
Читайте также:
|
1.Under perfect competition, there are so many firms that no one firm has any influence over_________________________________________.
2. Under perfect competition, all sellers sell a(n) ______________________________________product.
3. The determination that a product is identical takes place in___________________________________.
4. The perfect competitor's demand curve is a____________________________________; the marginal revenue curve is a____________________________.
5. A perfect competitor would never charge more than market price because_________________________________________; the perfect competitor would never charge less than market price because_________________________________________________.
6. In a perfectly competitive industry, price is set by________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
and_____________________________________________________________________________________.
7. The four main characteristics of perfect competition are (1)_______________________________________;
(2)______________________________________________________________________________________;
(3)______________________________________________________________________________________;
and (4)__________________________________________________________________________________.
8. In the short run, the perfect competitor may make a______________ or take a _____________; in the long run the perfect competitor will________________________________________________________.
9. In a perfectly competitive industry, if firms are making profits,_____________________________________
which will result in zero profits in the long run; if there are losses in the short run,________________________
resulting in zero profits (and losses) in the long run.
10. In the long run, economic profits are_______________________________________________________.
11. The perfect competitor operates at the____________________________________ point of her average total
cost curve in the long run.
12.In a decreasing cost industry, a firm that is a perfect competitor cannot keep growing because ultimately it will___________________________________________________________________________________.
13.If the firms in a competitive industry are earning profits, in the long run new firms will_________________
_____________________________________________________________________________. But, if most firms are losing money, then in the long run some of the firms will___________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________.
14.If the firms in a competitive industry are losing money, in the long run the market price will__________
_____________________________________________________. But, if most firms are making a profit, then in the long run the market price will_______________________________________________________.
Problems
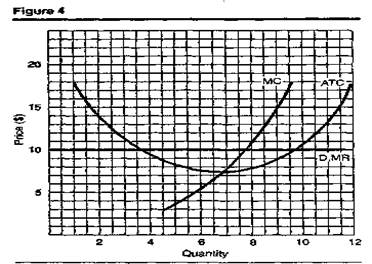
1. Given the information in Figure 4, how much are total profits (or losses)? Is the firm in the short or long run?
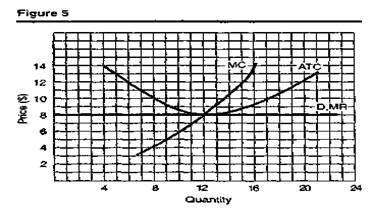
2. Given the information in Figure 5, how much are total profits (or losses)? Is the firm in the short or long run?
3. How much is the most efficient output (a) in Figure 4? (b) in Figure 5?
4. Given the information that follows, how much are (a) accounting profits? (b) economic profits? Sales: $400,000; total costs: $250,000; return you could have earned by investing your money elsewhere: $15,000; wages you and your family members could have earned doing the same work for another firm: $40,000.
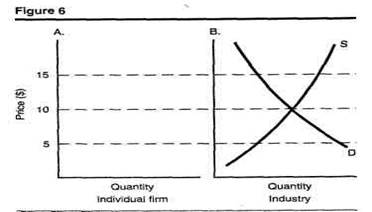
5. Given the industry supply and demand shown on the right side of Figure 6, use the left side of the figure to draw the perfect competitor's demand, marginal revenue, average total cost, and marginal cost curves for its long-run situation.
6. Given the information that follows, how much are (a) accounting profits? (W economic profits? Sales: $5 million; explicit costs: $3 million; return you could have earned by investing your money elsewhere: $50,000; wages you and your family members could have earned doing the same work for another firm: $120,000.
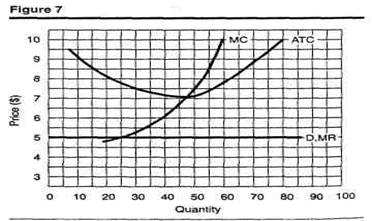
7. Given the information in Figure 7, how much are your total profits (or losses)? Is the firm in the short or long run?
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 74 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Multiple-Choice Questions | | | Письменное высказывание с элементами рассуждения: стратегии общие для двух типов |