
|
Читайте также: |
2) Cubital canal syndrome - compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. There is a bump of bone on the inner portion of the elbow (medial epicondyle) under which the ulnar nerve passes:
- numbness, tingling, and pain in the elbow, forearm, ulnar portion of the hund, V and IV fingers, hypothenar hypesthesia (Fig. 17).
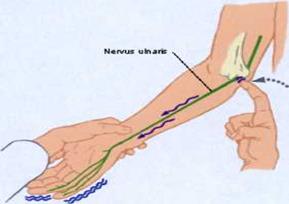
Fig. 17. Pain and paresthesia area at the ulnar nerve irritation in cubital canal.
3) Tarsal tunnel syndrome (compression of the tibial nerve in the tarsal tunnel. This tunnel is found along the inner leg behind the medial malleolus) (Fig. 18):
- numbness in the foot, radiating to the big toe and the first 3 toes,
- pain, burning, electrical sensations and tingling over the base of the foot and the heel.

Fig. 18. Pathological area at tarsal tunnel syndrome.
4) Entrapment of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (Bernhardt‐Roth syndrome, meralgia paresthetica, derived from the Greek word meros, meaning thigh, and algo, meaning pain) - entrapment or compression where it passes between the upper front hip bone (ilium) and the inguinal ligament (Fig. 19):
- paresthesia or burning pain, numbness in the lateral and anterolateral thigh
- symptoms worsen during walking and standing.

Fig. 19. Pathological area at tarsal tunnel syndrome.
9. General principles of the peripheral nervous system pathology treatment: vitamins, drugs to improve microcirculation, biostimulants, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, analgesics, massage, exercise, local anesthetic blockade, physiotherapy, surgery (at motor and sensory disorders).
Tunnel syndromes treatment: local corticosteroid application in place of compression - dexamethasone, diprospan, flosteron (Fig. 20, 21, 22), electrophoresis of novocaine, mechanical decompression.

Fig. 20. Blockade in the carpal tunnel.
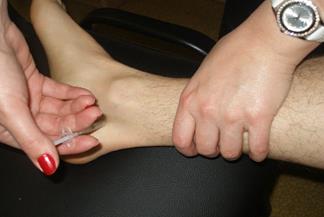
Fig. 21. Blockade in the tarsal tunnel.

Fig. 22. Blockade in the cubital tunnel.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 133 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Fig. 4. Herpetic eruptions. | | | Сохранение результатов вычислений в массиве |