
|
Читайте также: |
Analysis of the causes and characteristics of inflation in Kazakhstan allows an appropriate deflationary policy and implementation mechanism, i.e. methods, ways, methods of combating inflation, comprehensively and meaningfully proceed on the pockets of its occurrence.
Overcoming inflation conditions:
1) the higher the inflation rate, the more difficult it is to fight it;
2) all the way inflation is uncivil, that is painful for the vast majority of the population;
Scheme 2. Kazakhstan Inflation Rate
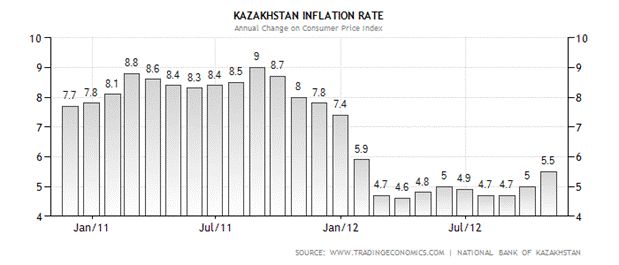
There are two options for state action on inflation:
1. Conducting adaptation policies or adapt to inflation when applied for indexation of income, wages, interest rates, investment; companies are implementing short-term projects, individuals are looking for additional sources of income, etc.;
2. Conducting complexes of anti-inflationary measures to reduce or suppress inflation.
Complex of measures to overcome inflation include effects on different sides of the productive and economic, social and legal, institutional, spiritual realms of society, although decisive is the base model, production and economic.
Overcoming inflation at a relatively ordinary demand macro-economic methods of using monetary and fiscal policy. [5; p 96]
Anti-inflation policy includes various techniques for controlling the money supply:
1. The decline in money supply through cash advance emission reductions by the Central Bank.
2. The increase in interest rates (refinancing) for centralized loans to all credit resources cost and reduce availability.
3. The increase in reserve requirements the Central Bank to commercial banks to meet the credit multiplier and compression limiting credit expansion of commercial banks.
4. The direct reduction credits from the Central Bank.
Transition to inflation targeting implies strengthening the regulatory role of the official rates of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Intensify efforts to increase regulation of liquidity open market operations, in particular, promoting the development of the secondary market of securities.
Anti-inflationary fiscal policy by raising taxes, cutting public spending and, on the basis of this, reducing the deficits.
Inflation tax policy aims to address two related but contradictory tasks: first, to increase the level of State budget incomes to achieve its balancing and eliminate the deficit; Second, to revive the economic activity of primary links of the economy – in the sphere of production and Exchange.
Anti-inflation policy of tax is the reduction of indirect taxation. Indirect taxes have inflation because the increase rates, reduces demand. The second aspect of high taxes is their pressure on production, limiting supply. Thirdly, a significant tax burden normally associated with the action of multiple taxes, complicating the tax system, leading to tax evasion.
So, when inflation is preferable to simple and reliable tax system, not weighed down by the terms of providing concessions, with an emphasis on taxing consumption. These requirements would best correspond to the income tax and property tax with a high degree of differentiation depending on the value of the property.
Cuts in public expenditure involves the dissemination of this process as the budgetary sphere and in the sphere of material production to public economic entities. Here it should be borne in mind that in the latter case, the anti-inflationary measures relate to the second component of inflation – inflation costs, or producers, so their influence will be considered separately. In this regard, there is a relationship causes two kinds of inflation and integrated ways to deal.
The budgetary cost of the national and local levels the focus is their maximum reduction on all possible articles. Of course, should be provided with vital social needs to protect pensioners, students, workers. [6; p 87]
Budget expenditure limit is reached:
a) Direct methods – persecution, i.e. by their forced reduction against the level reached by legislative acts or orders of the authorized State bodies;
b) sequestration is proportional reduction method of all expenditures under the given total size reduction as determined by different factors;
c)the control level of disposable incomes);
d) limit the level of State budget deficit
In any case, spending cuts affecting many national development programmers, giving up all sorts of prestigious projects, activities, does not give immediate feedback, etc.
The more difficult problem to overcome is the second type of inflation-inflation caused by rising production costs (inflation), resulting from:
1. Wage increases;
2. The fall in productivity in response to violations of the economic mechanism for reasons of institutional mechanism for reasons of institutional nature;
3. The inflationary expectations of owners of raw material and energy resources, whereby they raise the prices of original products. [7; p 98]
Scheme 3. Consumer and food price inflation rate in Kazakhstan
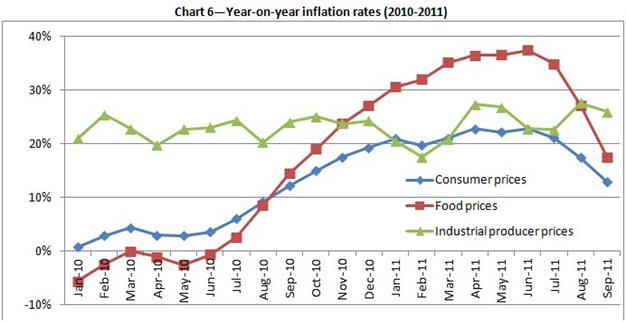
Source: http://www.google.kz/imgres?q=inflation+in+kazakhstan//
Firstly, enhancement of motivational incentives, productivity, interest in his effective results, rehabilitation of production work as a priority. This is achieved through the development of the private production sector, where the link between labour effort and results direct.
Production should be prioritized in relation to trade and mediation. Promote the development of the production achieved a preferential tax system, free access to credit and reduced interest rates on loans, establishing development-friendly economic standards, contributions to the funds, etc, necessary cases directly supported by financing investment priority activities of the productive sector.
Essential element in the system of measures to combat inflation is the creation of the mechanism of market competition and the economic responsibility of businesses of all types of ownership, these mechanisms limited to pattern: "reducing costs – falling prices – save masses of net income due to the increase of production – increase supply – satisfy demand»
Establishment of a mechanism of competition involves antitrust activities, the development of different forms of ownership, legislative ensuring their equality in the economic-financial activity. [8; p 67]
The most radical way to impact on inflation is controlling prices and wages is determined by short-term policy and programs varies widely, depending on the level of inflation, the rate of production, social protection needs. It is essential to regulate prices in a base technology redistribution – the production of raw materials, fuels and other raw products is their cost base of the pyramid is laid in the prices of products subsequent technological conversion products.
Wages regulation is of baseline in tough according to the real increase in productivity because the growth rates of nominal wages, equal rates of productivity growth.
The balance of payments, reflecting the activities of foreign-economic activity, inflation is to improve its structure. This primarily refers to the balance of payments on current account related to the movement of goods and services, export-import operations. The current account deficit reduction should be achieved as a whole by switching domestic demand with imported goods and services to the domestic, also by improving the elasticity of export production towards external demand. This is achieved through a policy of exchange rate at a realistic level, rational combination of trade and foreign exchange restrictions during times of inflationary Spike and liberalization of foreign economic relations by reducing the rate of inflation.
Theoretically it is possible to overcome inflation by ending the credit issue, but in our environment only at the cost of production; emission reductions, leading to the decline of production when reaching critical values in vital sectors of the economy or under the pressure of certain social groups has forced the Government to reopen the issue, and then another price increase. This process is repeated successively: the absence of market competition at the micro level and weak market environment leads to an inflation of the waves. When you save a similar economic policies in calculating only to switch on the automatic market-based mechanisms, the situation is infinitely long and leads to the destruction of the country's economic potential. [9; p 102]
To overcome the inflation of production costs, the need to overcome the recession. This requires strengthening of motivational incentives of productive labour, interest in his effective results, rehabilitation of production work as a priority. This is achieved through the development of the private production sector, where the link between labour and the result of the direct effort. The State encourages the sector by ensuring a favorable legal and economic treatment of its operation. In the public sector productivity is assured promotion by improving tariff wage system and a variety of achievement needed indicators and benchmarks of production efficiency.
The bankruptcy mechanism requires consistent institutional, economic and financial measures to transform loss-making industries, which include filling volume and range of products, find a job or retraining workers, reconstruction companies, financing of the activities.
The most radical way to impact on inflation is controlling prices and wages in the state regulation of the economy.
Selection of price and wage control is defined in the programmers of short-term policies and varies widely depending on the inflation rate, rate of production, social protection needs.
Simultaneous limitation is fundamental both factors – wages and prices. Separate restriction cannot succeed for the following reasons.
Regulation only when prices lifting of restrictions on pay, as well as the lag in growth, gives rise to a variety of deficits and, as experience shows, to the subdued inflation.
Regulation (or pre-emption regulation), only wages to reduce demand as well as the impact on reducing inflation manufacturers (sellers) can radically improve the situation.
First, organizations from the price factor cannot be implemented in the reproduction process when the flow is suppressed, the main factor of his labour, with capitalization of the funds due to the weakened (even lack of) labor activity incentives.
Secondly, the development of illegal ways to receive income, into use officially registered for possible implementation of nominal price of the product on the market; in their efforts to conduct national cash limits for Exchange will be held in foreign currency to increase barter operations; tighten control of illegal income sources will result in additional costs to the relevant State bodies.
Third, the difficulty with the implementation of output at the designated market prices within the country would entail an additional export it abroad, that in the context of domestic under-consumption, undesirable; because of the mediocre quality of domestic products and saturation of foreign markets for these products is available at prices lower than world prices, resulting in losses of the national economy.
The previously mentioned events can worsen the crisis, lead to further destabilization the economy of the Republic.
It seems more appropriate to a joint coherent regulation of prices and wages. The price regulation may take the form of restrictions of profitability. Primarily, this refers to the Basic, original products: oil, coal, gas, electricity and heat, grain, cotton, other primary agricultural products. It is their cost base of the pyramid is laid in the prices of products of subsequent technological conversion products.
Production of the monopolists must strictly be limited to prices and any increase is subject to scrutiny by the public authorities. Regulation of wages from the source in a rigid level according to the real increase in productivity because the growth rates of nominal wages, equal rates of productivity growth are not inflationary in nature.
In General, the regulation of prices and wages must be effected through careful study and harmonization of measures to changes in levels of wage rates and prices for joint discussions of trade unions, representatives of the administration of enterprises. The compromise agreement on levels of pay and prices shall be supported for a short period. In these circumstances, inflation will be manageable and gradual decline in its rate possible.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 417 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Causes and types of inflation. | | | The finance and inflation: interrelation and interaction. |