
Читайте также:
|
 A A
|  B B
| ||
 C C
|  D D
| ||
 F F 
|  G G
| ||
  H I
H I
|
Using these pictures remember some facts about reflection seismology.
Answer the following questions.
1. What do geophysicists interpret the seismic data for?
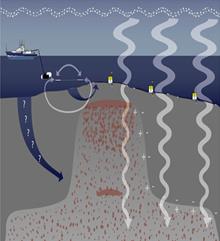
2. What are three environments for seismic exploration?
3. What is the general principle of getting seismic data?
4. Which exploration tool is typical for sub-sea survey?
5. What non-geophysical issues may influence the choice of exploration technology?
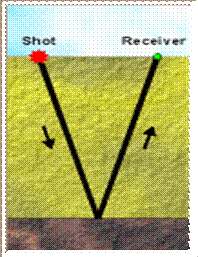
6. What is the reflection seismic method?
7. What does that mean “reflection seismology is similar to sonar and echolocation”?
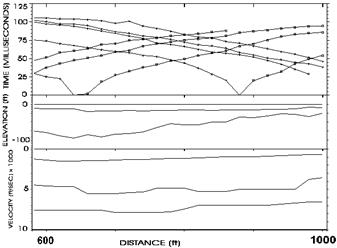
8. How are depths of geological structures determined?
9. In what case is a “spread correction” applied?
10. What is impedance?
Describe the method of geophysical exploration shown in the diagram.
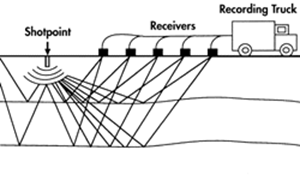
Reflection Seismology
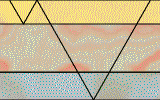
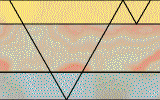
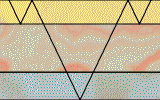
Read the following definitions and say in a brief form what the difference is between reflections and refractions.
Reflection – when an incident compressional wave strikes a boundary between two media having different velocities of wave propagation, part of the energy is reflected from the boundary. Possible ways of multiple reflections are endless.
| 
| 
|
| 
| 
|
Refraction - the portion of the incident energy that is not reflected and is transmitted through the boundary and into the second layer. The transmitted ray travels through the second layer with changed direction of propagation
Render the information from the text into English.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 99 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Reflection Seismology | | | Метод преломленных волн |