склад | голосна + r | голосна + re | Пояснення |
| O o | [∂u] note [n∂ut] нота | [פ] not [nפt] ні | [פ:] nor [פ:] також...ні (прийм.) | [פ:] more [mפ:] більше | Дві oo передають звуки - [u:] –school школа [u] - book – книга |
| Приголосні літери | Звуки, які вони утворюють в залежності від поєднання з іншими літерами | Приклади |
| W w | [v] – в – майже завжди [не читається] – або звук близький до у, але це приголосний звук. Іноді він може нагадувати звук [в] | wind - вітер window -вікно |
Read the words from the text, make stress on the right syllable.
| flowing | zero |
| combine | junction |
| too | station |
| before | downhill |
| conservation | loop |
TEXT
KIRCHHOFF’S RULES
In the last few examples we have been able to find the currents flowing circuits by combining resistances in series and parallel, and using Ohm's law. This technique can be used for many circuits. Sometimes a circuit is too complicated for this analysis. For example, we cannot find the currents flowing in each part of the circuits simply by combining resistances as we did before. For such complicated circuits we use Kirchhoff’s rules, invented by G. R.Kirchhoff in the mid-nineteenth century. There are two of them. They are simply convenient applications of the laws of conservation of charge and energy. Kirchhoff 's first or junction rule is based on the conservation of charge, and we already used it in deriving the rule for parallel resistors. Kirchhoff’s Law 1 states that the algebraic sum of all the currents meeting at a point is zero. This is also known as Kirchhoff’s current law. It states that: at any junction point, the sum of all currents entering the junction must be equal to the sum of all currents leaving the junction.
Kirchhoff’s second or loop rule is based on the conservation of energy. It states that: the sum of the changes in potential around any closed path of a circuit must be zero.
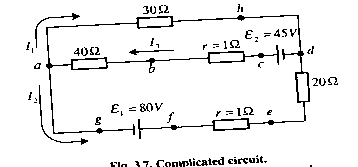
|
To see why this should hold, consider the analogy of a roller coaster on its track. When it starts from the station, it has a particular potential energy. As it climbs the first hill, its potential energy increases and reaches a peak at the top. As it descends the other side, its potential energy decreases and reaches a local minimum at the bottom of the hill. As the roller coaster continues on its path, its potential energy goes through more changes. But when it arrives back at the starting point, it has exactly as much potential energy as it had when it started at this point. Another way of saying this is that there was as much uphill as there was downhill.
Kirchhoff’s junction rule states that: around any closed loop in a circuit, the sum of the potential differences across all elements is zero.
Note that in a network, the two possible directions are existing: clockwise and counterclockwise. If clockwise is considered positive then anticlockwise becomes automatically negative.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 202 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| ЗАКОН СОХРАНЕНИЯ массы и энергии | | | Put the verbs into correct form and translate the sentences into Ukrainian. |