
|
Читайте также: |
| CELL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
| Erythrocytes | 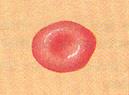
| Biconcave disk; no nucleus; 7-8 µm in diameter | Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide |
| Leukocyte Neutrophil | 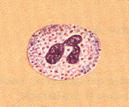
| Spherical cell; nucleus with two to four lobes connected by thin filaments; cytoplasmic granules stain a light pink or reddish-purple; 12-15 µm in diameter | Phagocytizes microorganisms |
| Basophil | 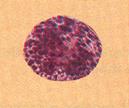
| Spherical cell; nucleus with two indistinct lobes; cytoplasmic granules stain blue-purple; 10-12 µm in diameter | Releases histamine, which promotes inflammation, and heparin, which prevents clot formation |
| Eosinophil | 
| Spherical cell; nucleus often with two lobes; cytoplasmic granules stain orange-red or bright red; 10-12 µm in diameter | Releases chemicals that reduce inflammation; attacks certain worm parasites |
| Lymphocyte | 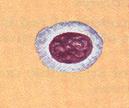
| Spherical cell with round nucleus; cytoplasm forms a thin ring around the nucleus; 6-8 µm in diameter | Produces antibodies and other chemicals responsible for destroying microorganisms; responsible for allergic reactions, graft rejection, tumor control, and regulation of the immune system |
| Monocyte | 
| Spherical cell; nucleus round, kidney, or horse-shoe shaped; contains more cytoplasm than does lymphocyte; 10-15 µm in diameter | Phagocytic cell in the blood; leaves the blood and becomes a macrophage, which phagocytizes bacteria, dead cells, cell fragments, and debris within tissues |
| Platelet | 
| Cell fragments surrounded by a cell membrane and containing granules; 2-5 µm in diameter | Forms platelet plugs; releases chemicals necessary for blood clotting |
Ex. 18. Choose the proper terms from the box for the definitions:
1. Liquid portion of blood containing water, proteins, salts, nutrients, hormones, vitamins. 2. Tiny cells, which are necessary for blood clotting. 3. These cells are biconcave disks made in the bone marrow, they transport oxygen. 4. Plasma minus the clotting proteins and clotting cells. 5. “Little body” refers to blood cells. 6. This substance is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin, is absorbed from small intestines; insufficiency of this substance may result in anemia.
| thrombocytes, serum, corpuscles, erythrocytes, lymphocytes, plasma, iron, protein. |
Ex. 19. Translate the following sentences without using a dictionary:
1. Red blood cells are tiny, biconcave disks that are thin near their centers and thicker around their rims. 2. This special shape is related to the red cell’s function of transporting gases. 3. Each red blood cell is about one-third hemoglobin by volume, and this substance is responsible for the color of the blood. 4. The number of red blood cells varies from time to time even in healthy individuals, the normal range for adult males is 4.2 to 5.8 million cells per mm3, and that for adult females is 3.6 to 5.2 million cells per mm3. 5. The number of red blood cells generally increases following exercises, a large meal, a rise in temperature, or an increase in altitude (висота над рівнем моря). 6. After an infant is born, the red blood cells are produced almost exclusively by the tissue that lines the spaces within the red bone marrow. 7. White blood cells function primarily to control various disease conditions. 8. Normally, five types of white cells can be found in the circulating blood. 9. They are distinguished by their size, the nature of their cytoplasm, the shape of their nucleus, and their staining characteristics. 10. The procedure used to count white blood cells is similar to that used for counting red cells. Normally, there are from 5.000 to 10.000 white cells per mm3 of human blood. 11. Since the total number of white blood cells may change in response to abnormal conditions, white blood cells count is of clinical interest.
Ex. 20. Try to choose which of the following sentences are incorrect (true or false choice):
1. Blood can be separated into solid and liquid portions. 2. The solid cellular portion is mostly white blood cells. 3. Red blood cells function to control disease conditions. 4. The plasma proteins are classified into three major groups: albumins, globulins, and fibrinogens. 5. Total blood volume does not vary by the sex (male or female).
Дата добавления: 2015-07-11; просмотров: 86 | Нарушение авторских прав