
Читайте также:
|
increase the rate of return on capital because capital becomes more productive
increase the marginal product of capital
reduce the capital-output ratio
A central bank purchases $1 million of government securities in a given week. If other things remain the same, total bank reserves will not increase if which of the following increases by $1 million?
(A) Gold in the hands of the central bank
(B) Borrowing by private banks
(C) Central-bank float
(D) Excess reserves
(E) Currency in the hands of the nonbank public
Assume the simple three-equation macroeconomic model given by
Ct = a0 + a1 Yt-1
It = b1(Yt - Yt-1)
Yt = Ct + It + Gt
where Ct is current consumption
It is current investment
Gt is current government spending
And Yt is current income
The best measure of the short-run effect on Yt of a change ΔG is
(A)  (B)
(B)  (C)
(C) 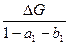 (D)
(D) 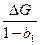 (E)
(E) 
Which of the following is not an automatic fiscal stabiliser?
(A) Corporation taxes
(B) Value added tax
(C) State retirement pension
(D) Unemployment benefit
(E) Food stamps
(повтор c 46) Other things being equal, what will cause a reduction in the stock of money?
(A) A balance of payments surplus
(B) An increase in the public’s demand for bank advances
(C) An increase in the public’s desired ratio of cash to bank deposits
(D) An increase in the public sector borrowing requirement
(E) All of the above
In the diagram, AD1 and AS1 are an economy’s initial aggregate demand and supply curves.

What will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to AD2?
(A) An appreciation of the national currency
(B) A decrease in taxes
(C) A decrease in interest rates
(D) A decrease in the price level
(E) None of the above
Which of the following best explains the classical economists’ conclusion that sustained involuntary unemployment in an economy cannot persist?
Full employment is guaranteed by government.
People will always want to work if there is no welfare system.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 187 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| The gradual exhaustion of natural resources | | | Prices, including wages, adjust quickly to bring about full employment. |