
Herpetic ganglioneuropathy lasts about 3-6 weeks and in most cases ends by recovery. Some patients develop postherpetic neuralgia in which the localized pain of shingles remains even after the rash is gone. Postherpetic neuralgia develops in 16-25 % of cases, often in people over 50 years of age, and can last for a long period of time (years).
Post-herpetic neuralgia is similar to the classic neuralgia but has some differences:
- pain occurs spontaneously, lasts for hours, occasionally enhanced, especially at night;
- no trigger zones and factors;
- pain is localized mainly in the area of innervation of the I branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Besides injury of the trigeminal nerve herpetic lesion of spinal sensitive ganglions can be observed, signs and treatment does not differ from that described above, vesicular rash on the extremities have the form of longitudinal stripes, on the body - a broad band on one side of the body (Fig. 5).
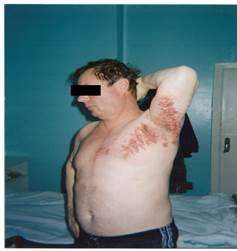
Fig. 5. Herpetic lesion of Th1-4 spinal sensitive ganglions.
In cases of recurrent herpetic ganglioneuropathy (more than 1 time in 3 months) HIV and oncology should be excluded.
Herpetic ganglioneuropathy treatment.
1. Antiviral medications (acyclovir (Zovirax), 5-10 mg / kg i/v or 800 mg oral 5 times daily for 5-7 days, valacyclovir (Valtrex), 1000 mg 3 times daily for 7 days).
2. Human Immunoglobulin (Bioven mono, Octagam – 50,0 i/v), desensitizing agents.
3. Acyclovir ointment on the affected skin.
4. Topical creams (Lidocaine cream) can relieve the itching. Do not scratch the skin where the rash is located. This may increase the risk of secondary bacterial infection and scarring.
5. Vitamins B.
Postherpetic neuralgia treatment.
1. Antiepileptic drugs: gabapeptin 300-2400 mg daily for 3 times, pregabalin (Lyrica) 75-600 mg, daily in 3 times.
2. Tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline 25 mg 3 times daily.
3. Local compresses (dimexidum, novocaine, lidocaine).
4. Laser therapy.
5. Ineffectiveconservative treatment - hormone or radiotherapy.
Plexopathy.
The defeat of the brachial plexus. Etiology: collarbone fracture, dislocated shoulder, compression between the clavicle and I rib or shoulder head, compression by cervical ribs, callus after fracture of the clavicle, scalene muscle contracture.
Clinic.
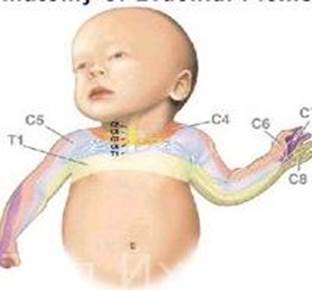
Upper brachial Erb-Duchenne plexopathy (damage to the upper primary trunk of the brachial plexus of the C5-C6 segment, Fig. 6) - loss of function of the proximal part of the limb - flaccid paresis of proximal muscles of hand (biceps, triceps, brachioradialis muscle), disorders of sensation at a polyneural type and pain in external surface of proximal arm part.
Lower brachial Dejerine-Klumpke plexopathy (damage to the lower primary trunk of the brachial plexus of the C8- T1 segment, Fig. 6) - loss of function of the distal part of the limb - flaccid paresis of distal muscles of hand, muscular atrophy of forearm and small muscles of hand, disorders of sensation at a polyneural type on distal arm part, Bernard-Horner syndrome (ptosis, miosis, enophthalmos) due to lesion or compression of one side of the cervical or thoracic sympathetic chain.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 92 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Fig. 1. Prosoparesis. | | | Fig. 16. Pathological area at carpal tunnel syndrome. |